Contents
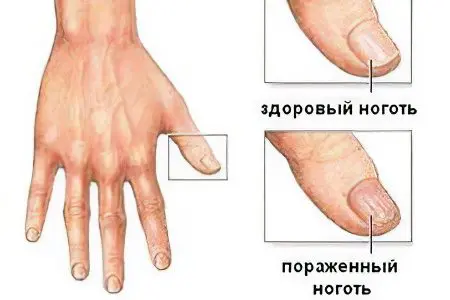
Nail fungus on the hands is an infectious lesion of the nail plate, which is provoked by pathogenic and opportunistic fungi.
According to available statistics, onychomycosis of the hands is caused primarily by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (in 44,5% of cases), followed by fungi of the dermatomycetes group (up to 36,4% of cases), mold fungi (16,5%) and other mycotic organisms (up to 0,5%). With a fungus of the hands, both one and several nail plates can be affected, a parallel lesion of the nails of the fingers of the lower extremities is possible.
Clinical observations indicate that the increase in the number of people suffering from nail fungus on the hands is increasing every year, which is explained by the factor of intrafamilial infection. Experts point to an increased number of patients with mixed non-dermatophyte flora on the nails. So, mixed flora occurs in 7,3% of cases. This is a rather dangerous trend, since there is an opinion that mixed non-dermatophyte fungi can enhance the sensitization of the human body.
The number of people with fungal nail infections, according to various sources, varies from 2% to 18,5% of the total human population.
Symptoms of a fungus on the hands
Symptoms of the fungus on the hands with the defeat of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Manifests the disease from the lateral and posterior ridges of the nails of the hands. They gradually become thicker, swell and redden. It is possible to visualize silvery scales that form along the edges of the ridges. As the fungal infection progresses, the inflammation spreads to the entire roller, it begins to peel off. The skin becomes thinner, the eponychion disappears. If you press on the roller, then an ichor, purulent contents (with the addition of a bacterial infection) or a small lump of white, crumbly mass can stand out from it.
The next stage of the disease is the defeat of the nail plate. It gradually fades, begins to separate from the bed in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe hole. Destruction proceeds according to the type of onycholysis, furrows and hills appear over the area of the plate. Such processes are caused by a failure in the blood supply of the plate in the area of the matrix. They are trophic in nature, and are provoked by infection of the roller.
When the nail is affected by yeast-like fungi along the lateral path, the destruction of the plate begins from the lateral edges. The nails become thinner, begin to separate from the bed, their color changes to yellow-brown. When examining the nail, a visual impression is created that it was cut off on the sides.
Sometimes fungi of the genus Candida infect the nail, but the roller does not become inflamed. In this case, the plate does not adhere to the bed, the nail gradually becomes thinner, but the roller remains intact.
Symptoms of the defeat of red trichophyton (nail rubromycosis). Light yellow, whitish or grayish spots and stripes form on the nails. Their localization is the center of the nail. As the disease progresses, the nail fades and undergoes deformation – normotrophic, hypertrophic, atrophic, or by the type of onycholysis.
Symptoms in the defeat of T.interdigitale. In the center of the nail plate, in its thickness, bright yellow spots or stripes appear. At the edge free from spots, thickening of the nail sometimes occurs. The plate deforms over time and has a corroded appearance.
Symptoms in case of damage by anthropophilic trichophytons. This type of fungal infection often occurs in parallel with the defeat of the scalp and smooth skin. Superficial trichophytosis most often manifests precisely from the nails of the upper extremities. A gray spot appears on the sides and from the distal edge of the nail, which gradually increases in size. It is also possible the formation of stripes on the nail plate. It thickens and begins to crumble. For a long period of time, deformation of the nail does not occur. Most often, such a lesion of the nail plates is observed in patients who have been suffering from favus for a long time.
Symptoms in case of defeat by zoophilic trichophytons and microsporums. This type of injury is quite rare. The disease proceeds according to the type of onychodystrophy. At the beginning, white spots and stripes appear on the nails, after which the plate is deformed and then destroyed from the proximal or distal edge. The nail ceases to grow to the bed, the color in this disease often remains unchanged. Sometimes the nail turns yellow.
Symptoms of a nail infection with mold fungi. Nail damage by mold fungi develops as a secondary infection, with untreated onychomycosis of any nature (see also: Onychomycosis – causes and prevention). Molds are difficult to irradiate from the nail plate and require the appointment of systemic drugs. In this case, the nail itself changes color, which varies depending on the type of pathogen. Color can be black, brown, blue, green or yellow.
Depending on the form of the lesion, the following symptoms of nail fungus are distinguished:
With normotrophic form there is only a change in the color of the nails. At first, color changes affect only that part of the nail where spots and stripes form, followed by the involvement of the entire nail in the process. At the same time, its thickness and luster remain unchanged.
