Contents
- Symptoms of obstruction of the fallopian tubes
- Causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes
- How are fallopian tubes checked for patency?
- Complications and consequences of obstruction of the fallopian tubes
- Pain in the fallopian tubes: what to do?
- Methods for restoring patency of the fallopian tubes
- Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes: what to do?
- IVF for obstruction of the fallopian tubes
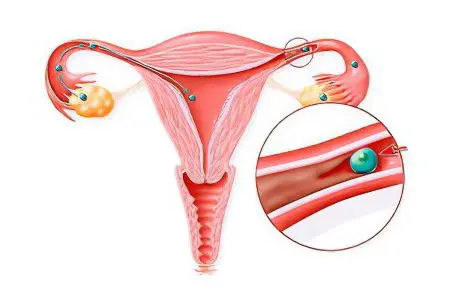
Whether a woman can become pregnant is directly affected by the patency of her fallopian tubes: whether it is complete or partial. It also matters whether one or both tubes show signs of obstruction.
Complete obstruction of the tubes makes it impossible for the egg to enter the uterus, since the lumen is closed. In such a situation, a woman will not be able to conceive a child naturally. However, modern reproductive technologies, namely IVF, can come to her aid.
If a woman has incomplete patency of the fallopian tubes, then this means that the lumen of the appendage is only partially closed. The egg has the ability to penetrate the uterus, which means that a woman can conceive a child on her own. However, the chances of successful fertilization in such patients are much lower than in healthy representatives of the beautiful half of humanity.
Also, natural conception can occur when only one fallopian tube is impassable, and the second is partially passable or absolutely healthy. Nevertheless, the problem of tubal infertility remains relevant in modern society. Primary infertility is diagnosed both in very young girls and in young women at the age of 30 years. Moreover, often they did not have abortions, did not undergo surgical interventions, they do not have any serious diseases in their anamnesis.
Statistics indicate that about 15% of families experience infertility. And in 20-25% of cases, it is the obstruction of the fallopian tubes that becomes his fault.
Symptoms of obstruction of the fallopian tubes

Obstruction of the fallopian tubes does not give bright symptoms. Therefore, a woman may not be aware of her problem for a long time. Her well-being is not disturbed, menstruation occurs on time, there are no failures in their cyclicity. Therefore, according to the woman, there are no obvious reasons for concern about her own health.
A sign that may indicate obstruction of the appendages is the absence of pregnancy for a long time – a whole year of regular unprotected intimate life. Moreover, in order to pay attention to this symptom, a woman should strive to become pregnant and not have hormonal or endocrine pathologies.
Depending on the cause that provoked the development of obstruction, the clinical picture may vary somewhat.
When adhesive disease has led to blockage of the pipes against the background of inflammation of the pelvic organs, from time to time a woman may be disturbed by pain in the lower abdomen of a aching nature.
If the obstruction of the tubes is the result of surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity (surgery for appendicitis, removal of the ovary, abortion, etc.), then the pain will be pulling. Sometimes they become quite intense and disrupt the quality of life.
A symptom indicating blockage of the tubes may be severe pain that occurs during the next menstrual cycle.
Often, even the passage of ultrasound and examination on the gynecological chair does not allow to identify the existing problem.
Sometimes, against the background of obstruction of the fallopian tubes, a woman may experience pain during intercourse, with deep penetration or sharp shocks, when the vagina is greatly stretched.
If the obstruction of the tubes is due to chronic inflammation in the pelvic organs, then abnormal vaginal discharge that appears against the background of periodic pain is not excluded.
So, the main symptoms that can indirectly indicate obstruction of the fallopian tubes are as follows:
Pain during menstrual bleeding.
Discomfort during intimacy.
Occurring from time to time pain of a pulling or aching nature with localization in the lower abdomen.
Pathological vaginal discharge.
Causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes

Two basic causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes can be distinguished – these are functional disorders and organic pathologies of the appendages.
