Contents
Spearmint is considered the most common representative of a large family. The plant grows wild and cultivated. Many gardeners specially grow mint on their plots to repel pests, make aromatic teas, and use for medicinal purposes.
What does garden mint look like?
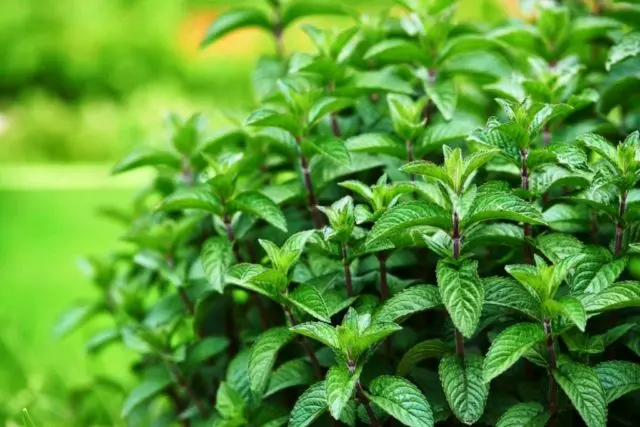
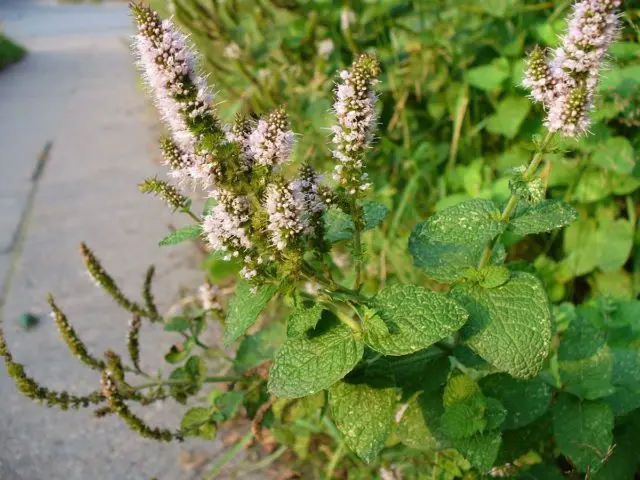
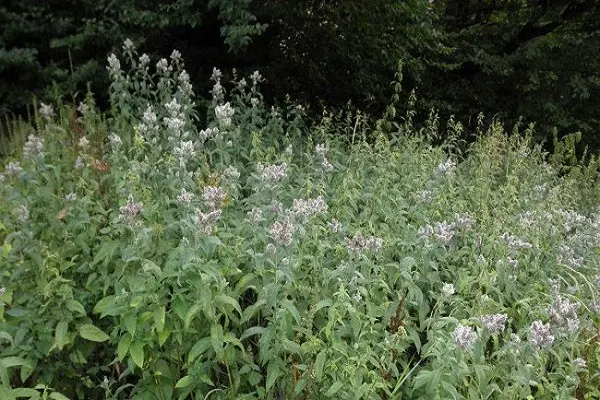
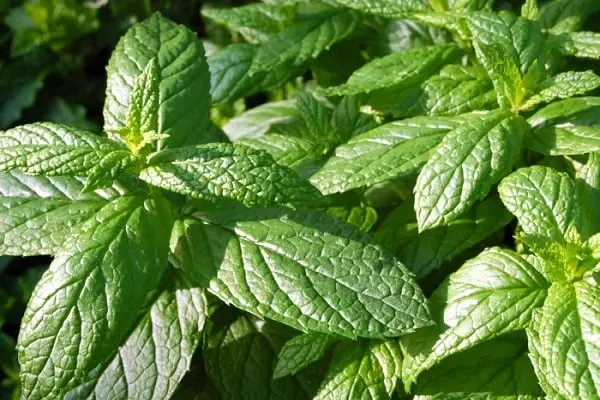
Outwardly, most varieties of mint have similar features. However, each variety has its own characteristics. Spearmint is also called garden mint. The plant has an even long stem. The leaf is elongated, slightly oval, up to 7 cm long. The width of the leaf blade reaches 2 cm. The photo shows garden mint during the flowering period. Small flowers in groups create a spikelet at the top of the stem. The color of the petals is snow-white, sometimes with a pink tint. The height of one flower is 3 mm.
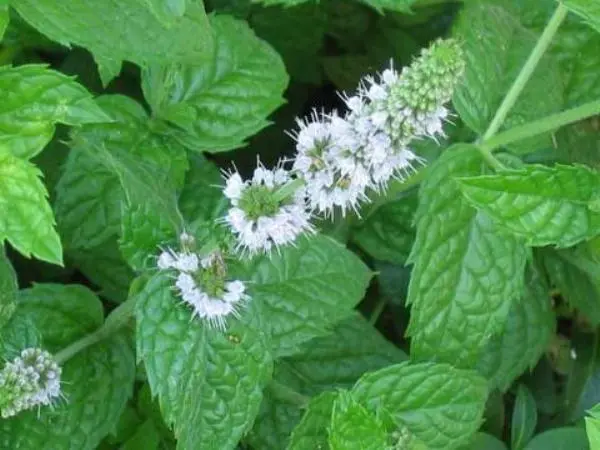

