Contents
Tomato stem necrosis is a disease that can completely destroy bushes or severely slow down their development. In both cases, the gardener is left without a crop. It is impossible to get rid of the causative agent of the disease and cure plants with the help of modern chemicals; varieties and hybrids resistant to the pathogen also do not exist. Therefore, special attention must be paid to prevention and competent agricultural technology.
What is this disease
The official name of the disease is core necrosis of tomato stems. The pathogen causes necrosis of cells and tissues, which leads to irreversible disruption of their functions.
In the vast majority of cases, stem necrosis is observed in tomatoes in a greenhouse, although “street” plants are not immune from it. The disease develops for a long time (the incubation period is more than 18 days), the first symptoms appear already at the fruiting stage.
Tomato stem necrosis is caused by a bacterium. The pathogen is transmitted mainly through infected planting material. It is also able to remain viable for a long time (up to 4-5 months) in dry plant residues. The bacterium does not live in the soil, it is quickly “forced out” by other soil microorganisms.
The disease has been known since the late 70s. It appeared in Our Country a little later, in the 90s: the active import of planting material from the Netherlands “contributed” to it.
In the best case, when the stem is damaged by necrosis, tomato crop losses are 50-80%. When using infected planting material, fruits can not be expected at all, the plants will quickly die.

In the people, the disease is sometimes called “hollowness”
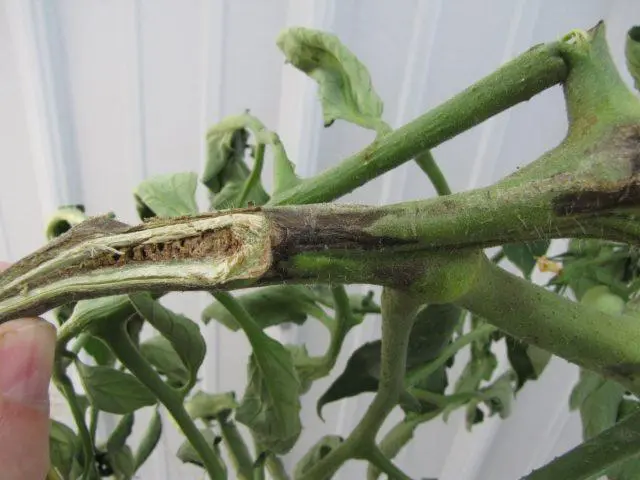

England is considered the “homeland” of necrosis of tomato stems.
Symptoms of infection
The first symptom of necrosis is elongated, slightly “depressed” spots and stripes, slightly darker than the main shade of the stem. Gradually, they become deeper, turn into cracks, from which a cloudy creamy-whitish viscous liquid oozes, resembling mucus – exudate.
At the same time, the process of “mass” formation of aerial roots begins, gradually “rising” along the stem from the base above and changing shade from brownish-beige to dirty brown. The core of the stem in tomatoes affected by necrosis is first watery-transparent, then cloudy brown. On the cut, the black vascular system is clearly visible.
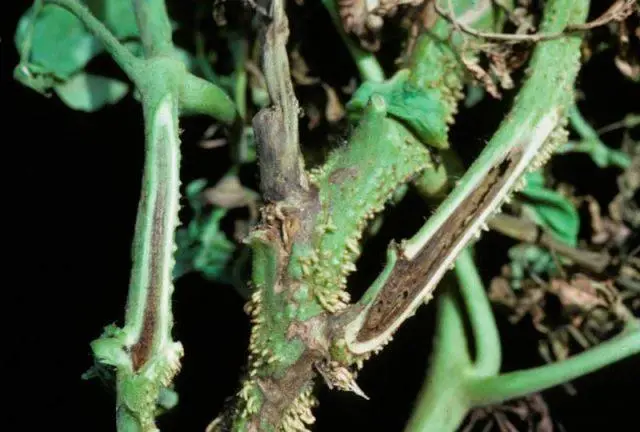