Functional disorders include disturbances in the normal contractility of the tubes, their hypo- or hypertonicity, adynamia of cilia and villi, and discoordination of their movements. At the same time, the structure of the appendages and their histology remain unchanged.
Factors that contribute to the formation of functional disorders:
Hormonal imbalance. At the same time, female sex hormones in the body circulate much less than necessary.
Failures in the work of the nervous system due to stressful situations.
A high level of biologically active substances in the blood and tissues against the background of inflammation of the uterus, ovaries or tubes. These substances include interleukins, prostaglandins, thromboxane A2, etc.
Organic lesions include adhesions formed in the abdominal cavity, torsion of the appendages, their clamping by various tumors, and underdevelopment of organs.
Factors that can provoke the development of organic lesions:
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, including venereal diseases.
The presence of a chronic infection, for example, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, etc.
Endometriosis.
Surgical operations on the uterus and appendages, or on other organs located in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostic or therapeutic procedures that were accompanied by invasive intervention in the organs of the reproductive system.
Postponed abortions.
Complications of childbirth or abortion.
So, obstruction of the fallopian tubes can be due to a number of different reasons that are functional or organic in nature.
What microorganisms can cause obstruction of the fallopian tubes?
Almost any pathogenic microorganisms are capable of causing inflammation of the genital organs, which in the future can lead to the development of obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Among the coccal flora, adnexitis is most often provoked by staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci. Although fungi, viruses and protozoa can also cause inflammation of the fallopian tubes.
The risk that a woman will develop obstruction of the fallopian tubes after suffering inflammation of the appendages is reduced to the following figures:
In 12% of women, obstruction develops after a single episode of inflammation.
In 35% of women – after 2 cases of inflammation.
In 75% of women – after 3 episodes.
How are fallopian tubes checked for patency?
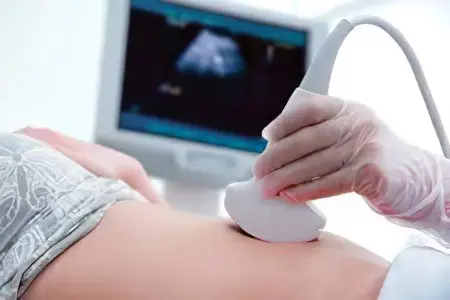
There are several diagnostic methods that allow you to establish obstruction of the fallopian tubes, among them:
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. With the help of a conventional ultrasound examination, the doctor will be able to determine the structure of the female genital organs, identify their inflammation, the presence of adhesions, tumors, hydrosalpinx.
UZGSG (echohysterosalpingography, hydrosonography). This procedure is carried out in much the same way as any other ultrasound examination: a gel is applied to the abdominal cavity and examined with a scanner. However, before the procedure, a sterile saline solution is injected into the cervix using a thin catheter, the movement of which is displayed on the monitor. If a woman has partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes, then this method is uninformative, and also less accurate compared to HSG.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG, metrosalpingography) – This is a study of the uterus and appendages using a contrast agent, after the introduction of which images are taken on an x-ray machine. In case of violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes, diagnostics should be carried out in the second half of the menstrual cycle. The effectiveness of the method is 98%. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, or in hospitals of gynecological departments. 2 days before it is necessary to abandon intimacy. A week before the diagnosis, you can not douche, administer vaginal preparations, except for those prescribed by the doctor. A contrast agent (cardiotrast, urotrast, verografin, triombrast) is injected into the uterus through a special tube, intravaginally. Then the doctor takes a series of pictures that allow you to evaluate the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes. For 3 months after the procedure, a woman must use protection to avoid pregnancy. Hysterosalpingography is the leading method for diagnosing obstruction of the fallopian tubes. A significant drawback of the study is that it allows you to establish the presence of an obstacle in the pipes, but its nature cannot be clarified. (Read more: HSG x-ray of the fallopian tubes: pros and cons).
