Contents
The liquid bubbling in jars delights, and the strength in the jet of 90% or more at the very first distillation of the mash makes you believe in the exceptional efficiency of multi-stage distillation systems, especially since it is difficult to even imagine a simpler and cheaper design. It remains only to figure out why such a successful solution for obtaining pure alcohol is not used in industry, and supporters of home distillation continue to improve their bulky and difficult to manage columns.
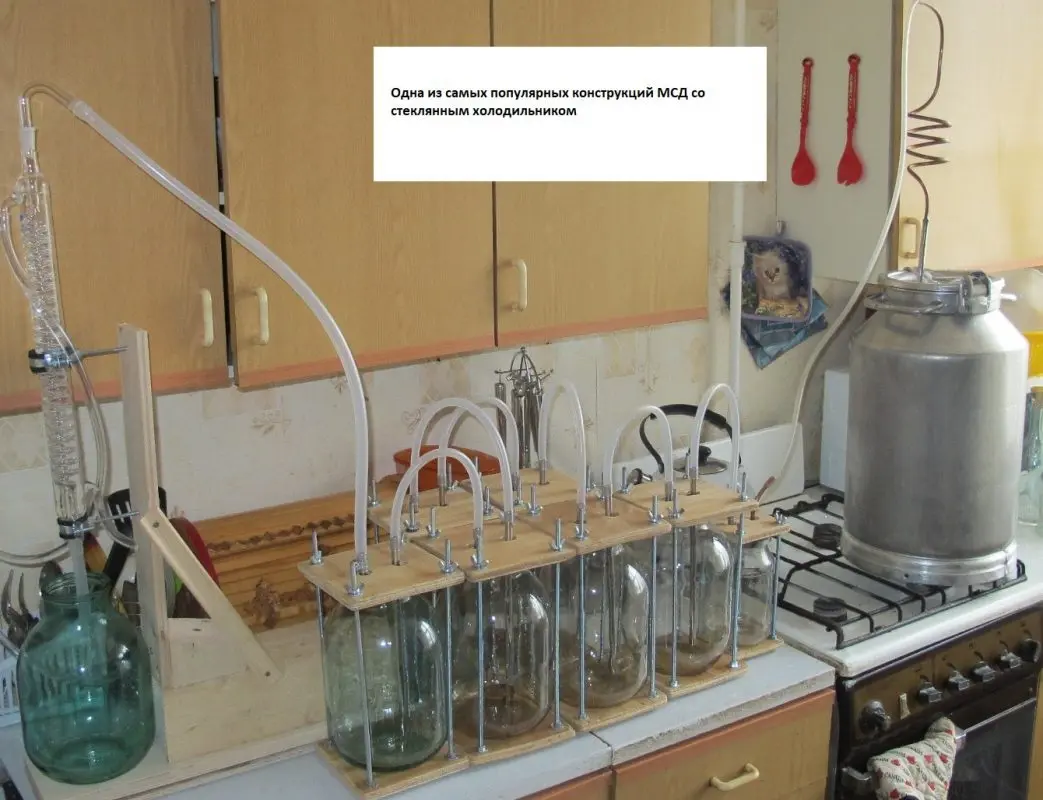
The MSD system is a separate module, consisting of 1-2 dry steamers (optional) and 4-15 bubblers, which are connected in series between the still and the refrigerator of the moonshine still.