Herbaceous garden plant is characterized by intensive growth. The stem is able to stretch from 30 to 100 cm per season. The leaf plate is wrinkled, the edges have notches.
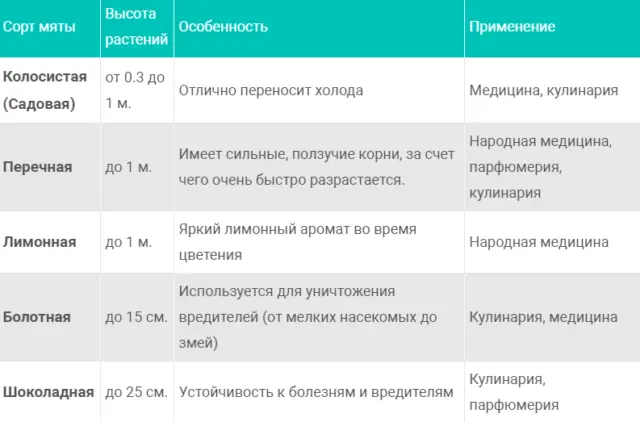
Varieties and varieties of garden mint
In the common people, mint is more often called peppermint or garden mint, which is not entirely true. These are two completely different varieties, and there are about 40 varieties in total. More often on home plots the following types of garden mint are found:
- Peppermint is high in menthol. The culture is a hybrid obtained by crossing garden and water grass. The plant is considered medicinal. It is used in medicine for the production of drugs that treat diseases of the heart, nervous system, respiratory organs and other ailments.

- In spearmint, menthol is weakly expressed. This is its main difference. In addition to spiked, the culture is also called field or meadow. In nature, the plant is found on lawns near water bodies, any other places where moisture is present. Due to the low content of menthol, horticultural crops are more often used in cooking, cosmetic preparations are made from it.

- Fragrant mint has more rounded leaves. A plant with a pronounced specific aroma. The culture is popular with bakers, and is also used to make tea, alcohol tinctures.

- Lemongrass or lemon balm is not a mint variety, but the plant is often referred to as garden lemon mint. The culture is widespread among gardeners, found in almost every yard. Mint is used for medicinal purposes, fragrant tea is brewed.

Other types of garden mint are less common and less widely used.
How spearmint reproduces
Garden culture is propagated by dividing the bush, layering and seeds. The first two methods are considered the simplest and most reliable. If there is a desire to start spearmint on your site, just ask your neighbors to dig a bush. It can be planted whole or divided into several parts so that each separated plant has a full-fledged root. The culture takes root in damp soil and quickly develops its root system. The next year, garden mint will grow. It will still have to be limited, otherwise the plant will crush neighboring crops.