Perturbation or “blowing out” of the fallopian tubes. During this study, gas is injected into the uterine cavity under pressure. It can be air, carbon dioxide, oxygen. The procedure is practically painless for the patient and does not take more than 5 minutes. When the gas fills the fallopian tubes, they begin to contract, it is this process that is recorded by special equipment. The results are displayed in the form of a graph. The doctor makes a conclusion about the patency of the pipes on the basis of the data obtained, and also evaluates some indirect signs: a characteristic noise in the abdominal cavity, pain in the patient’s collarbone area.
Laparoscopy with chromohydrotubation. This method belongs to minimally invasive surgical techniques. In order to detect only obstruction of the fallopian tubes, laparoscopy is used extremely rarely, most often the method is used for therapeutic purposes. The study allows not only to identify obstruction of the fallopian tubes, but also to eliminate the existing violations. The procedure is performed under anesthesia in a hospital setting. Two incisions are made in the abdominal cavity through which instruments are inserted. The term “chromotubation” means that a sterile solution is introduced into the uterine cavity, which, if the fallopian tubes are blocked, will not spread through them. After laparoscopy, the woman will remain in the hospital for several days under the supervision of doctors.
Fertiloscopy (transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy). This procedure is less traumatic than laparoscopy, since access to the tubes is not through the abdominal cavity, but through the vagina, on the back wall of which a small incision is made. The study can be carried out in an outpatient setting under local anesthesia. A saline solution is injected through the incision into the pelvic area to lower and straighten the fallopian tubes. Patency is checked with a contrast agent.
To determine which diagnostic method is a priority in a particular case, a medical consultation is necessary. Only a doctor is able to choose the appropriate procedure, based on the state of health of the woman. It should be taken into account that surgical diagnostic techniques are no less dangerous than a full-fledged operation. They require long-term preparation, the introduction of anesthesia, which means they put a significant burden on the body. Therefore, whenever possible, preference should be given to non-invasive methods of examination: hysterosalpingography or hydrosonography. Additionally, a woman must pass a blood and urine test, a smear for microflora.
Complications and consequences of obstruction of the fallopian tubes
Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes leads to the fact that a woman is not able to conceive a child naturally. With partial patency of the appendages, pregnancy can occur, but the chances of successful fertilization of the egg are significantly reduced. For a woman’s life, obstruction of the fallopian tubes does not pose a threat, but this problem becomes the cause of tubal infertility very often.
Another danger that awaits women with obstruction of the fallopian tubes is an ectopic pregnancy. As a result, a woman may lose one or even both appendages.
Pain in the fallopian tubes: what to do?

If severe pain occurs during inflammation of the fallopian tubes, then it is necessary to use drugs from the NSAID group, including:
Diclofenac, Dicloberl, etc. They can be released in the form of injections, or in the form of rectal suppositories.
You can also drink the drug in capsules or tablets. It can be Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Indomethacin, etc.
You can also eliminate pain by taking combined drugs, such as Baralgin or Spazmalgon. It is possible to use Paracetamol or Analgin as an anesthetic.
In case of acute inflammation of the fallopian tubes and uterus, you should follow a certain diet and exclude the following products from your menu:
Smoked meats and sausages;
Marinades and hot spices;
Canned food and fast food;
Mayonnaise, ketchup and mustard;
Beans;
Chocolate, confectionery;
Cocoa and coffee.
If the inflammation is chronic, then it is enough to exclude only smoked meats, marinades, canned food and ketchup from your menu. Dishes are best baked or boiled. You should not fry food more than 2 times a week.
It is important to enrich your menu with foods with a sufficient content of vitamins. First of all, this applies to vegetables and fruits. It is useful to drink freshly squeezed juices, fruit drinks with cranberries, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote, green tea. Be sure to include foods rich in vitamin C in the diet – these are kiwi, black currants, lemons, oranges, bell peppers, etc.
