Contents
What is microcephaly?
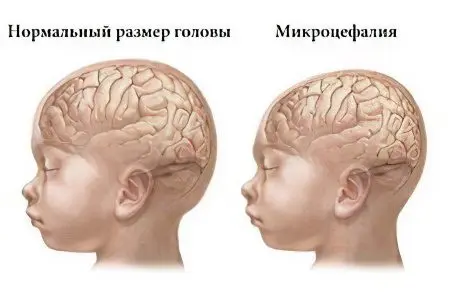
Microcephaly – This is a disease in which there is a decrease in the mass of the brain and, accordingly, a decrease in the size of the skull, head circumference. At the same time, other organs develop in accordance with age norms. Such changes in the state of the brain cause the development of mental insufficiency and neurological abnormalities.
According to statistics, the disease occurs in 1 child out of 10000, the relationship between the sex of the child and the occurrence of microcephaly has not been identified.
Microcephaly causes severe mental abnormalities. And it can be both a slight imbecile and a deep idiocy. Modern medicine does not give comforting forecasts for such children. A complete cure is impossible, the main task of doctors and parents is to restore motor activity, to teach the child basic self-care skills.
How long do children with microcephaly live?
According to statistics, the average life expectancy of a child with microcephaly is 12-15 years. In rare cases, a person lives up to 30 years.
Causes of microcephaly in children
Modern medicine distinguishes 2 types of microcephaly – primary and secondary. The mechanisms and causes of development are different depending on the type of disease. Primary, or true microcephaly can be triggered by various pathologies in the early stages of pregnancy. Injuries received in the last trimester of pregnancy, birth injuries, as well as some diseases that affected the newborn in the first months of life, can cause the development of microcephaly. It is important that children with primary microcephaly have great opportunities to lead an independent life in society, unlike those who have secondary microcephaly. The latter are usually not even able to stand and walk on their own.
The most common causes of microcephaly in children are:

Intoxication of the fetus with alcohol, narcotic and other toxic elements. Such a negative impact is especially detrimental in the early stages of pregnancy, when most of the organs and systems of the child are laid;
Infectious diseases of the mother during the period of bearing a child (most often the cause of microcephaly in a child is rubella and toxoplasmosis, transferred by a pregnant woman);
Endocrine disorders in a pregnant woman;
Exposure to certain antibiotics during pregnancy;
Toxic poisoning of a pregnant woman;
Exposure to radioactive radiation;
Genetic abnormalities of the fetus;
Birth trauma.
Quite often, in about 34% of cases of the development of the disease, microcephaly is caused by chromosomal mutations. This concept refers to the process of changing or redistributing the gene set, which causes abnormal development. When it comes to microcephaly, as one of the symptoms of gene mutations, it should be understood that in this case there is both primary and secondary microcephaly.
Most often, microcephaly accompanies gene mutations such as:
Edwards syndrome – Trisomy on the 18th pair of chromosomes. A fairly rare disease, which is characterized by numerous malformations that are incompatible with life. Usually a child dies in the first six months – a year of life.
Patau Syndrome – Trisomy on the 13th pair of chromosomes. It is also a rather rare disease. The clinical picture of the Syndrome: pronounced deafness, obvious microcephaly and mental insufficiency, “cleft lip” and “cleft palate”. The baby’s ears are lower than they should be; there is an abnormal development of the eyeball. Other defects include disorders of the cardiovascular and genitourinary systems, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The life expectancy of a child with Patau Syndrome – Trisomy, which accompanies microcephaly, on average does not exceed 1 year. The syndrome is quite well detected in the early and middle stages of pregnancy; if a gene mutation is detected, an abortion is recommended for medical reasons.
Down syndrome (most often there is a mutation on the 21st chromosome pair). Children with Down Syndrome have pronounced microcephaly. They have mental retardation, tongue-tied tongue, physical defects. The child has a sloping nape, a wide nose with an impressive bridge of the nose, and a protruding massive lower jaw. In addition, they have malformations of the kidneys, heart, gastrointestinal tract. Down syndrome also strikes at the immune system of the child, so he often suffers from infectious diseases, and the risk of developing malignant tumors is high.
Syndrome “cat’s cry”. It is a gene mutation that causes multiple malformations, including microcephaly. The child does not make the usual cry. He breaks out a cry that looks like a cat (hence the name of the disease). Such mutations are incompatible with life; the child dies in the first hours or days of life.
Symptoms of microcephaly in children
Microcephaly can be detected already after a visual examination of the child, since such an examination reveals quite pronounced symptoms of microcephaly:
Head circumference is 2-3 times less than normal. This sign is the most significant, reliable. While the volume of the head of a child is 35-37 cm, the volume of the head of a newborn with microcephaly is 25-27 cm, and sometimes less. At the same time, a decrease in the mass of the brain is natural – instead of 400 g in microcephaly, it weighs about 250 g in the early stages of development.
The size of the facial skull exceeds the size of the head. In other words, the child’s face grows, while the head itself remains disproportionately small. Children with microcephaly have a high, steep forehead with protruding brow ridges and disproportionately large protruding ears. Quite often, microcephaly is accompanied by such developmental anomalies as “cleft lip” and “cleft palate”, strabismus. With the growth of the child, the disproportionality of the facial and brain zones of the child becomes more and more apparent.
Early, during the first month of life, the closure of the fontanel; sometimes a child is born with an already closed fontanel. This syndrome in most cases becomes a signal of developed microcephaly. However, in some situations, a closed fontanel may not be a symptom of microcephaly, but a factor that will further provoke its appearance. In other words, with the timely resolution of this pathology by surgery, it is possible to avoid microcephaly due to the fact that the brain gets the opportunity to grow and develop normally.