Aerial roots – a deliberately unsuccessful attempt by an infected plant to compensate for the lack of water and nutrients
Obviously, in diseased bushes, the aerial part does not receive sufficient water and nutrients. Therefore, the leaves of tomatoes affected by stem necrosis quickly turn yellow and wither. Often they look as if “scalded” with boiling water.
Since in most cases the active development of the bacterium that causes necrosis of the stem of tomatoes coincides with the beginning of the ripening of the crop, the tomatoes themselves also suffer. On the surface of the skin, a “network” of light yellowish veins appears, which does not disappear during ripening.
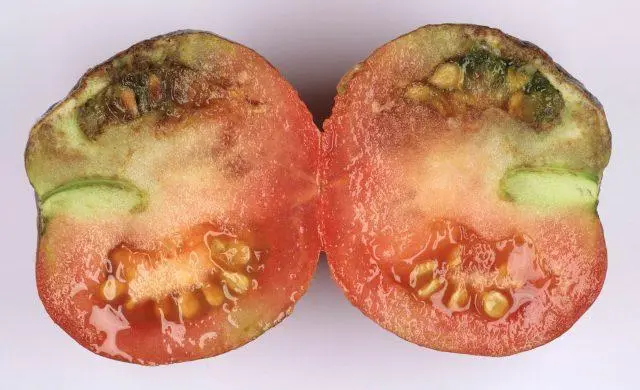
The seed coat of tomatoes affected by stem necrosis is also black, dead
Causes of tomato stem necrosis
In most cases, the primary source of infection of tomatoes with stem necrosis is planting material. The bacterium lives in the shell or germ of the seed. The “second wave” of the spread of the pathogen is provided by exudate oozing from the stems of diseased plants, penetrating into any microdamages. Its drops are carried by the wind, fall from infected bushes to healthy ones with water when watering.
The gardener himself can become a “peddler” of tomato stem necrosis. The pathogen gets on garden tools, tools, gloves and is transferred to healthy plants if regular disinfection is neglected.
In addition to serious errors in agricultural technology and neglect of preventive measures, there are other “risk factors” that increase the likelihood of infection of tomatoes with stem necrosis:
- constantly increased humidity of air and soil;
- large differences between day and night temperatures, rather cold nights;
- excess nitrogen in the soil.

It is quite possible that drops of juice from diseased bushes get on the “neighbors” in the garden during pruning
Development of the disease
Getting on tomato bushes, the bacterium that causes necrosis “introduces” into the core of the stem and actively multiplies there, forming entire colonies, which are whitish mucus of exudate. As a result, all vital processes in cells and tissues, including photosynthesis and metabolism, are “knocked down”.
There are two main scenarios for the development of events. If the tomato bush is initially “weakened”, does not have good immunity and endurance, it dies. Healthier, stronger, and pathogen-resistant specimens survive, in which the disease becomes chronic.
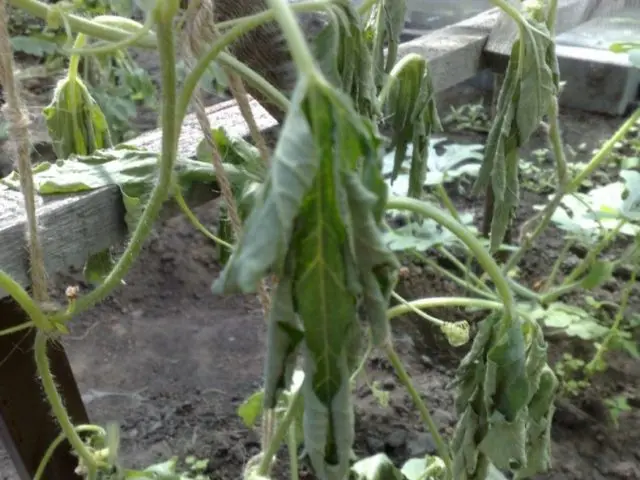