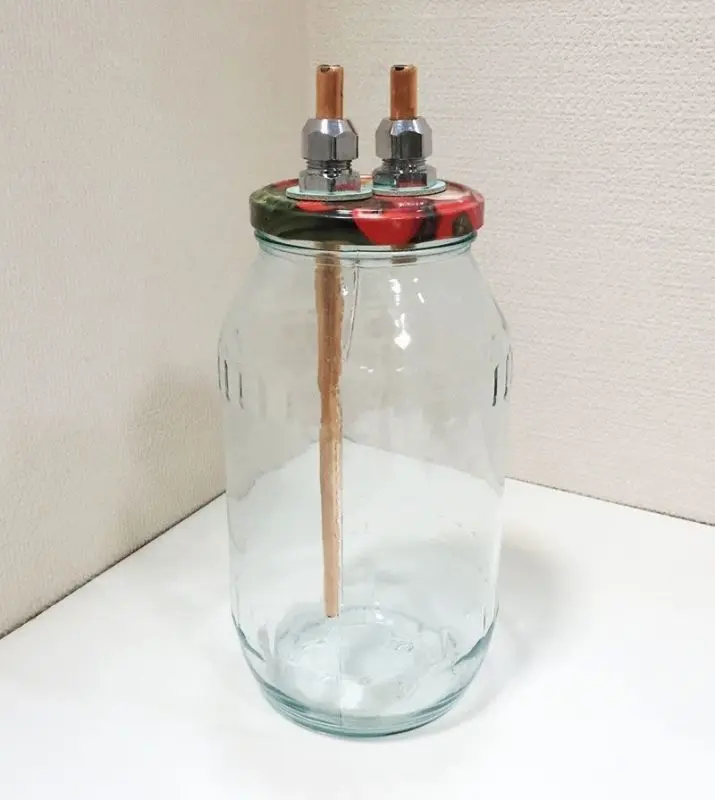
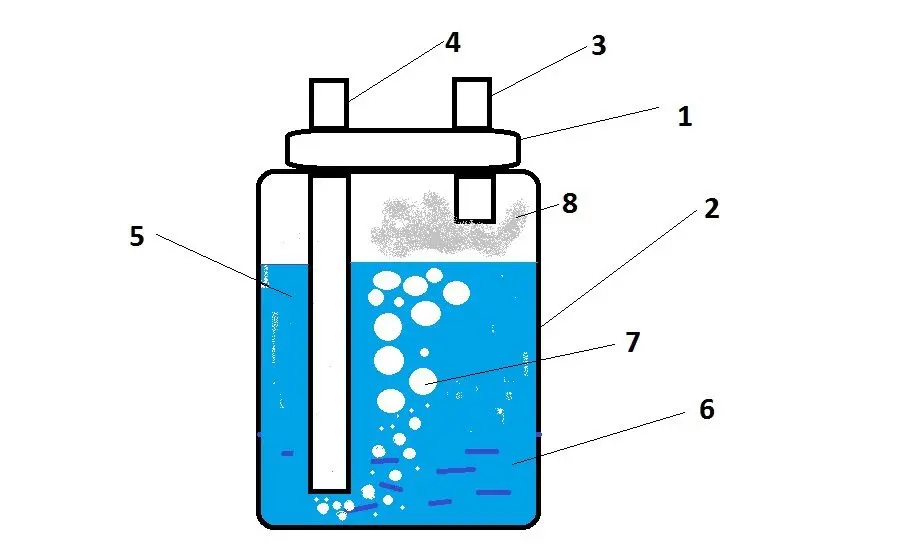
Bubbler (mokroparnik) – any hermetically sealed cylindrical container with two holes in the upper part. A long tube is inserted into the first hole, which reaches almost to the bottom of the container (a gap of 2-4 cm remains). In the second hole, the tube is much shorter and only slightly penetrates into the container.
The sukhoparnik differs from the bubbler only in a short inlet tube, which is located near the lid at the same level as the outlet tube.
In most home-made multi-stage distillation systems, conventional two- and three-liter jars with metal lids are used as dry steamers and bubblers, in which holes are made with a drill to match the diameter of the inlet and outlet tubes. The advantage of this solution is the ease of manufacture and subsequent sealing of the entire system. Also, thanks to the transparency of the glass, you can see what is happening inside the jar. The bubbler circuit is shown in the photo.

The principle of operation of a dry steamer and a bubbler of a moonshine still
The heated vapors of mash through a long tube fall from the distillation cube to the bottom of the bubbler, where water and some other impurities partially condense, forming a layer of liquid. In turn, alcohol, a certain part of the water and other volatile substances again turn into a gaseous state and leave the jar through the outlet tube of the bubbler. Gradually, the liquid level rises above the steam supply pipe. As a result, the new steam that comes from the distillation cube first passes through the liquid layer and only then rises up.
Alcohol vapors also partially condense in the steamer, but due to the short supply tube they do not pass through the liquid layer, so the degree of purification is slightly worse, but the whole process takes less time than in a bubbler. In most multi-stage distillation systems, one dry steamer is installed immediately after the distillation cube, which protects the entire system from splash entrainment (foam and liquid hot mash entering the distillation channel).

Scheme of operation of the moonshine still MSD
The operation of the MSD system is based on partial condensation, in which only part of the vapor of a multicomponent mixture passes into the liquid state, and the rest of the vapor moves further along the pipeline and enters the next stage (bubbler), where it also partially condenses.
