Having your own vineyard in your garden is a dream of many. But he needs proper care. Part of this care is the process of reproduction. Having bought a seedling once, it can be easily propagated in the future. The most common method is the propagation of grapes by layering. This is what our article will be devoted to.
Vertical layering
There are several ways to propagate grapes using layering. They are all sufficiently applicable and appreciated by gardeners.
A significant plus of propagation of grapes by layering is that the resulting vines very quickly come into fruition.
One of these methods is the vertical method. In order to carry out reproduction using vertical layering, certain rules must be followed.
Instructions for propagating a grape bush by the method of vertical layering:
- the vine to be propagated must be planted at the bottom of a furrow up to 40 cm wide and approximately 20 cm deep;
- then it needs to be cut short;
- in the year when the planting was made, it is necessary to ensure the survival of the plant as efficiently as possible so that it gives good growth;
- the next year, in the spring, on this bush, all shoots are shortened by two eyes;
- when the shoots grow back, the strongest of them pluck the tops. This will temporarily stop their growth and stimulate the growth of side shoots (they will align in terms of growth strength);
- when the side shoots reach 30 cm in length, the first hilling of the grape bush can be carried out while covering the base of the shoot with moist soil;
- before that, the soil is fertilized with humus, which is mixed with a small amount of superphosphate;
- when the shoots reach a length of 50 cm, they are watered, and after a couple of days they re-hill up with moist soil so that a hill about 30 cm high is eventually formed;
- after a couple of days, the upper shoot is minted, while about 4 or 5 leaves should remain above the mound on each shoot. As a result, you will get a seedling with fairly branched shoots, the height of which reaches 40 cm.
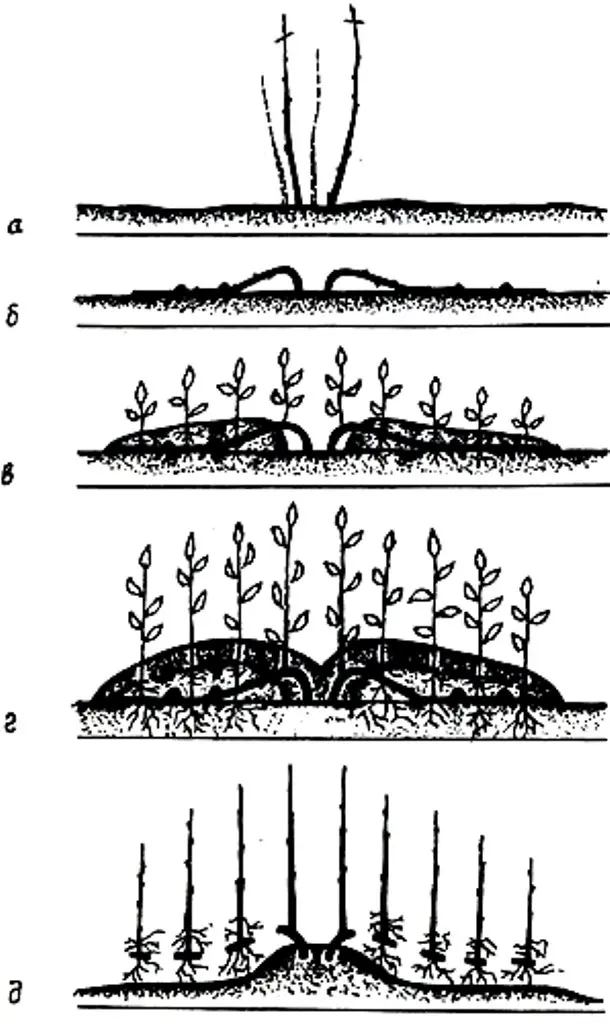
Scheme of reproduction by the method of vertical layering
After you have carried out the above steps, you will only have to keep the soil loose and moist. You also need to remove weeds. At the end of summer (mid-August), we pinch the top of the shoot, stimulating its better ripening. Then, in the autumn, they carry out loosening, as well as rooting of the shoots, separating them from the bush with the help of a pruner. Cut off unrooted shoots.
At the end, at the end of all the above manipulations, you will get small stumps rising above the surface of the bottom of the furrow. From these stumps, young shoots will grow next year.
These mother bushes for the winter, subject to early and prolonged snowfalls, can not be covered, as they will well tolerate wintering under the snow. In another situation, they need to be covered. Usually, vegetable tops, hay, sawdust, birch or oak leaves, and other materials are used for shelter. After that, the next year, when the shoots of the branch, repeat hilling.
