Contents
Kidney nephrosis is a disease that develops against the background of dystrophic changes in the tubules of the kidneys and is accompanied by a violation of protein metabolism. The causes of nephrosis (nephrotic syndrome) are varied. Nephrosis can occur as a result of damage to the kidneys themselves, or as a result of other diseases of the body. Accordingly, primary and secondary nephrosis are distinguished.
With kidney nephrosis, the renal tubules, which are responsible for filtering urine, suffer. The permeability of the tubules increases, and blood proteins begin to seep through them, which leads to their loss during urination. As a result, the body begins to suffer from a failure in metabolic processes.
Causes of kidney nephrosis:
Protein metabolism disorders at the genetic level.
Complications of infectious diseases that are chronic or severe.
Systemic diseases: rheumatism, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis.
Kidney disease: nephroptosis or glomerulonephritis.
Tumors.
Nephrosis of the kidneys is a disease that is not widespread. It is most common in children and adolescents, although it can develop at any age. The first signs of nephrosis most often appear between the ages of 2 and 6 years. Girls suffer from the disease less frequently.
According to statistics, out of 7 million people, nephrosis is diagnosed in 50-60 children. The increase is from 20 to 25 new patients per year. Out of 100 thousand children under the age of sixteen, nephrosis is diagnosed on average in 2 people.
Classification of the disease
Kidney nephrosis is usually classified according to the etiological factor, since depending on this, the symptoms of the disease will differ.
Lipoid nephrosis or nephrosis with minimal changes
Lipoid nephrosis is extremely rare and is characterized by damage to the tubules of the kidney, which proceeds according to the dystrophic type. Lipoid nephrosis is a consequence of any disease of the body. So, tuberculosis, malaria, dysentery, syphilis, lymphogranulomatosis, heavy metal poisoning can provoke dystrophic changes in the kidneys.
The capillaries of the renal glomeruli lose their ability to normal filtration due to a sharp failure in lipid and protein metabolism.
Plasma proteins leak through the capillaries and accumulate on the epithelium of the renal tubules. This leads to the development of dystrophic changes in them. Most scientists believe that the cause of lipid nephrosis are autoimmune processes occurring in the body.
Necrotizing nephrosis or necronephrosis
This type of nephrosis develops as an infectious-toxic lesion of the kidneys. In this case, there is a violation of their blood supply, which leads to the death of tissues lining the renal tubules. The patient begins to experience symptoms of acute renal failure, he develops anuria.
Blood circulation in the kidney is disturbed, the reabsorption of water does not occur in full. As a result, toxic substances remain in the tubules of the kidneys, the concentration of which is constantly increasing. This leads to a worsening of the patient’s condition. It will be the harder, the more aggressive the bacterial or chemical toxins that affect the epithelium of the tubules. Shock kidney syndrome may develop.
Amyloid nephrosis or renal amyloidosis
Amyloidosis of the kidneys develops against the background of a chronic failure in protein metabolism and is characterized by the deposition of amyloid complexes in the tissues. Amyloid nephrosis is a consequence of amyloidosis.
In primary amyloidosis, the renal tubules suffer due to genetic abnormalities in the process of protein synthesis. With secondary amyloidosis, the kidneys lose the ability to function normally due to a malfunction in protein metabolism that occurs against the background of infections such as: osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, syphilis, actinomycosis.
Infection leads to the fact that the synthesis of proteins is disturbed, and they begin to be produced with certain disorders. The immune system, with the help of antibodies, begins to attack these mutated proteins. Proteins combine with antibodies and form amyloid. It begins to be deposited in various organs and tissues. With the accumulation of amyloid in the kidneys, the vessels of the glomeruli suffer, urine filtration is disturbed and nephrosis develops.
