Contents
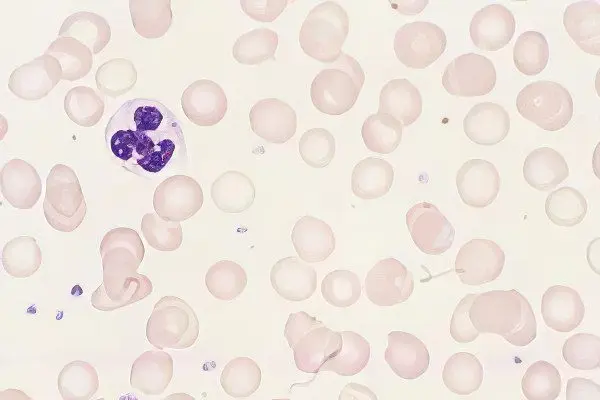
The study of the morphology of erythrocytes makes it possible to identify various disorders in the hematopoietic system at an early stage. In particular, this is true for diseases such as microcytic anemia.
Erythrocytes are red blood cells that are shaped like a biconcave disc. The size of one erythrocyte is 7-8 microns (80-100 femtoliters). With a change in the structure, structure, number and composition of red blood cells, doctors diagnose anemia. Microcytic anemia is characterized by the appearance of small red blood cells in the blood.
Norm and pathology
Red blood cells help maintain the vital activity of the human body. Normally, their sizes are 80-100 fl.
Depending on this indicator, there are:
Microcytic anemia (microcytosis) in which the size of red blood cells is less than 80 fl.
Macrocytic anemia, in which the size of red blood cells exceeds 100 fl.
If the size of red blood cells remains within the normal range, then doctors talk about normocytosis.
Color
The color index of blood is of no small importance in the diagnosis of various diseases. Anemia can be hypochromic, hyperchromic, and normochromic. Hemoglobin, which is part of red blood cells, is responsible for the color of blood. If it is not enough in the blood, then microcytosis is accompanied by hypochromia. This condition is called microcytic anemia.
What is microcytosis?
Microcytosis is a common disorder in which red blood cells acquire small volumes. When examining blood, it is possible to detect a large number of small red blood cells, which is a deviation from the norm.
It is not enough just to establish the fact of microcytic anemia, it is required to identify the cause that led to this violation. This is especially true during the initial diagnosis. It should be taken into account that microcytosis accompanies various pathologies. Therefore, a differential diagnosis must be made.
Some types of anemia themselves lead to the development of microcytosis. Therefore, it is important to understand which condition arose earlier: anemia or microcytosis. Often, hypochromic anemia develops precisely because red blood cells decrease in size.
iron deficiency and anemia

Iron deficiency microcytic anemia is the most common disease that occurs among all other types of anemia.
Iron deficiency microcytic anemia can be caused by the following reasons:
Anemia against the background of hemoglobinuria, when damaged red blood cells undergo massive death, and the hemoglobin released from them begins to circulate freely in the blood. Anemia due to hemosiderinuria, when hemoglobin accumulates in the kidneys. In this case, an increase in the level of hemosiderin (a product of hemoglobin oxidation) will be observed in the urine.
Chronic posthemorrhagic anemia, which develops against the background of various diseases of the digestive system. At the same time, latent or overt bleeding (uterine, renal, nasal, gastrointestinal) is observed in a person on an ongoing basis.
Anemia that develops with errors in nutrition. When there are too few foods containing iron in a person’s menu.
Anemia that develops during certain periods of life when the body needs increased doses of iron. For example, during childbearing, during breastfeeding, with frequent childbirth, with participation in blood donation.
Anemia that develops when there is a violation of the process of absorption of iron, or with problems in its transportation. Often, such failures are observed in people suffering from cancerous growths in the digestive tract, with chronic inflammation affecting the organ system of the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of anemia
Although iron deficiency anemia is the most common variant of anemia, nevertheless, we must not forget about other varieties of this disorder.
These include:
Hemoglobinopathy: hereditary microspherocytosis, Minkowski-Choffard disease, thalassemia.
Sideroblastic microcytic anemia. This is the general name for anemia that develops against the background of a violation in iron metabolism. Such anemia often occurs in parallel with microcytosis, hyperchromia, and is accompanied by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Sideroblastic microcytic anemia can be inherited by blood or acquired during life. For example, anemia of this type often accompanies malignant tumors in the body, or chronic alcoholism.
Anemia developing against the background of chronic infectious diseases.
Anemia that develops against the background of poisoning the body with poisons, heavy metals and other pathogenic substances. All this negatively affects the processes of iron absorption and the production of hemoglobin. Symptoms of intoxication anemia are: microcytosis, hyperchromia, the presence of Jolly bodies in the blood, basophilic granularity.
Congenital anomalies in iron absorption and utilization are rare, but these disorders will lead to the development of microcytic anemia.
Microcytic anemia in childhood