With hypertrophic form the nail loses its luster, fades and thickens. Deformations of varying severity occur, up to the development of onygryphosis. The nail collapses on the sides and resembles a bird’s claw.
With onycholytic form there is a tarnishing of the nail, it acquires a grayish tint in the part where the lesion occurred. Possible rejection of the plate from the bed. After exposing the nail area, an area with loose layers is found under it. For a long time, the proximal part of the plate remains uninvolved in the pathological process.
The main symptoms of onychomycosis of the hands are as follows:
The nail to some extent changes its color, which depends on the type of pathogen. Most often this occurs with total dystrophy.
The surface of the nail becomes rough. Roughness can be determined both visually and by palpation.
Stratification of the nail most often occurs with a distal-lateral lesion. As the disease progresses, the area of the dissection increases.
The appearance of white spots under the nail.
Loss of healthy shine. This happens gradually, perhaps for a long time there will be no other manifestations of mycotic lesions.
Strengthening the formation of burrs. This symptom is observed when the skin roller is damaged, when the skin along the edge of the nail begins to quickly die and burst.
Detachment of the entire nail plate. This symptom is characteristic of total dystrophy.
Peeling of the skin of the hands. Sometimes fungi affect not only the nails, but also the skin of the hands and it begins to exfoliate in the form of small scales.
The appearance of crumbs on the surface of the nail plate. This symptom can be observed with a white superficial form of a fungal infection. Subsequently, small depressions form on the surface of the nail.
Causes of the appearance of fungus on the hands

It is known that the fungus on the hands appears as a result of infection with mycotic organisms, or due to an increase in the pathogenic activity of a person’s own fungal microflora.
The following factors may influence this:
The development of a fungus on the hands can be affected by a violation of cellular immunity, which is often provoked by various diseases, including HIV infection, diabetes mellitus. (read also: Causes, signs and symptoms of diabetes)
Unjustified intake of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, especially for prophylactic purposes with self-treatment. This also includes the widespread use of drugs that have an immunosuppressive effect (cytostatics, glucocorticoid hormones).
The use of false nails, under which a favorable environment is formed for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Frequent contact with water, which may be due to professional activities. The risk group includes: restaurant staff, hotels, workers in metallurgical industries, rest homes, sanatoriums, canteens, etc. The longer the hands and nails are in a humid environment, the higher the risk of developing the disease, especially candidal nail lesions.
Exposure to nails with chemical and alkaline substances, frequent degreasing of the nail plate (especially when performing a manicure) weakens the nail’s own protection, contributes to the thinning of the plate, and therefore increases the risk of developing the disease. The factors of exogenous impact also include frequent contact of brushes with soil and solutions containing sugars. Therefore, the risk group also includes workers in confectionery shops and the agricultural industry.
Mature and advanced age is another risk factor for the development of pathology. Every 10 years, the risk of the disease increases by 2,5 times. Experts attribute this to a slowdown in the growth rate of the nail plate, malnutrition of the nail, and the development of angiopathy.
Any injury to the nail, both during manicure and as a result of bruising, clamping, compression, etc. This also includes any destruction of the nail, hemorrhages with the formation of channels and cavities, onycholysis. A separate risk group for nail injuries are musicians, guitarists, and PC operators.
The presence of a sick relative living in the same territory. Sharing towels, manicures, and sharing bathrooms and showers all increase the risk of infection.
Foot fungus. It is known that most often mycotic lesions of the nails of the hands are preceded by untreated onychomyosis of the legs. As the disease progresses, with a weakening of the immune system and under the influence of other risk factors, the infection spreads with the involvement of fingernails in the pathological process.
psychological reasons. The risk of fungal infection increases with the presence of a bad habit of biting your nails. There are also two psychogenic pathologies: onychophagia (uncontrolled nail biting) and onychotillomania (an obsessive desire to destroy one’s own nail).
What is dangerous fungus on the hands?
Fungus on the hands is not only an aesthetic problem. This is a serious disease that can lead to various complications, especially if this process is ignored. Often, the fungus does not cause a person significant concern for a long time, however, with a weakening of the immune forces, as well as as a result of age-related changes, mycotic organisms increase their activity and lead to serious health problems.
Possible consequences of the lack of therapy for mycosis of the hands:
The spread of the pathological process to the skin of the hands.
The likelihood of developing inflammation due to the addition of bacterial flora. A damaged nail and skin roller is the entrance gate for various bacteria.
The development of chronic erysipelas of the limb.
Development of invasive mycosis.
The development of aspergillosis, that is, damage to the nail plate by mold fungi.
The development of multivalent sensitization against the background of prolonged excretion of waste products by fungi. This, in turn, entails an increase in allergic skin reactions, their intensification and the difficulty of therapeutic correction, the formation of drug resistance.
Exacerbation of existing skin pathologies: dermatosis, psoriasis, hemoderma, atopic and seborrheic dermatitis (see also: Dermatitis – causes, symptoms, treatment and diet).
In addition, a person who ignores treatment becomes a carrier of infection and poses a danger to other people in terms of infection.
Hand nail fungus treatment

Traditional therapy of any onychomycosis involves the use of systemic and external antimycotics. As for the surgical removal of the nail plate, all modern doctors have refused this method. It is practiced only with the addition of a bacterial infection, or with a long-term absence of effect from local and systemic antimycotic therapy.
As an alternative to the surgical method, avulsion or dissolution of the nail may be prescribed. This procedure is performed using drugs such as Nogtivit or Nogtimycin. In this case, it is possible to perform the procedure at home, but a medical consultation is first necessary.
Means of topical application
When mycosis of the nails of the hands is diagnosed in the early stages of development, it is possible to get rid of the disease by using only local preparations. It can be creams, varnishes, ointments, gels, aerosols, solutions and other medicines.
Their advantages over systemic antimycotics are as follows:
The possibility of long-term treatment, which is not always possible with oral administration.
The number of side effects is not so great compared to systemic antimycotics.
Allergic reactions and individual sensitivity of the body to the components of preparations for topical application are much less common than when taking drugs inside.
The risk of overdose is minimized.
The indications for starting treatment exclusively with local antimycotics are as follows:
Less than 50% of the nail has undergone a pathological process;
Several nails are affected, but the lesions are punctate;
The shape of the nail plate is not changed;
There are contraindications to oral administration of antimycotics;
The form of the lesion of the nail plate is distal-lateral.
However, despite a number of advantages, it is not always possible to abandon systemic antimycotics. After all, local preparations are not able to penetrate deep into the nail plate. Often it is in the bed of the nail that fungi accumulate, which have increased keratinization. To achieve penetration of the local drug deep into the nail, it is necessary to remove its horny structures, which is possible due to the use of special nail files (mechanical method) or due to the application of keratolytic patches, which allow softening the structure of the plate.
The main remedy for topical application is varnish. (Read more: Nail fungus polish: A review of 11 drugs.)
In addition to varnishes, preparations of the Azols, Allylamines group, hydroxypyridone derivatives, as well as keratolytic agents are used.
Local treatment should be long and can be up to six months. However, if no effect is observed after two weeks from the start of therapy, it is necessary to reconsider the chosen tactics with a possible replacement of the drug.
Preparations for nail fungus on the hands
Oral administration of antimycotics is indicated in the following cases:
More than 50% of the nail plate was affected.
Subungual hyperkeratosis was diagnosed.
More than three fingernails affected.
There are associated diseases.
The patient’s age exceeds 50 years (in the absence of contraindications).
Antifungal drugs contribute to the destruction of fungal spores, have an effect on the keratinized parts of the nail, softening them. The dosage and frequency of administration, as well as the duration of the course of treatment, are determined exclusively by the doctor.
Despite the availability of medicines, you should not engage in self-treatment of onychomycosis of the nails of the hands. In order for the treatment to be comprehensive, you will need to consult a doctor, undergo a diagnosis, follow the treatment regimen and laboratory control of its results.
What else can be used to treat fungus on the hands?
Laser treatment
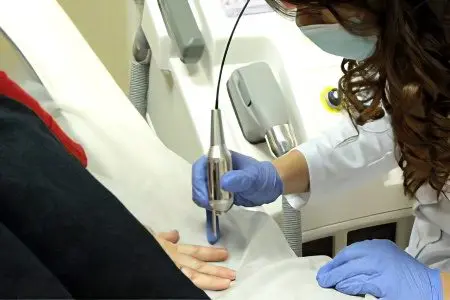
You can also treat the fungus on the hands with a laser. This method of getting rid of onychomycosis refers to physiotherapeutic methods and has proven high efficiency. The diseased nail during the procedure is exposed to radiation with adjustable intensity.
The laser is able to penetrate deep into the nail and locally destroy mycotic organisms. It is possible to prescribe laser therapy as an independent method of treatment if it is impossible to use local and systemic antimycotics. In all other cases, a combination of laser therapy with conservative methods of treatment is desirable. In addition, when irradiated with a laser, the delivery of the drug into the nail improves. The duration of the procedure does not exceed 25 minutes, to achieve the maximum effect, you will need to perform up to 4 exposures. However, most patients notice a visible effect after the first session of physiotherapy.
There are no side effects from the procedure, it is completely painless for the patient. The only drawback of such therapy is the likelihood of recurrence of the disease when used as an independent therapeutic method.
Hardware cleaning
Another method – hardware cleaning of the nail makes it possible to get rid of its upper layer, which has undergone the most mycotic damage. This procedure is necessary for use in the case when the fungus has destroyed the nail in a large volume. The procedure is painless and helps to speed up the recovery time by half. After all, the exposure of the nail bed will allow you to directly deliver athymicotics into it.










муу