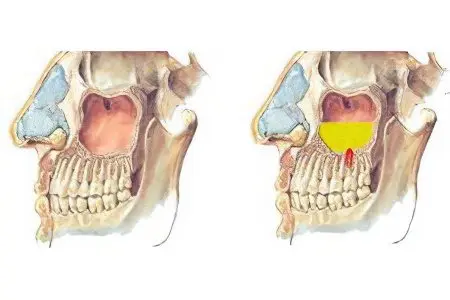
Odontogenic sinusitis is a special type of this disease that develops in the paranasal sinuses. Unlike ordinary sinusitis, which is most often the result of colds, it occurs under the influence of pathological processes in the oral cavity. They are associated with inflammation of the upper molars and premolars. The roots of these teeth are located near the bottom of the maxillary sinuses. This leads to the fact that an odontogenic infection that develops in the oral cavity also spreads to the nose.
Diplococci, staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci are its main pathogens.
Suppuration of the maxillary cyst also often contributes to the development of infection. However, it extends to the maxillary sinuses in the following cases:
In case of non-compliance with oral hygiene. It includes regular brushing of teeth, rinsing after meals and routine check-ups at the dentist. A visit to the doctor is often postponed in the absence of pain. But caries in most cases delivers tangible discomfort already with necrosis of the nerve of the tooth. In this case, the pain is difficult to endure. Therefore, it is important to conduct an examination at the dentist in time and not to neglect the rules of personal oral hygiene.
With improper treatment and growth of teeth. Removal can provoke the destruction of the septum between the maxillary sinuses and the upper jaw. This is due to the large size of the roots of the teeth, especially the molars. As a result, an odontogenic infection quickly spreads from the oral cavity to the sinuses. Inaccurate installation of the filling can lead to the fact that part of the medicine placed in the tooth will fall through the canal into the maxillary sinus. It also leads to inflammation. Promotes the development of odontogenic infection and periodontium. The reason for it is the wrong growth of teeth.
Odontogenic sinusitis in the absence of timely treatment can lead to serious complications, including brain abscess. Therefore, it is important to monitor the oral cavity, observing all the rules of hygiene and visiting the dentist regularly.
Symptoms and diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis
It is possible to determine odontogenic sinusitis by characteristic discharge from the nose. They have a watery consistency, have an unpleasant odor. At the initial stages of the development of the disease, the patient feels pain in the area of the inflamed tooth. It is felt in the frontal part of the head, under the eye area on the same side. Decreased ability to distinguish odors. As a rule, odontogenic sinusitis is unilateral, so pain is felt only in one half of the body.
If the disease is not diagnosed in time, the sinuses can completely fill with mucous secretions. This process is accompanied by an increase in edema. Discharge from the nose in this case is a mixture of mucus and pus. Any touch to the site of inflammation causes severe pain. Breathing and smell are disturbed. The outflow of secretions from the nose in a natural way is no longer possible. These symptoms indicate a purulent form of odontogenic sinusitis.
The patient experiences weakness, constant malaise. He may have a fever, a fever appears. Outwardly, swelling of the cheek and redness on the face from the side of the inflamed tooth are noticeable. The patient cannot sleep peacefully. In some cases, even photophobia is observed.
Make sure that the patient really odontogenic sinusitis allows radiography. The picture should show blackouts in the area of the maxillary sinuses. Sometimes special dyes are used to obtain a clear image. This is necessary in the case of a polypous form of odontogenic sinusitis. During rhinoscopy, an increase in the mucous membranes of the nose is usually noticeable. In the blood of a patient with this type of sinusitis, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased and neutrophilic leukocytosis is present. During the puncture, pus is released, which also confirms the diagnosis.
Treatment of odontogenic sinusitis

Endoscopy. If odontogenic sinusitis is caused by a filling entering the canal, inflammation of the tooth or root, this problem is first eliminated and the oral cavity is sanitized. Then, with the help of endoscopy, purulent discharge is removed. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. In particularly difficult cases, general anesthesia is used. Similarly, the infection is eliminated in cases where it develops in soft tissues.
Conservative treatment after getting rid of the cause of the development of the disease, it is carried out with the help of pharmaceutical preparations. Nasal lavage and physiotherapy are carried out daily. Antibiotics are often used to avoid complications or if they occur. Pain medications can alleviate discomfort and discomfort. For the duration of treatment, the patient should avoid increased stress.
Operation. The chronic form of odontogenic sinusitis requires not only conservative methods. Surgery may be required, during which the doctor expands the anastomosis. This is necessary to facilitate the release of pus from the sinuses. After surgery, saline lavage is carried out for several days.
Puncture or puncture – Another type of operation for odontogenic sinusitis. First, a cotton swab with lidocaine is placed in the nose. This is how anesthesia works. After that, the doctor makes a puncture with a needle, and the discharge from the maxillary sinuses is removed through the mouth.
This operation is not considered difficult and rarely causes complications. However, many avoid puncture, fearing pain. Thanks to anesthesia, it can be avoided, so this is not a cause for concern. Of course, in general, the procedure gives the patient discomfort, but in many cases, surgery is the only way to get rid of odontogenic sinusitis.
If you refuse to carry out this procedure, you can get a complication in the form of inflammation of the sphenoid and frontal sinuses, meningitis, and even a brain abscess. It is not worth it to treat odontogenic sinusitis on your own. As practice shows, folk methods are ineffective in this case.