Children in order to determine any type of anemia are required from time to time to donate blood for analysis. This study is performed as part of an age-related medical examination, or more often, as the need arises.
Symptoms that can suggest anemia:
Distortion of taste, desire to eat unusual food.
Behavioral disorders: excessive apathy, decreased activity, increased fatigue.
Weight loss.
Lag in mental development.
Most often, iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed in children with such symptoms. The lack of this trace element leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, which provokes hypoxia of tissue organs of varying severity.
To prevent the development of anemia in childhood, it is necessary to monitor the nutrition of the child. The menu should be designed in such a way that the baby’s body does not experience a deficiency in essential minerals and vitamins.
Children who are breastfed are less susceptible to anemia than children who receive cow’s or goat’s milk. After introducing complementary foods, you need to gradually include foods that are a source of iron in the baby’s diet. Naturally, according to the age requirements of the body.
If a child develops microcytic anemia, then it is necessary to consult a doctor and donate blood for analysis. The main sign of trouble is a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
What is the danger?

If the level of iron in the body decreases, then this leads to the development of the following pathological reactions:
Decreased stocks of hemo-forming components that are found in the bone marrow and liver.
Deterioration of ferritin production, which leads to a decrease in its level. This protein is responsible for the preservation of iron in tissue cells.
Increased iron-binding capacity of the blood.
An increase in the level of protoporphyrin in erythrocytes.
Decreased activity of enzymes responsible for iron binding inside erythrocytes.
If the disease is not treated, it will progress. The level of iron and hemoglobin can drop to critical levels. Erythrocytes will decrease in size all the time. As a result, microcytes will predominantly circulate in the blood. In addition, the hemogram will give poikilocytosis and hypochromia. This can be detected by conducting a biochemical and clinical blood test. These studies will confirm the diagnosis of hypochromic microcytic anemia.
It is imperative to carry out a differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia with other types of anemia. So, anemia provoked by intoxication of the body will be indicated by: basophilic inclusions in erythrocytes, an increase in the level of lead in the blood, the presence of protoporphyrins and coproporphyrins in urine. With high blood levels of HbF and HbA2, thalassemia can be suspected.
Treatment of microcytic anemia

Treatment of microcytic anemia requires timely treatment. Be sure to adjust the menu of the patient.
Provided that the disease develops against the background of chronic blood loss, they need to be stopped. In women, heavy menstrual bleeding often leads to the development of anemia. Therefore, all patients should be examined by a gynecologist. Sometimes treatment of the digestive system is required. To do this, attract a gastroenterologist.
Often the doctor prescribes iron supplements. When possible, preference is given to oral administration of drugs. Injection of iron is associated with the risk of developing allergic reactions, and also gives many side effects. Self-medication is unacceptable, since an excess of iron in the body is no less a threat than its deficiency.










7-жастагы балага микроцитоз диагнозы койылса, оны кандай дарiлермен емдейсиз?