When heated, steam from the distillation cube enters each bubbler in turn. Ultimately, concentrated alcohol vapors (containing a minimum of water) enter the cooler (usually a coil) of the apparatus, where they are finally condensed, and the resulting very strong moonshine (88-94 degrees) is taken into a receiving container.

Proponents of this method believe that thanks to multi-stage distillation, it is possible to obtain a drink without impurities – almost pure alcohol, like on a distillation column, since many stages effectively retain harmful substances, and well-purified alcohol vapor enters the coil.
In fact, the MSD system, like any other distillation method, does not completely separate substances with close boiling points into separate fractions. Water and a small part of fusel oils remain in the bubblers, while the most harmful substances (methyl alcohol, acetone, acetaldehyde and others), which have a low boiling point, enter the selection along with alcohol.
How to drive moonshine on the MSD machine
With the most competent distillation, the “head” is taken with the MSD system turned off (steam enters from the cube directly into the refrigerator), you can leave only one dry steamer to protect it from splashing. In this case, the most harmful substances will not accumulate in bubblers and get into the distillate with alcohol vapor. Before the selection of the “body” (the main fraction), the steamer is washed or completely turned off.
The strength of the “body” depends on the number of bubblers in the system (the more there are, the stronger the moonshine at the exit).
“Tails” begin to be taken (or finish distillation) when the temperature at the inlet to the refrigerator of the moonshine still rises to 84-85 ° C, the liquid in the last jar begins to become cloudy, and the strength of the distillate in the stream decreases.
Attention! If you miss the moment of the beginning of the collection of “tails” on the MSD or drive it “to the water”, then the moonshine will turn out to be much more harmful than on a conventional apparatus, since harmful substances from the distillation residue will fall into the selection, which, during classical distillation, are determined by turbidity or low strength of the output ( moonshine has become white or no longer burns in a spoon). Due to the design features, even very harmful moonshine from the MSD apparatus continues to burn and is not always cloudy, therefore, an alcohol meter is required for control.
For efficient operation of the system, at the initial stage of distillation (until there is a layer of liquid in the jars blocking the inlet), ordinary water is added to the bubblers. Sometimes the last 2-3 cans are filled with cleaning moonshine with a substance: soda, salt (to lower the boiling point) and even coal, and a thermometer is installed in the very last bubbler to control the temperature. The most advanced moonshiners fan the cans to remove heat, promoting condensation.
Myths, cons and pros of MSD systems
Myth number XXUMX. Thanks to multi-stage distillation, almost pure alcohol comes out, since the strength is above 90% – strong does not mean clean, not a single MSD system can get a 96-degree drink, there is always a minimum of “a couple of degrees” missing. The problem is that it is in these few degrees that all harmful substances are collected, and almost all water is removed from the solution, due to which the fortress increases.
This means that compared to conventional moonshine stills, MSD systems have no advantages in terms of product purification. Harmful substances remain in moonshine, but in a very concentrated form.
It’s funny that drinking moonshine with a strength of 88% or more is almost impossible, so the water removed with the help of bubblers is added again when the drink is diluted to an acceptable 50-40%. It turns out Sisyphean labor.
Myth number XXUMX. With multi-stage distillation, it is not necessary to select the “head” and “tail” (do fractional distillation) – the separation of the yield into fractions is mandatory even for distillation columns, there are no exceptions, the only difference is in the selection methods.
Myth number XXUMX. On MSD, you can get good moonshine in one distillation – with proper fractionation, one distillation of mash on an MSD apparatus will give a mediocre drink, it is advisable to do 2-3 distillations.
Disadvantages of the MSD system
- In addition to increased output strength, it has no other advantages over conventional moonshine.
- Cumbersome design. If the distillation column is overall in height, then the MSD apparatus takes up a lot of space in terms of area.
- Service complexity. After distillation, each jar has to be opened and washed, which takes a lot of time. Bubblers made of glass are very fragile, there is a risk of accidentally damaging one of the jars during the distillation process, which is fraught with burns from hot steam.
- If used improperly, moonshine from MSD turns out to be much more harmful than during classical distillation, since hazardous substances from the distillation residue enter the drink.
The advantage of multi-stage distillation devices: high-strength moonshine. It remains to find a practical application for this feature.
conclusions
Do not assume that a high fortress is a guarantee of cleaning. It makes sense to use moonshine stills MSD only if you need a very strong distillate, which then does not need to be diluted with water, in all other cases you can get by with a classic moonshine still with one steamer and without bubblers.
Review compiled Alcofan.