Growing spearmint from seeds is a complex process. First, grains in February are sown in pots with earth or peat. There is a standard process of growing seedlings for two months. Grown up and hardened young plants of spearmint are planted in the spring on the beds. If desired, several garden crop seedlings can be left to grow in a pot on the windowsill.
The video tells in detail about the sowing of mint:
What is the difference between garden mint and peppermint
Distinctive features of popular varieties are displayed in the table. If we talk about the main difference between spearmint and peppermint, then it lies in the aromatic substances. Garden spike culture is less fragrant. When chewing the leaf, the minty taste in the mouth quickly disappears. Peppermint contains a lot of menthol. After chewing the leaf in the mouth for a long time there is a feeling of cold.
What is the aroma of garden mint
The aroma of spearmint is similar to menthol, but it is mild. There is not a cold in the mouth, but a sweetish aftertaste. The aroma freshens the breath when chewing the leaf, but does not clog it with cold.
Medicinal properties of spearmint
Despite its limited menthol content, spearmint has medicinal properties. Garden culture is used to eliminate nausea, headache and toothache, and calm the nervous system. Infusions help remove sand from the kidneys, disinfect wounds, and strengthen the gums. Spearmint menthol has a freezing effect on a sore joint or an area of the body affected by a blow.

The use of spearmint
The scope of horticultural culture is so extensive that it is impossible to imagine many medicinal and cosmetic preparations, culinary products without her participation.
In pharmacology
Since mint’s medicinal properties extend to many human organs, pharmaceutical companies use it to make tablets, tinctures, and aerosols. The culture is a part of biologically active additives (BAA). Based on it, drugs are produced for the treatment of the respiratory tract, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
In folk medicine
Folk healers from garden culture make decoctions, infusions, oil, use fresh leaves of the plant. There are many prescriptions for diarrhea, constipation, headache and toothache. Peppermint oil is used as an antiseptic, astringent and anesthetic. In folk medicine, a garden plant is used in childbirth, the treatment of female diseases.
In cosmetology
Based on fresh mint leaves, women make face masks. By adding various ingredients, they prepare formulations for oily and dry skin, getting rid of acne. Peppermint extract is often found in creams, shampoos, and cleansers.
in mass production
In cooking, fragrant mint leaves are used as a spice. They are added to pastries, first and second courses, sauces, salads. Mint desserts, carbonated drinks, sweets are popular. Spearmint menthol is used as a flavoring agent for cigarettes, tea, and alcoholic beverages.
Location on
The garden plant has a good decorative effect. Spearmint is planted along paths, on mixborders and rock gardens. The culture is considered a good honey plant, and the smell of menthol repels harmful insects from the site.
Rules of landing
In one place, decorative garden mint can grow for many years. The site must be selected immediately, so as not to be transplanted later. The roots remaining in the ground for the next season will give a new growth, which is quite difficult to get rid of. The place is selected illuminated in partial shade, preferably wet. Under the trees, garden culture grows, but develops poorly. The plant stretches on thin stems, grows small leaves.

If the site is not wet, mint plantings will need to be watered frequently. The soil is preferably loose, fertile with good water permeability. Sandy loams and loams are excellent. If the area is swampy or groundwater is high, a drainage layer 15 cm thick is arranged on the bed.
Spearmint can be grown on the site of the previous habitat of legumes. It is undesirable to plant it near vegetables, root crops, fruit and berry bushes. Firstly, spraying with chemicals from insects and diseases cannot be performed for a particular plant. Scattered fog will fall on the leaves of spearmint and it is temporarily impossible to use it. Secondly, spearmint’s fast-growing root system will clog neighboring plants.

The optimal time for planting a garden plant is spring or autumn. If seedlings grow in a flower pot, they can be sent to the garden even in summer. Seeds are bought in trusted outlets. Sowing is carried out in separate cups or in a common container. Seeds are buried in the soil to a depth of 5 mm. Seedlings are grown from February until the onset of steady heat outside.

