Contents
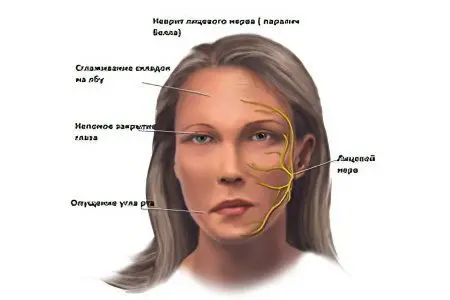
Neuritis of the facial nerve is a disease characterized by inflammation of the 7th pair of cranial nerves. Another disease is called Bell’s palsy. Because of this disorder, the patient’s facial expressions suffer, but he cannot express his emotions, he is not even able to chew food normally. The face becomes asymmetrical.
It is the facial nerve that suffers more often than others, as it stretches along the narrow canals of the facial bones. Therefore, even a slight inflammation can lead to its clamping. The nerve undergoes hypoxia, which entails the corresponding symptoms. Most often, neuritis is a unilateral lesion, but in about 2% of people, the face becomes inflamed on both sides.
Neuritis of the facial nerve is widespread, every year 25 people out of 100 of the population suffer from it. Gender does not matter. The disease develops mainly in winter.
The illness does not go away quickly. People have to stay in the hospital for 3-4 weeks. It may take about six months for the nerve to fully recover. On average, 5% of people do not cope with the disease, that is, the nerve does not begin to function as before. This situation is typical for cases where neuritis is the result of an injury, or a consequence of a growing brain tumor. In about 10% of cases, the disease recurs.
Causes of neuritis of the facial nerve
The following factors can provoke neuritis of the facial nerve:
Transferred herpes. This virus infects the nerve fibers, causing them to swell and become inflamed. Also, mumps, polio, adenoviruses and enteroviruses are capable of provoking neuritis.
Hypothermia of the body. It is especially dangerous if the face is exposed to cold. His muscles and blood vessels spasm, which can lead to inflammation of the facial nerve.
Alcohol abuse. Alcohol poisons the nervous system, causing inflammation of the nerve fibers. In addition, the brain suffers to a large extent.
Arterial hypertension. With this disease, intracranial pressure increases, the nuclei of the facial nerve suffer. Another danger of high blood pressure is a stroke. If a hemorrhage occurs near the facial nerve, then it is damaged.
Pregnancy. In terms of the development of neuritis, the 1st trimester is of particular danger, when a hormonal surge occurs in the body.
A brain tumor. If it compresses the nerve fibers, then they are not able to transmit signals normally, which causes the development of neuritis.
Postponed craniocerebral trauma and ear trauma. In this case, the nerve can be severely damaged or even torn.
Treatment of dental diseases. If a nerve is damaged during manipulations to remove a tooth or eliminate caries, this can lead to its inflammation.
Otitis and sinusitis. When the pathogenic flora spreads to tissues adjacent to the nasal sinuses or to the internal structures of the ear, inflammation of the nerves in them develops, which can become the basis for the development of neuritis.
Diabetes. Failures in metabolic processes often cause inflammation of nerve fibers.
vascular atherosclerosis. Those collaterals that feed the facial nerve are clogged with plaques. Hypoxia of the nerve develops with the gradual death of its cells.
Depression, stress. Any emotional shock leads to the fact that a person’s immunity is weakened. This causes the development of neuritis.
Multiple sclerosis. In this disease, the myelin sheath that surrounds the nerve is affected. Plaques form on it. In patients with multiple sclerosis, the optic and facial nerves often become inflamed.
Classification of facial neuritis
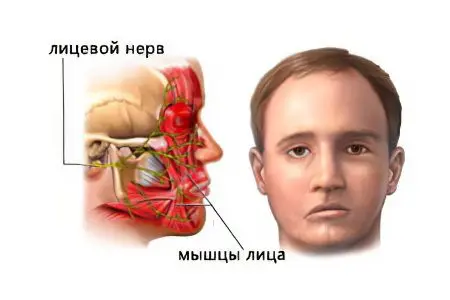
Neuritis of the facial nerve can be primary and secondary. The primary form of the disease can manifest against the background of hypothermia or other external factors. Secondary neuritis is a consequence of another disease, for example, inflammation of the middle ear.
In addition, the following forms of neuritis are distinguished:
Hunt syndrome. This neuritis develops against the background of herpes zoster. A person has not only symptoms of neuritis, but also other signs of the underlying infection: spots on the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, in the pharynx, on the auricles. Neuritis develops due to the fact that the herpes virus damages the ganglion, from which the palate, auditory apparatus and tonsils are innervated. Branches of the facial nerve are located next to this ganglion. The first symptoms of the disease are painful sensations of the type of lumbago. The pain is concentrated in the ear. As the pathology progresses, facial asymmetry develops, taste suffers, as sensitivity in the anterior part of the tongue disappears. The patient may feel dizzy, he is disturbed by tinnitus, involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyeballs may be observed.