Methods for restoring patency of the fallopian tubes
There are 4 methods for restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes, we will consider them in more detail.
Laparoscopy
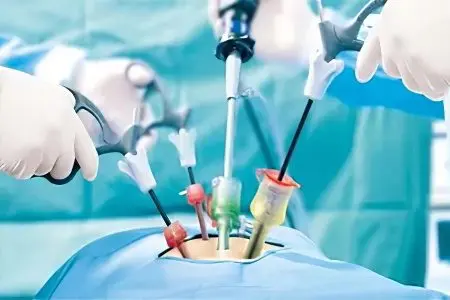
Laparoscopy is a modern method of surgical intervention, which is carried out through a puncture on the anterior abdominal wall. The procedure is carried out using special laparoscopic equipment and an endoscope.
With obstruction of the fallopian tubes, laparoscopy is not always performed, but only in the case when the blockage of the appendage is diagnosed near the ovary and there is no pronounced adhesive process.
The procedure requires the introduction of general anesthesia. A small amount of inert gas is injected through the navel into the abdominal cavity to raise the wall of the peritoneum. Gas is supplied through a special thin needle. Then 3 small incisions are made on the life, through which the doctor inserts the instruments into the woman’s body. With their help, the doctor pushes and rotates the fallopian tubes, excised adhesions and hydrosalpinx, sews up the incisions, if necessary.
Laparoscopic operations to restore the fallopian tubes can be of the following types:
Fimbriolysis – release of the cilia of the tube from adhesive joints;
Salpingoanastomosis – removal of the damaged section of the pipe with its subsequent stitching;
Salpingostomatoplasty is the cutting and formation of the correct anatomical hole in the tube from the side of the ovary;
Salpingolysis – cutting and removal of pathological areas around the fallopian tube, elimination of its kinks and curvatures.
The procedure is performed from the 7th day of the menstrual cycle, but no later than 10 days before the onset of ovulation. Although, if the operation needs to be carried out on an emergency basis, the day of the cycle does not matter.
After the procedure, the woman is in the hospital for 3-5 days. The seam heals on average in 10-15 days. The operation is considered effective, sparing and does not damage healthy tissues.
In the event that the surgical intervention is successful, after a few months the woman may try to conceive a child. It is worth remembering that laparoscopy is not the operation of choice for obstruction of the fallopian tubes. If the adhesions are inside the tube, then it is possible to get pregnant in 10% of cases. When they are located outside of it, the chances of successful conception increase to 60%.
Fertiloscopy
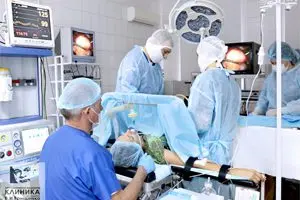
Fertiloscopy is one of the options for endoscopic surgery using the same equipment as for laparoscopy. However, unlike laparoscopy, access to the fallopian tubes is obtained through the posterior fornix of the vagina. The procedure can be performed under local or general anesthesia.
A thin optical system is inserted through the posterior fornix of the vagina, which allows you to examine in detail the condition of the pelvic organs. If obstruction of the fallopian tubes is detected, salpingoscopy is performed on site with the same endoscope. At the end of the procedure, the endoscope is removed, and the fluid flows freely from the pelvic cavity through the trocar channel. No sutures are required at the injection site. The procedure lasts about 20 minutes.
A contraindication to the procedure is a fixed retroflexion of the uterus, that is, its posterior curvature.
hydrotubation

This method of treating tubal obstruction is outdated, and surgeons are trying to move away from it. It boils down to the introduction of an isotonic solution of sodium chloride and a drug mixture under a certain pressure into the fallopian tube. The therapeutic effect is based on mechanical (rupture of adhesions) and medicinal effects on the fallopian tubes from the inside. Medicinal substances are used both individually and in combination with each other.