Using this technique, you can get vertical cuttings from one mother vine for several years. The advantage of this method is the good survival rate of layering, while non-rooted shoots can be used as cuttings.
In the spring, the vines of the mother vine bush should be cut short (three buds). This will stimulate the growth of shoots at the base of the bush.
Green layering
Another way to propagate grapes is the green layering method.
Instructions for propagating a grape bush using the green layering method:
- carried out only on a healthy uterine bush, which gives a good harvest, both in terms of volume and taste;
- this bush should grow either in a free place or next to a bush that needs to be replaced;
- two (one can be) green shoots are chosen on the bush. Their base should be close to the soil or on a replacement knot;
- during the growth of the selected green shoots, they are tied vertically to the stake;
- stepchildren must be removed at their first appearance;
- in late July or early August, when the shoots reach the required length (about 2,2 meters), we place them in a ditch;
- the ditch should have the following parameters: 40-60 cm deep and wide, the walls are sheer, and the bottom is inclined at an angle of 35 ° to 45 ° towards the trunk of the original bush. During the digging of a ditch, the top layer of the earth should be thrown out in one direction, and the bottom layer in the opposite direction;
- it must be remembered that when placing a shoot in a ditch, all leaves must be removed from it, as well as antennae. You also need to blind your eyes;
- compost (up to 10 kg) or manure must be placed at the bottom of the ditch. Then the bottom is dug up on the bayonet of a shovel so that the earth moves with fertilizers and the prepared green layers are placed;
- the layers must be carefully bent and drawn along the bottom of the ditch to the place where you want to grow a new bush;
- in place of the future grape bush, we display the top, which contains about four leaves, and its growth point should be located above the surface of the earth;
- from above, the layering is covered with the top layer of soil (about half the depth of the dug ditch), and after that it is trampled down;
- then, the planted green layer is watered with 1-2 buckets of water, and only after the water is completely absorbed, the ditch is completely covered. During the summer, depending on its weather conditions, you need to do one or two waterings.
Reproduction scheme by green layering
The advantage of this propagation method is that the vine takes root better and faster. You can also use shoots that have not yet reached the desired length.
Horizontal Lines
Last on the list, but not in terms of applicability, is the method of propagating grapes using horizontal layering. This option assumes that there is no need to separate the cuttings from the source bush (mother bush). In this case, the method of falling asleep with earth horizontally to the main plant in small grooves is used. Let’s consider this method in more detail.
Rules for the propagation of grapes using horizontal branches:
- during autumn pruning, it is necessary to leave a couple of extra shoots for this propagation method;
- in spring, grooves are dug near the selected bush, the depth of which should not exceed 20 cm;
- soil mixed with organic and mineral fertilizers is placed in these grooves, and fresh black soil and manure are also introduced;
- after that, a vine is placed in it. It should be carefully pinned in some places. You can strengthen the escape with iron staples and soft wire. The apical bud of the vine should be on the surface;
- then the fixed vine is covered with loose earth by 5 cm;
- on the part of the shoot that is not covered by the ground, you need to remove all the lower eyes with a sharp garden knife;
- you can finally fill up the groove only after the vine is completely rooted (it will begin to grow).
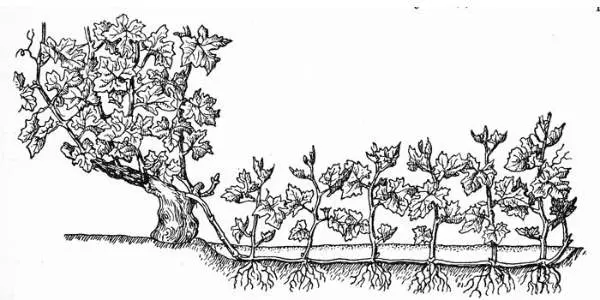
The scheme of reproduction by the method of horizontal layering
After the above manipulations, roots and shoots will form on all nodes of the vine. New cuttings need to be watered and fed two or three times during the summer (mineral fertilizers are used for this).
It must be borne in mind that the frequency of watering depends on how hot the summer was. In hot and dry weather, the number of waterings is once a week.
In the autumn, after all the leaves have fallen from the grape bush, they dig out the horizontal layers and then cut them and get new seedlings. They are planted already in a permanent place of growth.
The main advantage of the above method is the high survival rate of seedlings and their fruiting in the first or second year after planting.
Video “Propagation of grapes by layering”
In this video, you can clearly see the nuances of applying this method in practice.
The choice of breeding method depends on your preferences, the main thing is to follow the rules in order to achieve the expected result in the end.
Author: Svetlana Galitsina
Loading…