Dysmotility, developmental delay, delayed speech development, inability of the child to reproduce sounds, poor vocabulary. It is noteworthy that the child not only does not speak himself, but also understands the speech addressed to him quite poorly.
The occurrence of convulsions, increased muscle tone, muscle dystonia, paralysis.
Microcephaly can also be detected during a diagnostic study using special medical equipment. In this case, in addition to the symptoms already identified as a result of an external examination, the following are added:
Underdevelopment of the cerebral hemispheres, in particular – the frontal lobes .;
Increase or decrease in the convolutions of the brain;
Smoothness or complete absence of convolutions;
The development of cystic cavities in the brain tissues.
A fairly common clinical picture is the accompaniment of microcephaly with epilepsy and cerebral palsy. In this case, signs characteristic of concomitant ailments are added to the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Speaking about the symptoms of microcephaly, it should also be noted changes in the emotional sphere of a sick child. Here, both lethargy and hyperactivity can be observed. In the first case, when a sick child is lethargic, motionless, indifferent to what is happening around, it is said about his torpid type of temperament.
Hyperactive, fussy children with microcephaly disease belong to the group with an erect type of temperament.
Diagnosis of microcephaly
prenatal diagnosis, carried out using an ultrasound machine, suggests the development of microcephaly in the fetus. Similar conclusions are made after comparing the data obtained during the ultrasound on the size of the head and body of the child with the norm. At the same time, reliable information is possible only with the most accurate determination of the timing of pregnancy. To avoid obtaining false positive or false negative data, the fetal head circumference is compared with the circumference of the abdomen, the total body size. However, reliable information about the presence or absence of fetal microcephaly can be obtained no earlier than the 27th week of pregnancy.
If there is a suspicion of the development of the disease, the pregnant woman should undergo an invasive prenatal diagnosis, as well as a karyotyping of the fetus.
Invasive diagnostics is the study of mutations of chromosomes and genes. It can only be possible with a puncture of the amniotic bladder, since the material for analysis is amniotic fluid, particles of the epithelium or villi of the fetus that are in the amniotic fluid.
Prenatal screening, which is a complex of laboratory and ultrasound studies, allows obtaining statistics on the probability of having a child with microcephaly. Thanks to these procedures, it is possible to identify the pregnant woman’s belonging to the risk group of women whose fetus is susceptible to the development of microcephaly.
prenatal screening includes ultrasound and biochemical blood tests. In addition, the patient fills out a questionnaire of a special form, in which, among other questions, there is a column on the duration of pregnancy. Questionnaire data, test results and indicators obtained during ultrasound examination are processed using a special computer program that provides information on the risk of many fetal diseases, including microcephaly.
Diagnosis of a newborn is carried out in the first minutes of his life on the basis of visual parameters of the volume of the child’s head. If microcephaly is confirmed, a more serious comprehensive examination is required (MRI of the brain, X-ray of the skull, neurosonography).
At the birth of a child with this disease, parents are advised to be examined by a geneticist to identify the causes of the pathology, as well as to consult on ways to avoid gene mutations during repeated pregnancy.
Prognosis of microcephaly
The prognosis for microcephaly, unfortunately, is disappointing, since it is impossible to completely recover from this disease. The prescribed treatment has, rather, a supporting effect, trying to ensure that the functioning of the affected organs is close to normal.
The prognosis also depends on the diagnosis. So, with a shallow imbitility, it is possible to educate and educate a child, the result of which will be the mastery of minor speech skills by the patient; children are able to perform simple tasks; able to independently hold a spoon; express wishes.
With oligophrenia or idiocy, patients are most often unable to move, they lack speech and understanding of what is happening around. The form of microcephaly is also important. So, with primary microcephaly, complex treatment can be relatively effective – the child will be able to lead a simple life in society. If microcephaly is secondary, the child will probably not even be able to sit, will not learn to stand.
In addition to the inability to get rid of the disease, it should be mentioned that the immune system of the child is vulnerable. The death rate of children from infectious diseases is high.
As a rule, children are placed in special institutions for mentally retarded children, where they are taught the necessary skills of self-care, or are at home.
Treatment of microcephaly
Microcephaly is an incurable disease. Therapeutic measures only help to reduce the rate of development of defects, and also help to adapt the patient to life. At the same time, it is important that the treatment takes place in a complex and includes drug therapy, therapy through physiotherapy procedures, as well as psychological and social rehabilitation.
Each of these procedures allows you to solve the particular manifestations of the disease. taking medications allows you to activate metabolic processes in the brain. In addition, their action is aimed at relieving muscle tension, spasm and convulsions, which are usually frequent companions of microcephaly. Also, in the presence of increased intracranial pressure, drugs are prescribed that contribute to its normalization. Finally, most medicines have a calming effect on the child.
The therapeutic effect can be divided into symptomatic (that is, slowing down the processes that are symptoms of the disease) and specific (the purpose of such treatment is to influence the cause of the development of microcephaly). With symptomatic exposure, drugs that stimulate metabolism and biogenic stimulants, as well as vitamin B, are used. Specific treatment is impossible without the use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
Physiotherapy sessions, which include physical therapy, massage, electrotherapy, as well as therapeutic exercises in water, can relieve muscle tension in microcephaly, help to activate the motor functions of organs.
As for the psychological and social adaptation of children, the main role is assigned to parents. It is they who must fight for the life of the child, control the receipt of funds, attend all medical procedures prescribed by the doctor. In addition, parents should talk with the child as much as possible, explain the usual actions again and again.
Of course, such behavior of parents is hard work, for which you need to be prepared, first of all, psychologically. Psychological assistance should also be organized for them, which contributes to the preparation and education of parents in the norms of behavior when raising children with microcephaly.
Comprehensive treatment should be started as early as possible, only in this case we can hope for a positive trend.









