Contents
Mint is used not only in nutrition, but also in the manufacture of creams, toothpaste, perfumes and soaps. All thanks to its unique aroma.
In medicine, mint acts as a sedative, a remedy for headaches, and for vision problems. Mint teas and essential oils are popular. This plant is one of the most used in the world.
We found out what are the benefits and harms of mint for the human body.
The history of mint in nutrition
There is a beautiful legend about the origin of mint. Persephone, the wife of Pluto (Hades), was very jealous. Somehow she got angry with the nymph Minta, who showed excessive attention to her husband, and turned the girl into a plant. Pluto failed to turn Minta back into a human. But he endowed mint with a pleasant aroma and taste: it reminded him of his beloved.
The Assyrians were the first to use mint as a medicine: it helped with headache, toothache and stomach pain. The ancient Romans sprinkled the rooms with a decoction of mint: it cheered up, refreshed the room.
И римляне, и египтяне добавляли мяту в блюда как приправу. Трава придавала пище не только характерный вкус, но и яркий аромат.
Mint is widely used in medicine for the treatment of various diseases. Its beneficial properties are explained, first of all, by the content of menthol, an essential oil that gives the plant a characteristic recognizable smell. Mint is used both topically and taken orally, – says gastroenterologist, integrative therapist, nutritionist and nutritionist Elena Krasnopeeva.
The composition and calorie content of mint
The main component of mint is menthol, which is found in the essential oil of the leaves. It has anti-inflammatory and disinfectant properties. The plant contains a lot of manganese (more than 50% of the daily requirement), copper and vitamin C.
– Mint is rich in vitamins A, C, B vitamins, it contains many trace elements: potassium, calcium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, iron, phosphorus. Including the plant in the diet, you can overcome some infectious diseases, – Elena Krasnopeeva adds.
Mint is also rich in amino acids: lysine, alanine and glutamic acid. One of the varieties of this plant, spearmint, contains a large amount of carotene, which stimulates the brain.
| Mint calories per 100 g | 44 kcal |
| Proteins | 3,29 g |
| Fats | 0,73 g |
| Carbohydrates | 8,4 g |
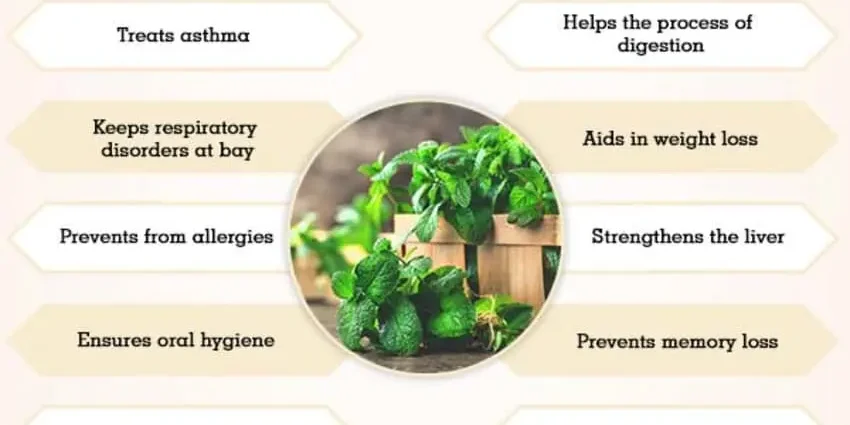
The benefits of mint
No wonder the ancestors of the Dali believed that mint prolongs life. The concentration of nutrients makes this herb an assistant in the prevention and treatment of many diseases.
Peppermint contributes to the improvement of cognitive functions in young people. The positive effect of mint extract on the brain function of people aged 50 to 70 years who suffer from memory problems has been proven. (one)
Peppermint infusion or peppermint tea helps reduce headaches due to the presence of menthol in the composition – often such pain is caused by intense tension. The plant is relaxing and soothing. (2)
Another plus of mint: it relieves nausea, vomiting and dizziness. It is used for toxicosis of pregnant women and seasickness. The plant helps relieve spasms and soothes the gastrointestinal tract. (3)
The benefits of mint for women
Mint is prescribed for spasms: it relaxes, relieves pain. It also helps to stop the symptoms of gastritis and peptic ulcer, alleviate the manifestations of heartburn and diarrhea. Peppermint tea has a diuretic, sedative and anti-inflammatory effect. It should be drunk with problems with the functioning of the kidneys, the nervous system, or frequent colds. (four)
Women use peppermint essential oil for facial skin care: they add a drop to masks, include cream and tonics with menthol in their daily care.
The benefits of mint for men
Mint contains arginine, a substance that improves blood circulation in the brain and reduces vasospasm. This amino acid enhances blood flow to the genitals, increasing potency.
It should be noted that frequent use of mint tea (more than twice a day) can lead to a decrease in testosterone levels in the blood. If the hormone is produced in insufficient quantities, problems arise with the functioning of the reproductive system.
The benefits of mint for children
It is worth starting to add mint to dishes for the baby no earlier than 3 years. But you can drink tea with mint earlier: from 5-6 months. But before that, you should consult with a pediatrician.
Peppermint relieves irritation and allows you to cope with overwork. This is no less true in childhood than in adults. Toddlers often cannot sleep due to emotional overexcitation.
This spice is also able to reduce inflammation and itching: therefore, it is added to creams and ointments. The main thing is to make sure that the child does not have an allergic reaction to this plant.
Harm mint
Mint should not be consumed while breastfeeding. Menthol can reduce the ability of the female body to produce milk.
