Contents
Muscle soléaire
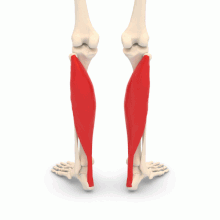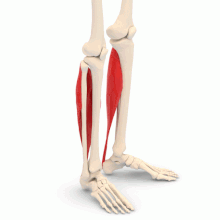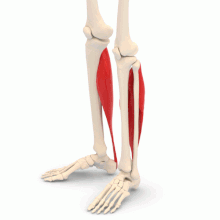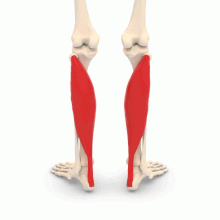
The soleus muscle (from the Latin solea meaning sole of the foot) is a bundle of the triceps sural muscle, a muscle belonging to the calf.
Anatomy
Shape and position. The sural triceps muscle gives the fleshy shape to the calf. The latter is located on the posterior part of the leg, between the back of the knee and the ankle.
Structure. The soleus muscle is a skeletal muscle, that is to say a muscle placed under the voluntary control of the central nervous system. The soleus muscle is one of the three bundles of the triceps sural muscle (the lateral gastrocnemius, the medial gastrocnemius, and the soleus muscle, located under the two gastrocnemius) (1).
Origin. The soleus muscle is inserted at the level of the posterior surface of the head of the fibula, also called the fibula, and of the body of the tibia (2).
Termination. The soleus muscle is inserted over the lamina of the calcaneal tendon, or Achilles tendon, to attach to the tuberosity of the calcaneus (2).
Vascularization and innervation. The soleus muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve (3).
Extensor muscle of the foot
The soleus muscle allows the extension of the foot, also called plantar flexion. (2)
Soleus pain: muscle and tendon
Muscle pain without lesions. (4)
- Cramp. Sometimes occurring in the soleus muscle, it corresponds to an involuntary, painful and temporary contraction of a muscle.
- Contracture. It is an involuntary, painful and permanent contraction of a muscle such as the soleus muscle.
Muscle injuries. The soleus muscle can suffer muscle damage, accompanied by pain. (4)
- Elongation. First stage of muscle damage, elongation corresponds to a stretching of the muscle caused by micro-tears and resulting in muscle disorganization.
- Breakdown. Second stage of muscle damage, the breakdown corresponds to a rupture of muscle fibers.
- Rupture. The last stage of muscle damage, it corresponds to a total rupture of a muscle.
Tendinopathies. They designate all the pathologies that can occur in the tendons. (5) In the soleus muscle and the Achilles tendon, they are mainly manifested by pain in the foot during exertion. The causes of these pathologies can be varied. The origin can be intrinsic as well with genetic predispositions, as extrinsic, with for example bad positions during the practice of sport (6).
- Tendinitis: It is an inflammation of the tendons.
Achilles tendon rupture. It is a tearing of tissue that causes the Achilles tendon to rupture. Symptoms are sudden pain and inability to walk. The origin is still poorly understood (7).
Treatments
Drug treatments. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, different treatments may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the type of pathology diagnosed, surgery may be performed.
Physical treatment. Physical therapies, through specific exercise programs, can be prescribed such as physiotherapy or physiotherapy.
Examination of the soleus muscle
Physical examination. First, a clinical examination is performed in order to observe and assess the symptoms perceived by the patient.
Medical imaging examination. X-ray, CT, or MRI exams can be used to confirm or further the diagnosis.
Anecdote
“Tennis leg”. Common pathology in tennis, the term « tennis leg » refers to muscle damage in the calf, most often a strain.