Contents
 Myopia of the eye – causes, symptoms, degrees and treatment
Myopia of the eye – causes, symptoms, degrees and treatment  Myopia 1 weak degree
Myopia 1 weak degree Myopia 2 moderate
Myopia 2 moderate Myopia 3 high degree
Myopia 3 high degree Progressive myopia in children
Progressive myopia in children

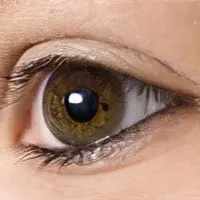
Myopia is a refractive error in which the focus of rays from a visual object does not occur on the retina, but in front of it. Since the disease is very common among the world’s population and affects up to 30% of people, pregnant women with myopia are seen by doctors quite often.
Symptoms of myopia during pregnancy
The unequivocal and most striking symptom of the development of myopia is the deterioration of vision when trying to see objects located far away. If a woman knows about her illness, then she knows about its characteristic symptoms that will be present throughout the pregnancy.
However, it happens that for the first time they can be experienced during the bearing of a child, so it is worth paying attention to the following signs and diagnosing them correctly:
Flashes before the eyes.
The appearance of outbreaks.
Clouding of visible objects, distortion of their shape.
Rapid eye fatigue.
Loss in the field of view of objects, which is characterized by its narrowing.
Feeling of discomfort in the eyes.
Headaches and pains in the forehead and eye sockets.
Since during the bearing of a child, a woman undergoes changes in all systems and organs, even in the absence of vision problems before, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist at least once.
Causes of myopia during pregnancy
The main reason for the development of the disease is its transmission by inheritance from parents to children. In addition, myopia can be acquired as a result of the negative impact on vision of prolonged stress, with frequent illnesses, due to craniocerebral injuries, etc.
However, during pregnancy, there are additional risks of developing myopia, due to the fact that:
During pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, tissue elasticity increases, so pre-existing low-grade myopia can cause serious problems, up to retinal detachment.
If a woman suffers from toxicosis, then myopia can be significantly aggravated, and vision can drop to 5 diopters. The reason for this is an increase in the permeability of the lens capsule for water, its swelling and curvature, which will lead to an increase in refractive power.
Degrees of myopia – what is the risk of caesarean section?
If a woman was diagnosed with the first degree of myopia, which does not progress and is characterized by a focusing distance to the retina from 1 to 3 diopters, then this in no way affects the method of childbearing. Childbirth can take place naturally, if there are no other contraindications to this.
When the diagnosis of “non-progressive moderate myopia” is established, then a woman can also give birth on her own.
If earlier in obstetrics caesarean section was almost always practiced for high myopia, now this is a thing of the past. It was found that retinal hemorrhage and detachment can occur in any healthy woman, and not just in those who suffer from myopia. Moreover, it has been proven that the risk of such a complication is in no way related to the existing myopia. Therefore, it is quite possible that a woman, even with a high degree of myopia, will be able to give birth on her own, without consequences for her own vision. However, you first need to undergo a series of examinations aimed at identifying changes in the retina.
If a woman has grade 3 myopia, but there are no complications in the form of retinal dystrophy or she is at an early stage, then the child comes out through the natural birth canal, but perineotomy is indicated.
When it comes to a high degree of myopia complicated by severe retinal dystrophy, it is worth taking into account the recommendations of an ophthalmologist and gynecologist, assessing the size of the pelvis of the woman in labor and the weight of the fetus, and only then decide on the method of delivery.
Retinal detachment after surgery on a single eye is an indication for a caesarean section. Under the same rule, the situation is suitable when the detachment was detected after the 30th week of pregnancy, and an operation was also performed.
No relationship has been established between the risk of retinal detachment and the number of subsequent pregnancies. However, a woman should be under special control of an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of myopia during pregnancy

Laser coagulation of the retina. As for the treatment of myopia during pregnancy, laser coagulation of the retina is an absolutely safe method. With its help, it is possible to strengthen and, as it were, solder it. This will prevent further retinal detachment and its dystrophy. Since the procedure is absolutely painless, it can be performed during pregnancy. It is important that the woman does not have signs of preeclampsia, that is, widespread vasospasm. After the blockade of tears and injuries, a woman needs to visit an ophthalmologist every month. A month before the birth, he evaluates the reliability of the coagulation performed and gives a conclusion on whether the woman is able to give birth on her own, or whether a caesarean section is necessary. When new retinal breaks occur, repeated laser exposure is required. If the retina begins to peel off, then emergency surgery is required.
Vision correction. As for vision correction, you can use both lenses and glasses throughout your pregnancy. Here, a woman should be guided by her own feelings and the doctor’s recommendations. If you wish, you can take disposable lenses with you to the maternity hospital, which do not need care, and you can stay in them for up to 12 hours.
It is important to be examined by an ophthalmologist, regardless of whether there are complaints about vision or not. The doctor should pay special attention to the fundus, which is examined after pupil dilation. The timing of the ophthalmological examination varies from 10 to 14 weeks. In the case when myopia is absent, you will need to come to the ophthalmologist again – a month before the expected birth. Thus, it will be possible to avoid complications and give birth to a child in a natural way.
Author of the article: Degtyareva Marina Vitalievna, ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist