Contents
Microalbuminurie
Microalbuminuria is the determination of albumin in the urine. This test allows early detection of kidney damage, especially in people with diabetes.
Definition of microalbuminuria
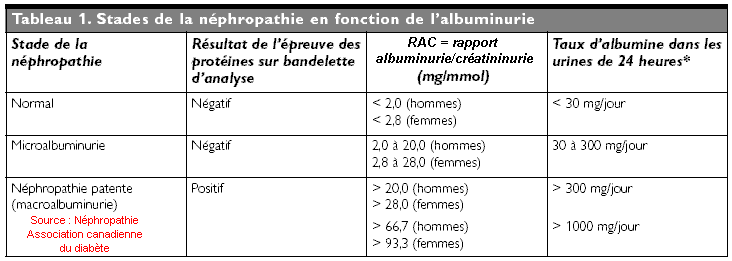
Microabbuminuria is the determination of albumin in the urine. The term microalbuminuria denotes the presence of abnormal amounts of albumin in the urine. Microalbuminuria is defined as an excretion of 30 to 300 mg of albumin per 24 hours. Albumin is one of the main proteins found in the blood. A healthy kidney does not pass albumin in the urine. A damaged kidney, on the other hand, allows some albumin to pass through. Microalbuminuria is therefore a marker of renal damage.
Why have microalbuminuria?
Microalbuminuria is a medical examination performed annually as part of the surveillance for diabetes. It is only dosed more frequently if it is positive, that is to say greater than 20 μg / min or 20 mg / l or 30 mg / 24h.
The microalbumin assay is also used to screen for patients at risk of developing nephropathy (kidney disease): diabetic patients (type 1 and 2), hypertensive patients, subjects with monoclonal dysglobulinemia, systemic disease (lupus, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis) or heart failure.
How does microalbuminuria work?
The determination of urinary albumin excretion can be done on a urine sample on the first morning urine, on 24-hour urine or on a timed urine sample.
Before confirming the diagnosis of elevated microalbuminuria, it is necessary to perform 3 assays over 6 months. Transient high concentrations can indeed be the consequence of intense physical exercise, the presence of blood in the urine, urinary tract infections, dehydration or the taking of certain drug treatments.
What results can you expect from microalbuminuria?
The values defining microalbuminuria are:
- Urine excretion of albumin of 24-30 mg / 300 h in 24-hour urine;
- On a urine sample: 20-200 mg / mL or 30-300 mg / g urine creatinine or 2,5-25 mg / mol (in men) or 3,5-35 mg / mol (in women) creatinine urinary
- On a timed urine sample: 20-200 μg / min
Moderate albumin concentrations indicate early renal damage. High concentrations indicate severe damage.
In people with diabetes (type 1 and 2 diabetes), microalbuminuria is a marker of cardiovascular and renal risk and total mortality.
In people without diabetes, microalbuminuria is a marker of cardiovascular risk, risk of diabetes, impaired renal function and total mortality. It is a risk marker for developing high blood pressure with normal blood pressure.
Microalbuminuria is also a marker of risk of unfavorable outcome or death in cancer and lymphoma.
Elevation or persistence of elevated urinary albumin excretion over time is also associated with a poor prognosis in some hypertensive patients.
Microalbuminuria can also be observed in certain lipid abnormalities and several immune disorders.
Treatments for microalbuminuria
Treatment of a person with microalbuminuria involves weight loss and excess sodium intake (
People with diabetes are treated with an ACE inhibitor (type 1 diabetes) or angiotensin 2 receptor blocker (type 2 diabetes) to ensin on the reduction of UAE.
Antihypertensive therapy is prescribed for people who do not have diabetes.