Neuritis in swine. In a person with mumps, neuritis can affect one or both sides of the face. In parallel, his body temperature rises to high levels, his head hurts, and the salivary glands increase in size.
Neuritis in borreliosis. With this disease, the face is always affected on both sides. A person’s body temperature rises, erythema develops, and neurological symptoms appear.
Neuritis in otitis. At the same time, a person is worried about severe pain in the ear, it is impossible to endure them. Neuritis develops due to the fact that the infection from the middle ear spreads to the branches of the facial nerve.
Merkelsson-Rosenthal Syndrome. This is a disease that is transmitted to a person by inheritance. It develops rarely and is accompanied by a wave-like course. In the acute phase, the face becomes edematous, signs of neuritis appear, the tongue becomes folded.
The mechanism of development of neuritis
Due to the influence of a pathological factor, arterial spasm occurs, blood stasis develops, small vessels expand. Plasma sweats through their wall, accumulates in the intercellular space. The tissues swell, put pressure on the veins and lymphatic vessels, which leads to disruption of the lymph flow.
The nerve begins to suffer from the fact that its nutrition is deteriorating, it receives less oxygen. The affected trunk swells, blood vessels burst in it, which leads to a deterioration in the transmission of impulses. Thus, neuritis develops.
Symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve always has an acute onset. Other symptoms are shown in the table.
The symptom is neuritis | Manifestations of the disease | Main reasons |
Pain behind the auricle, which occurs 1-2 days before the first violations of facial expressions. | The pain radiates to the face and back of the head. A few days later, the eye begins to hurt. | Discomfort is due to swelling of the nerve. It will be pinched at the exit from the auditory opening, which is located in the temporal bone. |
The symmetry of the face is lost, it begins to resemble a mask. | The eye on the side of the lesion is wide open, the corner of the mouth is down, the nasolabial fold is smoothed, as well as the frontal folds. If a person tries to express some emotions, then the asymmetry becomes even more noticeable. | There is no control of the brain over the mimic muscles of the face on one side. |
The eye on the side of the lesion remains open. | If a person wants to close his eyes, then he fails, the eye does not close, a gap remains. In this case, the eye turns up, and the protein is visible through the gap. | The circular muscle of the eye is not innervated in full, the muscles of the eyelid do not obey the commands of the brain. |
The corner of the mouth is down. | Liquid food flows from the side of the lesion, but the patient can move his jaw and chew. | The buccal branches extending from the facial nerve do not control the muscles of the mouth. |
The muscles of the cheek cease to obey. | While eating, a person bites the inner surface of the cheek all the time, food falls behind it. | The facial nerve does not transmit signals from the brain to the cheek muscles. |
Mouth is always dry. | A person is constantly thirsty, little saliva is secreted, it is not enough to chew food. Sometimes, on the contrary, there is profuse salivation. | The brain sends signals to the salivary glands, but the facial nerve does not transmit them in full. |
Speech worsens, it can become slurred. | One half of the mouth does not take part in the articulation of sounds. Consonants suffer more: b, c, f. | The facial nerve does not fully provide the work of the cheeks and lips. |
The eye dries up. | The tear fluid is secreted in insufficient volumes, and the eye itself does not close completely, the person rarely blinks. | Damaged branch of the facial nerve, which is responsible for the production of tears. |
Lachrymation. | Sometimes tear fluid, on the contrary, is produced too much. Tears do not flow into the lacrimal canal, but stand out. | The lacrimal gland is too active. |
One half of the tongue does not taste. | From the side of the lesion, the tongue loses sensitivity. | Such a situation is observed during inflammation of the fiber of the intermediate nerve, so the brain does not receive signals transmitted by the receptors of the tongue. |
Hearing becomes heightened. | One ear hears better than the other. | The nerve is inflamed in the temporal bone. |

Depending on the symptoms of neuritis, we can conclude which part of the facial nerve was inflamed:
Damage to the nerve in the cerebral cortex is indicated by violations of the facial expressions of the lower part of the face, its muscles make involuntary movements, and a nervous tic may be observed.
Nystagmus, numbness of the face, twitching of the palate and pharynx indicate damage to the nuclei of the facial nerve, the patient cannot wrinkle his forehead.
When a nerve is damaged in the pyramid of the temporal bone and in the cavity of the skull, the facial muscles are completely immobilized, little saliva is produced, the sensitivity of the tongue worsens, hearing becomes more acute, the eyeball dries up.
A person needs to go to the doctor as soon as possible if he notices the following symptoms:
There is no way to frown.
Can’t hang or blow.
Unable to get water into mouth.
Unable to blink or close the eye completely.
Diagnosis of neuritis of the facial nerve

When signs of neuritis appear, you need to contact a neurologist. As a rule, the external examination of the patient is enough for the doctor to make the correct diagnosis. Instrumental methods of examination are required to identify the cause of neuritis.
The patient may be prescribed such diagnostic procedures as:
MRI.
CT scan of the brain.
Electroneurography.