The procedure is carried out in the intermenstrual period. To achieve a positive result, 5-6 sessions may be required, which are repeated every 1-2-3 days for 1-5 menstrual cycles.
Hydrotubation is performed both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital. Some experts suggest combining hydrotubation with ultrasound, electrophoresis, diathermy, gynecological massage.
Contraindications to the procedure:
Acute inflammation of the genital organs;
The presence of any infectious process;
Severe extragenital diseases.
Recanalization
This method is designed to remove minor adhesions located in the fallopian tube. In addition, adhesions should be located in the initial sections of the appendage.
Method of carrying out the procedure: a catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted into the cavity of the tube through the uterus. The doctor gradually advances the catheter deep into the appendage, forcing air into the balloon. As a result, the pipe is straightened and its patency is normalized. The procedure begins and continues under the continuous control of laparoscopic equipment.
After recanalization, all patients are prescribed antibiotic therapy in a short course of 3-5 days. A course of anti-inflammatory and anti-adhesion treatment is also indicated.
Recanalization of the fallopian tubes is not used to eliminate extensive adhesive processes, since there will be no effect from the operation.
Leeches for obstruction of the fallopian tubes
Hirudotherapy or treatment with leeches is widely used for obstruction of the fallopian tubes. The saliva of these annelids contains many biologically active substances that help eliminate inflammation, improve blood circulation, and resolve adhesions.
During a hirudotherapy session, 3-4 leeches are placed on the lower abdomen, in the area where the uterus is located. Sometimes leeches are placed in the vagina. They are left until the moment when they themselves drink blood and fall away. The course of treatment consists of 10-15 daily sessions. After two weeks, the course can be repeated.
For the procedure, you should contact a specialist. It is strictly forbidden to independently introduce leeches into the vagina.
Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes: what to do?

Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes is subject to treatment if the normal structure of the organ is not too damaged, or when adhesions are located only outside the appendage, but they are not in its cavity. It is possible to start therapy provided that the woman does not have chronic inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
It will not be possible to get rid of obstruction of the fallopian tubes in the following situations:
There is inflammation of the urinary tract.
Diagnosed with genital tuberculosis.
The patient is over 35 years old.
Often there are exacerbations of inflammatory diseases of the organs of the reproductive system.
An impressive hydrosalpinx was found.
In the abdominal cavity, many adhesions are found, which splice the organs with each other.
The adhesions are located inside the fallopian tubes.
It should be understood that even after the restoration of the patency of the fallopian tubes, it is not always possible to solve the problem of infertility. An important condition is the full operation of the fallopian tubes so that they are able to move the fertilized egg into the uterus. Otherwise, there is a high risk that the woman will have an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, doctors warn their patients in advance that the normalization of the patency of the fallopian tubes is not a guarantee that the organs will function correctly and fully.
IVF for obstruction of the fallopian tubes
If a woman is diagnosed with obstruction of the fallopian tubes, then she can undergo an in vitro fertilization procedure. However, first you need to get rid of all chronic inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system, treat all infections, and, if necessary, remove the fallopian tubes. This may be required when the appendages are too deformed or disrupt the normal position of the uterus, which leads to an increased risk of miscarriage with a successful conception.
Other indications for removal of pipes:
Lack of chances to restore their patency.
The inability to qualitatively and fully eliminate the inflammatory process.
IVF is a woman’s only hope for a successful conception and gestation with complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Therefore, the procedure should not be abandoned.
IVF in 60% of cases allows you to conceive a child (a woman’s age is up to 35 years). While operations to eliminate obstruction of the fallopian tubes equate the chances of conception to 40-70% in the initial adhesive process and to 15-20% in the advanced stage of the disease. With IVF, the risk of ectopic pregnancy does not exceed 2%, and after surgery it reaches 30%. Whether the conception was successful after in vitro fertilization becomes known after 14 days. And the effectiveness of the operation can be judged for certain at the end of the whole year.