Post-transfusion nephrosis
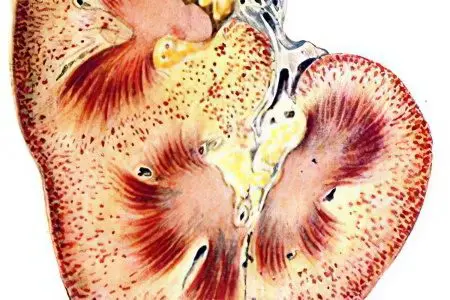
This type of nephrosis occurs due to the fact that a person has been transfused with blood that is incompatible with his group. As a result, erythrocytes begin to break down inside the vessels, acute renal failure develops, which can lead to shock.
Separately, it should be noted nephrosis against the background of fever accompanying any infectious disease. In this case, the patient does not feel the symptoms of nephrosis, and it can be determined only by urinalysis. It increases the amount of protein. As a rule, such nephrosis does not need specific therapy and goes away on its own when the human body copes with the infection.
The main symptoms of kidney nephrosis

Common symptoms of kidney nephrosis are as follows:
The presence of dystrophic changes in the tubules of organs;
Increased permeability of blood vessels and capillaries of the tubules;
Failure in metabolic processes against the background of increased excretion of albumins from the body;
A drop in the level of protein in the blood by 3,5-5,5% with a drop in the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma;
Since the oncotic pressure drops, the vessels cannot fully prevent the penetration of fluid into the tissues, and the patient develops edema;
The volume of urine excreted decreases;
Urine becomes dark in color.
It is the darkening of urine, and a decrease in its volume, that are early signs by which kidney nephrosis can be suspected.
Treatment of kidney nephrosis

Treatment of renal nephrosis is a difficult task. Therapy should be built on the basis of the form of the disease.
Principles of treatment of necrosis:
Elimination of the cause of the disease.
Getting rid of edema.
Normalization of the amount of protein in plasma.
For therapy to be successful, it is necessary to get rid of the cause that led to the development of nephrosis. To get rid of lipid nephrosis, it is necessary to determine which infection provoked the development of the disease. Taking into account this factor, antibiotic therapy is selected.
For the treatment of necrotic nephrosis, it is necessary to conduct detoxification therapy, as well as measures that will prevent the development of a shock state in the patient.
For the treatment of amyloid nephrosis, the patient is prescribed a special diet enriched with fruits, vegetables, vitamins and foods containing potassium. During the acute phase of the disease, the patient is given a blood transfusion, diuretics and albumin preparations are prescribed.
To reduce the swelling that accompanies any form of nephrosis, patients are advised to eat a reduced salt and water diet. No more than 1-2 g of salt should be consumed per day. In parallel, the patient is prescribed diuretics.
Diet
Since all patients with renal nephrosis suffer from protein loss, it is necessary to restore its level. During an exacerbation of the disease, patients are prescribed blood transfusions, intravenous administration of albumin and diuretics.
In addition, a high-protein diet is recommended for all patients. The emphasis is on eggs and meat dishes. Calculation of the daily dose of protein: 2-3 g/kg of body weight.
Patients with glomerulonephritis, in which a protein diet is prohibited, increase the calorie content of meals, introduce foods rich in fats and carbohydrates into the menu. The patient should consume no less protein per day than he loses in the urine.
Patients with any form of nephrosis are shown to undergo therapy, which is designed to reduce swelling and bring the state of the body back to normal.
Upon reaching remission, the patient is prescribed a diet based on the following principles:
Limiting salt and fluid intake.
Increasing the content of protein products in the menu.
The intake of vitamins with food.
If the disease has a chronic course, then the dietary regimen is not adhered to on an ongoing basis, but periodically.
Treatment prognosis
The prognosis for recovery with nephrosis largely depends on the form of the disease. The earlier the treatment was started, the higher the chances of its successful completion. An unfavorable prognosis persists with amyloid nephrosis.
During an exacerbation of any form of nephrosis, a person is disabled. In chronic nephrosis, it is necessary to undergo spa treatment.
Self-treatment of kidney nephrosis is impossible. Therapy should take place under medical supervision.
It is very important to correctly isolate the cause that provoked the development of nephrosis. The success of treatment is largely determined by how timely therapy was started and how accurately the patient follows medical recommendations.