Planting material is planted in the wells, watered abundantly. The ground is mulched on top to retain moisture. A border tape or pieces of slate are dug along the contour of the bed to limit the spread of roots around the site.
Growing garden mint
Caring for spearmint plantings is easy. The plant needs regular watering, otherwise the stems will develop poorly. If the area is dry, water can be poured every day. The optimal time for watering is late evening, but before dark.
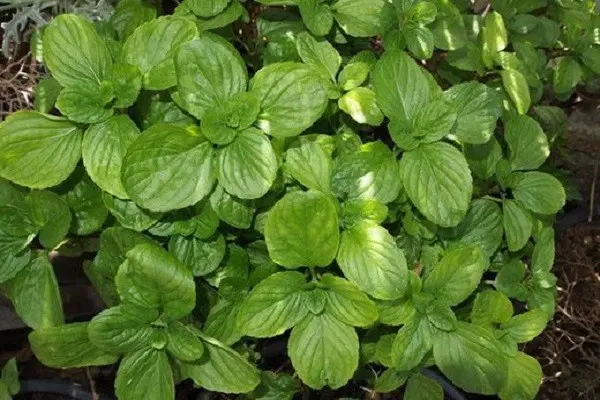

It is not necessary to feed the horticultural crop. Spearmint grows well in fertile soil. Chemical fertilizers can change the taste and aroma. If the site is depleted, once in the spring it is watered with a weak solution of complex fertilizer.
To form a bush, pinching is performed. Cutting off the top promotes the growth of side shoots. If spearmint is grown for harvesting leaves, flower stalks are removed at the formation stage.
The soil on the beds is loosened shallowly. Weeds are removed manually. This specificity of care is associated with the superficial location of the root system. Usually, weed grass is pulled out at the stage of mint growth. When the bushes gain their strength, they will crowd out the weeds.
How to get rid of garden mint on the site
The excellent vitality of a garden plant is a plus and a minus at the same time. When the need arises to get rid of it, it is not easy to do so. Manual uprooting or digging with a shovel is not always successful. The remaining small roots in moist soil instantly give new shoots.

Herbicides help to reliably get rid of an annoying plant, but they can not be applied everywhere. When sprayed, the drugs fall on the leaves of neighboring crops, and they also die. If the use of herbicides is not possible, the area with mint is covered with old linoleum or roofing material. Under the opaque material, it will disappear.
Pests and diseases
Spearmint is rarely subject to disease and pest destruction, but sometimes such cases occur. The problem of combating ailments is to limit the use of chemicals. The leaves cannot be used as a spice. It is better to try to prevent the problem. For example, rust is a common disease. It comes from excessive moisture. Bushes need to be thinned out for better ventilation, reduce the intensity of watering.

The appearance of a white coating on the leaves indicates the presence of powdery mildew. The bushes are sprayed with a solution of ground sulfur. Anthracnose is recognizable by brown spots. For the treatment of plantings, they are treated with a solution of Bordeaux mixture. In order not to wait for the appearance of ailments, they resort to early harvesting – in July.
Peppermint mites and leafhoppers are considered dangerous pests of the crop. Here you can not do without the use of insecticides. For the duration of the drug, the leaves should not be used for any purpose.
When to harvest garden mint and how to dry
The timing of harvesting spices is determined visually. The stems are cut when they reach a length of 25 cm. Harvesting time usually falls in July – August. Cut off 2/3 of the plant so that the bush recovers faster. It is best to cut the mint stems before flowering. At this time, the leaves accumulate the maximum dose of aroma.
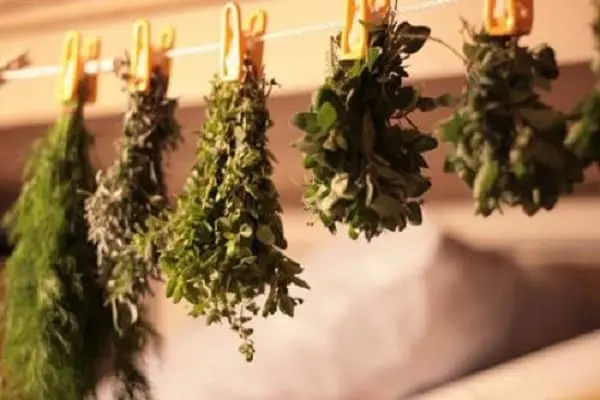

How to properly store dried garden mint
After harvesting, drying is considered the best way to preserve it. The finished product is stored in bundles suspended on ropes under the ceiling of a dry shed. The leaves can be crushed into a fine powder, packaged in plastic bags or glass jars.
Conclusion
Spearmint retains its medicinal properties and aroma even when dried. The duration of storage of the crop depends on the conditions created, but it is better to renew stocks every season.













