Contents
Noonan syndrome is a disease that is inherited, clinically manifested in the low growth of the patient, as well as in other anomalies of somatic development. The syndrome can occur sporadically, that is, by chance, and can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
The disease can affect both men and women. According to statistics, it is detected in one child out of 8000. The disease was first described by pediatric cardiologist J. Noonan, whose name was given to this syndrome in 1971.
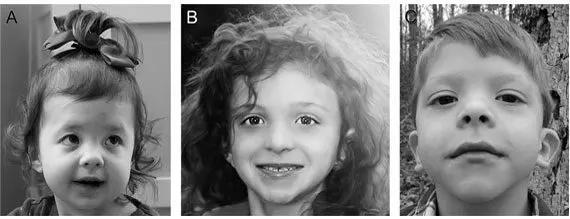
Symptoms of Noonan Syndrome
The symptoms of Noonan syndrome are as follows:
Low rise. At the same time, the final height in men does not exceed 1 m 62 cm, and in women 1 m 53 cm.
Violations of the outflow of lymph from the lower extremities, which leads to the formation of edema.
Pterygoid folds form along the body and on the neck.
The growth limit at the back of the head is underestimated.
Ocular hypertelorism is characteristic, that is, the organs of vision in such people are abnormally widely spaced. Often there is ptosis of the upper eyelid, that is, its omission. The section of the eyes is anti-Mongoloid, the ears are set low.
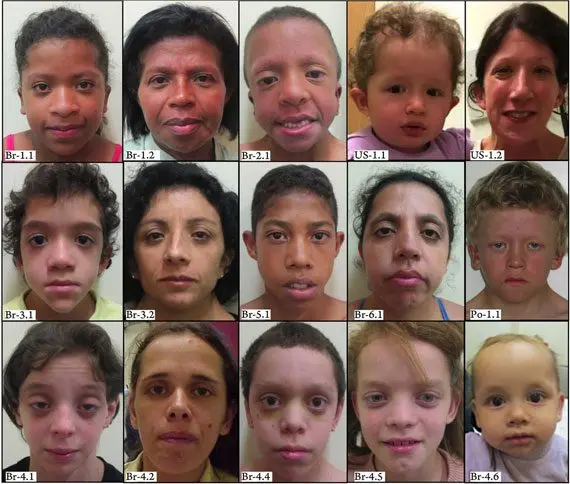
In general, the face of such patients is asymmetrical, its shape is triangular, the bridge of the nose is disproportionately wide. Such external anomalies make people with Noonan syndrome look alike.
The neck of the patients is short, the elbow joints are deformed according to the type of hallux valgus.
The sky is located high, the bite is pathological.
The structure and shape of individual vertebrae is disturbed, the chest is sunken in the distal part and protrudes in the proximal part.
Such patients are characterized by a ventricular septal defect and other congenital malformations of the heart and blood vessels.
Puberty may be normal or may be abnormal. In girls, a late onset of menarche is often observed, or vice versa, menstruation debuts in a timely manner and fertility is observed at puberty. Possible hypoplasia of the external genitalia.
With regard to the sexual development of boys, they often have hypogonadism (insufficiency of the testicles against the background of a low level of production of sex hormones) and cryptorchidism (delayed descent of the testicle). Often a manifestation of Noonan syndrome in men is gynecomastia, that is, an increase in the mammary glands (one or both). At the same time, secondary sexual characteristics are not developed enough, hair is scanty, muscles are weak.
Possibly mental retardation.
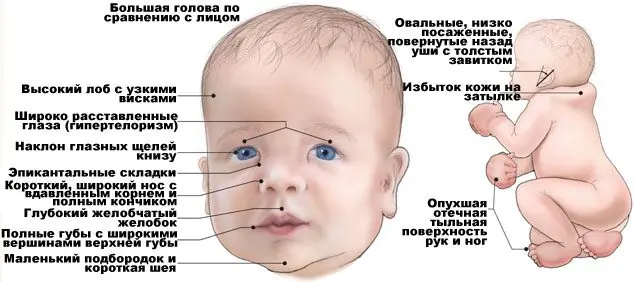
Causes of Noonan Syndrome
The causes of Noonan syndrome lie in genetic mutations that can occur by chance, or can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, that is, simply carrying a mutation in a parent is enough for the disease to manifest itself clinically in their children. At the same time, the risk that a sick child is born is reduced to 50%. The rest, healthy children will be carriers of the gene, but will not have clinical signs of the disease.
As a rule, the mutant gene is transmitted through the maternal line, since men in the overwhelming majority of cases are infertile, which is due to serious malformations of the reproductive system.
Diagnosis of Noonan syndrome
There are no specific markers to identify the syndrome. Therefore, predominantly the diagnosis of Noonan syndrome consists in examining the patient and identifying clinical signs in him.
Sometimes it is possible to make a diagnosis due to the result of a molecular genetic study. It is equally important to differentiate Noonan syndrome from Turner syndrome, Williams syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, etc.

Treatment of Noonan syndrome
Treatment of the Noonan syndrome primarily comes down to ridding the patient of existing heart and vascular defects. In addition, it is important to normalize mental activity, stimulate growth and correct violations in the genital area.
Balloon valvuloplasty is used to correct pulmonic valve dysplasia, which is often found in patients with Noonan syndrome.
Nootropic drugs, as well as vascular agents, are used to treat mental disorders.
Stimulation of sexual development is indicated for identified cryptorchidism. To correct hypogonadism in adolescence, chorionic gonadotropin preparations are used, and as the patient grows older, testosterone preparations are used.
Growth preparations are gaining more and more popularity in modern medicine, which are used to correct existing disorders in this area in patients with Noonan syndrome. Such an active introduction of growth hormones into practice is due to the available clinical data that confirm their effectiveness. Thus, some patients receiving appropriate therapy had a height higher than the average height of members of this family.
As for the prognosis for the development of the disease, it completely depends on how severe the severity of the cardiovascular disorder is.