Surviving plants practically stop in development, turn into a source of pathogen spread
Cases of “spontaneous healing” of tomatoes affected by stem necrosis are much less common. The mechanism of this phenomenon has not yet been explained. Usually, the pathogen spreads along the aisles, but in some bushes, the characteristic symptoms disappear completely or almost completely 3-4 weeks after their appearance, they continue to grow and bear fruit. However, it is strongly discouraged to use seeds extracted from such tomatoes for planting next season.
Methods for the treatment of tomato stem necrosis
Methods and means to cure tomatoes infected with stem necrosis do not yet exist. The bacterium does not “succumb” to either agrochemicals, or biological products, or folk recipes. They can only be used for prevention to reduce the number of primary infections.
Folk remedies
Gardeners who want to prevent infection of tomatoes with stem necrosis, folk remedies are used exclusively at the stage of preplant seed preparation. During the active growing season, their treatments will be completely useless.
To “etch” seeds wrapped in gauze or a linen napkin, use compounds with antiseptic properties:
- Aloe juice. A large bottom leaf from an adult (over 4-5 years old), an absolutely healthy plant, is peeled, the pulp is crushed into gruel. It is mixed with water in approximately equal proportions. Seeds are kept in liquid for a day.
- Potassium permanganate solution. Crystals are added to water until bright pink. For the prevention of tomato necrosis and the destruction of other pathogenic microflora, planting material is treated for 5-6 hours.
- Infusion of onion or garlic. Leaves, heads, and cloves are used as “raw materials”. It is crushed, poured with warm water in a ratio of 1: 2, left in a warm dark room under a tightly closed lid for 3-4 days. Before use, filter and dilute with water 1:1. In the finished infusion, the seeds are soaked for 2-3 hours.
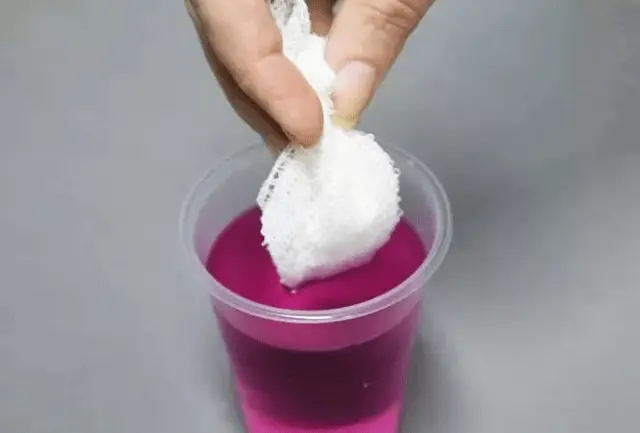

Potassium permanganate solution is a very popular disinfectant for any seed.
Chemicals
Since it is impossible to fight tomato stem necrosis, including through the use of agrochemicals, the bushes are pulled out and destroyed, getting rid of the sources of bacteria. After that, it is recommended to shed the soil with a fungicide solution for disinfection. Suitable drugs:
- Acrobat MC;
- Quadris;
- Baileton;
- Ridomil-Gold;
- Abiga Peak;
- Oksikhom;
- Cuprozan;
- Topaz;
- Speed;
- Strobe.
The concentration of the working solution is determined according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Approximate consumption 4-5 l / m². The bed is watered from a watering can.

The entire procedure, starting from the moment the solution is prepared, takes place with the use of personal protective equipment
Biopreparations
Biological products – an alternative to folk remedies for preplant seed treatment. To destroy the bacteria that cause necrosis of the stem of tomatoes on the surface of the shell, they are soaked in a solution:
- Maxim;
- Previcura;
- Phytosporin;
- Phytoavalanche;
- Aliryna-B;
- Bactophyta;
- Gamaira.
The solution is prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It also defines the etching time.