It is also necessary to exclude mint for those who suffer from varicose veins or low blood pressure. If vascular tone decreases, the likelihood of an exacerbation of a chronic disease becomes higher.
But mint causes pronounced harm only if a person is allergic to this plant.
The use of mint in medicine
In addition to the main treatment, mint is prescribed for disorders of the nervous system to relieve tension and relaxation. It helps with insomnia, but also only as part of therapy.
The plant relieves inflammation and is a natural antispasmodic, reduces gas formation in the intestines. With increased acidity of the intestine, peppermint helps, which reduces the production of hydrochloric acid. With low acidity, field mint is preferred.
– Mint has anti-inflammatory properties that allow it to be used in the treatment of bronchitis, tonsillitis, runny nose. The plant is also beneficial for the digestive system. It can also be used to relieve stress, it is a mild natural sedative. Mint is used for headaches, nasal congestion, and chronic pancreatitis. Helps strengthen the cardiovascular system, and has antibacterial properties, says Elena Krasnopeeva.
Мяту считают природным муколитиком. Трава разжижает мокроту, делая ее отведение быстрым и эффективным. Пить мятный чай рекомендуют не только при мокром кашле, он хорошо помогает облегчить все симптомы простуды. В мяте содержится довольно много витамина С и других микроэлементов.
The use of mint in cooking
Spicy herbs are widely used in cooking: both as a seasoning and as a main ingredient. Mint is no exception. It can be found in almost all cuisines of the world.
In England, mint is traditionally used in meat sauces. This is especially true at Christmas. In America, they make drinks with it: for example, mojitos and other cocktails. Italian cuisine is rich in dishes in which mint is added as a spice: to meat, to vegetables, to hearty, rich soups.
Desserts with mint are a separate kind of pleasure. Its tart and rich taste perfectly sets off the sweetness of cookies, cream tartlets, cheesecake or eclair. Mint in a small amount is added to the cream or the finished dish is decorated with leaves.
Spring Pasta
In a duet with vegetables, the taste of the dish is revealed in a new way.
| Penne pasta | 400 g |
| Green string beans | 200 g |
| Carrots | 200 g |
| Frozen green peas | 350 g |
| Courgettes | 150 g |
| Chopped mint and parsley | 20 g |
| Olive oil | 3 Art. spoons |
| Lemon juice | 1 lemon |
| Salt pepper | to taste |
Heat the olive oil in a heavy bottomed saucepan. Add parsley and mint to it, mix well. Do not bring the mixture to a boil. Remove from heat and let cool.
Peel the carrots and cut into thin strips. Cut the beans in half, and the zucchini in cubes. While peeling and chopping vegetables, boil pasta in salted water according to package directions. Boil vegetables in another saucepan: carrots – 4 minutes, peas, beans and zucchini – 8 minutes.
Drain the penne in a colander and then return to the pot. Add the olive oil mixture and lemon juice to the pasta. Mix well. Then add vegetables, season with pepper, salt and arrange on serving plates. Sprinkle mint leaves on top of the pasta.
Strawberry non-alcoholic mojito
Moderately sweet and invigorating: both children and adults will like this cocktail.
| Sparkling mineral water | 500 ml |
| strawberry syrup | 100 ml |
| Orange fresh | 150 ml |
| Strawberries | 150 g |
| Lime | 1 piece. |
| Mint | 40 g |
| Ice | 20 g |
Finely chop the lime. Take glasses in which you will serve drinks. Put 5 mint leaves, 2 strawberries, 1 lime wedge on the bottom. Pour this with 100 ml of strawberry syrup. Take a crusher and crush the resulting mixture well. Add ice to it, 40 ml of orange juice and 150 ml of sparkling water. Mix well.
Garnish the glasses with mint leaves and remaining lime wedges.
Submit your signature dish recipe by email. [email protected]. Healthy Food Near Me will publish the most interesting and unusual ideas
How to choose and store mint
When choosing mint, you should pay attention to its appearance and smell. The leaves must be intact, without damage. They should not have inclusions, darkening and large spots. The leaves themselves may be slightly rough, but not dry or rotten.
After buying mint, you need to rinse the sprigs of the plant with cool water, wrap them in a wet towel and put them in the refrigerator. So it will be stored for 3-4 days. Another option is to place the mint in a container of water and place it in the refrigerator as well.
If you only need mint leaves, for example, for tea, then they can be placed in an airtight container after washing.
To use mint in winter, it is dried. To do this, the branches are placed in a dry place where the rays of the sun do not penetrate. After the grass dries, it must be crushed and put in a separate container.
Another interesting storage method, which is more suitable for hot summers, is to make ice with mint. The grass must be crushed and added to ice molds along with water. In this form, it is suitable for making drinks.
Popular questions and answers
Elena Krasnopeeva, a gastroenterologist, integrative therapist, nutritionist, nutritionist, answers questions from readers.
When does mint season start and end?
How is mint different from lemon balm?
How much mint can be consumed in one day?
Sources of
- K V Peter. Introduction to herbs and spices: definitions, trade and applications.Handbook of Herbs and Spices.2012. URL: https://www.elsevier.com/books/handbook-of-herbs-and-spices/peter/978-0-85709-039-3
- Diane L McKay , Jeffrey B Blumberg. A review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of peppermint tea. 2006. URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16767798
- Jane Buckle RN. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. PhD, in Clinical Aromatherapy (Second Edition). 2003. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/peppermint
- Andrea Gordon MD, Abigail Love MD. Disease-oriented approach. MPH. in Integrative Medicine(Fourth Edition), 2018. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780323358682/integrative-medicine