Electromyography.
If a viral or bacterial nature of neuritis is suspected, blood is taken for a general analysis.
Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve
Drug group | Name of the drug | How does the drug work? | How to take the drug? |
Diuretics | Furon or Furosemide | The drugs help to remove excess fluid from the body, due to which the edema subsides, the vessels do not overfill with blood, the nerve will not be clamped. | 1 tablet 1 time per day, in the morning. |
NSAIDs | Friend or Nurofen | Drugs relieve inflammation, reduce pain. | 1 tablet 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. |
GCS | Dexamethasone or Prednisolone | The drugs reduce pain, relieve swelling and inflammation, improve the conduction of impulses along the nerve fibers. | In the first days, 2-3 mg of the drug, after feeling better, the dose is reduced by 3 times. The course of treatment is 10 days. |
Antivirals | Zovirax or Acyclovir. | The drugs destroy the herpes viruses. | 1 tablet 5 times a day with meals. The course of treatment is 5 days. |
Antispasmodics | No-shpa or Spazmalgon | They relieve spasm from blood vessels, dilate arteries, improve blood supply to the affected area, and reduce pain. | 2 tablets 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days. |
Neurotropic drugs | Phenytoin, Levomepromazine, Carbamazepine. | Nerve cells begin to function better, metabolic processes stabilize, pain disappears, nervous tics decrease, muscles stop contracting involuntarily, and the functioning of the nervous system improves. | ½ or 1 tablet 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days. |
B vitamins | Thiamine, Pyridoxine, Riboflavin (B1, B6, B12) | These vitamins are essential for the nervous system to function properly. | 1-2 tablets 1 time per day. The duration of treatment is 30-60 days. |
Anticholinesterase drugs | Proserin, Galantamine | The drugs improve the transmission of impulses along the nerve fibers, increase muscle tone, normalize the work of the salivary and lacrimal glands. | 1 tablet 1-2 times a day from the second week of illness. The course of treatment is 1-1,5 months. |
Physiotherapy
Procedure name | When appoint? | What is the effect? | Multiplicity of holding |
UHF | Inflammation of the facial nerve, violation of its blood supply, insufficient outflow of lymph. | Improvement of metabolic processes, heating of tissues, removal of edema and inflammation. | The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. The course consists of 5-15 sessions, which are carried out every other day. |
UV | Acute or subacute neuritis of the facial nerve, starting from the 7th day of illness. | Increase immunity, reduce the intensity of inflammation, relieve pain. | The course of treatment is 5-20 procedures, 1-2 biodoses per session. |
Decimeter therapy UHF | Acute and subacute neuritis of the facial nerve | Heating of tissues, activation of metabolic processes, vasodilation, improvement of nerve nutrition and its restoration. | One procedure lasts 5-15 minutes. The course consists of 3-15 procedures. |
Electrophoresis with dibazol, prozerin, nivalin, potassium, vitamin B1. | Inflammation of the facial nerve, metabolic disorders, muscle atrophy. | Removal of inflammation and edema, reduction of pain. | The course of treatment consists of 10-20 procedures, each of which lasts 10-30 minutes. |
Diadynamotherapy | Muscle paralysis, contractures, pain in the affected area, damage to the facial nerve. | Reduction of edema and inflammation, improvement of metabolic processes, rapid tissue regeneration. | The course consists of 10-30 sessions of 10-20 minutes each. |
Applications with paraffin or ozonokerite | Subacute inflammation of the facial nerve, paralysis of the facial muscles | Rapid regeneration of the nerve fiber. | The course consists of 10-20 procedures of 40 minutes each. |
Massage

Massage can be started no earlier than 5-7 days from the onset of the disease. Features of its implementation:
Before starting the procedure, you need to stretch the neck muscles by turning your head back and forth, making head rotations in different directions.
First massage the back of the head and neck.
Then perform a massage of the diseased and healthy part of the head.
Carefully work out the face, mastoid process, neck, collar zone.
Massage movements are superficial. In the future, you can make light vibrations.
All movements should be directed along the lymph flow.
The face is massaged with fingers from the center of the chin, nose and forehead to the ears.
You can not massage those areas in which the lymph nodes are located, as this can cause their inflammation.
Then do the exercise. Put your thumb behind your cheek and stretch their muscles. At the same time, with the index and thumb of the other hand, the cheek muscles are worked out from the outside.
Finish the massage with exercises aimed at working out the muscles of the neck.
The massage should last at least 10-15 minutes. It is performed until the symptoms of inflammation completely disappear. It is best to trust your face to a professional.
Complications of neuritis of the facial nerve

Possible complications of the disease:
Atrophy of the muscles of the face.
Contractures of the muscles responsible for facial expressions.
Blepharospasm, facial hemispasm.
Facial synkinesis.
Keratitis and conjunctivitis.
Nerve fibers recover slowly. To speed up this process and avoid complications, you need to follow all the doctor’s instructions and seek medical help in a timely manner.