As a rule, a solution of a biological product does not even have a short shelf life, it must be used immediately.
Treatment of stem necrosis in tomato seedlings
Stem necrosis in tomato seedlings is an infrequent occurrence. Even if the germ of the seed itself is infected with a bacterium, it needs a fairly long period for development and reproduction. During this time, the gardener manages to transfer the seedlings to the garden or to the greenhouse.
From the photo of the plants, it is clear that it is difficult to identify stem necrosis in tomato seedlings. It does not reach the appearance of cracks, the seedlings just look lethargic. The only way to make a definitive diagnosis is to cut off the stem and look at the core.
Trying to treat stem necrosis on tomato seedlings is a waste of time. Seedlings are guaranteed not to be viable. Affected instances can only be destroyed.
preventive measures
Prevention is, in fact, the only thing a grower can do to really reduce the risk of stem necrosis infection in tomatoes. It includes the following activities:
- The purchase of seeds produced by well-known agricultural companies with a solid reputation, able to guarantee the quality of planting material. In addition, the seller must be able to confirm their “originality” with a certificate of conformity.
- With self-collection of seeds – careful selection of “donor” bushes and no less careful rejection of planting material before sowing seedlings.
- Compliance with the scheme of planting plants. It is determined taking into account the dimensions of an adult plant and the type of bush. With “cramped” plantings, the bacterium that causes stem necrosis of tomatoes spreads much faster.
- Disinfection of the substrate and containers for planting seeds for seedlings, any tools and garden equipment every time after work.
- Competent care of landings. Proper watering and fertilizing are especially important for the prevention of tomato stem necrosis.
- “Support” immunity. During the season, regular (every 2,5-3 weeks) foliar feeding with biostimulants and immunomodulators will be useful to strengthen overall endurance.
- Timely ventilation of the greenhouse to maintain comfortable air humidity for plants.
- Mandatory cleaning after harvest. All tops and other plant debris are raked from the garden and burned. In the greenhouse, it is desirable to disinfect the substrate or replace its top layer.
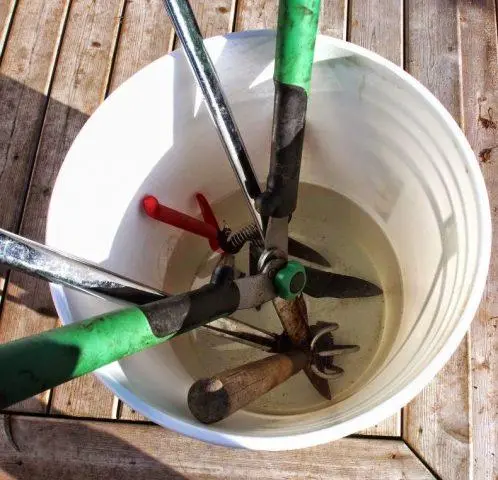

Without disinfection, it is likely that the gardener himself will become a “peddler” of a bacterium that causes necrosis of the tomato stem
Sustainable varieties
There are no varieties and hybrids of tomatoes that are immune to the bacterium that causes stem necrosis. Even if the manufacturer indicates in the description the presence of “relative resistance” to the disease (as, for example, in the Red Arrow F1, Maeva F1, Resento F1 hybrids), it is very likely that this is just a publicity stunt.
Based on the experience of gardeners, tomato varieties and hybrids are less likely to suffer from stem necrosis, which are distinguished by their ability to successfully resist negative external influences and overall good immunity. These include, in particular:
- Vologda F1;
- Ural F1;
- Bohemia F1;
- Koenigsberg;
- Chio-Chio-san;
- Waterfall;
- Geisha;
- Crimson giant;
- Eagle heart;
- Cap of Monomakh;
- Golden domes;
- De Barao.
Conclusion
Tomato stem necrosis is currently an incurable disease. Neither folk remedies, nor biological products, nor “heavy artillery” in the form of agrochemicals are capable of helping infected bushes. Varieties and hybrids of tomatoes that are immune to the bacterium that causes stem necrosis also do not exist.









