Contents
The most severe course is in bacterial meningitis. Such meningitis can damage the nervous system and sometimes be fatal. Viral meningitis usually proceeds more favorably and rarely leads to complications.
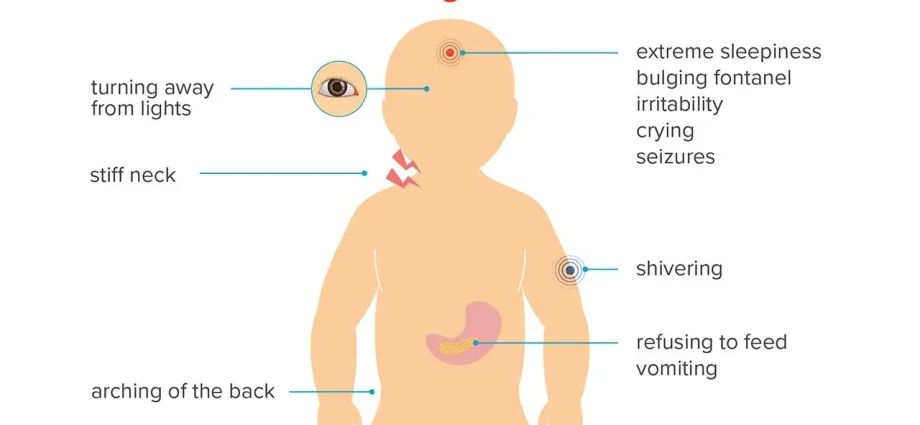
Symptoms of meningitis in children
The cause of the development of the inflammatory process in the meninges can be various viruses (enteroviruses, Coxsackie viruses, poliomyelitis, mumps, etc.), as well as bacteria (meningococci, pneumococci, staphylococci, hemophilic bacilli, etc.). The infection can enter the human body through airborne droplets, through unwashed hands, contaminated food and water.
Some children are at higher risk of developing meningitis. These include:
- Premature babies, since such children have very weak immunity;
- Newborns whose mothers had a severe course of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as fetal hypoxia, infections;
- Children at an early age, if they have other foci of infection (sinusitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, endocarditis), SARS, intestinal infections;
- Children with dysfunction of the nervous system;
- Children with brain and spinal cord injuries.
The development of meningitis is accompanied by:
- An increase in temperature to 39 ° C and above;
- Headache is the main symptom of meningitis. It usually increases with sudden movements, in bright light;
- Tension in the neck muscles, due to which the child cannot tilt his head to his chest;
- Nausea and severe vomiting;
- convulsions
- Confusion of consciousness;
- photophobia.
In newborns, the symptoms of the disease are more blurred. Diarrhea, lethargy, lack of appetite, regurgitation may occur. If any of these signs appear, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
The incubation period
Symptoms of meningitis usually develop rapidly and at the first suspicion of a child’s illness, the child should be hospitalized immediately. In some cases, an incubation period of 2 to 10 days is possible. During this period, the symptoms of the disease are not yet so pronounced.
Rash
The characteristic “star-shaped” rash occurs in about a quarter of cases of all meningitis. She says that meningitis is caused by a meningococcal infection. Meningococcus, entering the body, begins to secrete a toxin that damages the wall of blood vessels. This leads to hemorrhages in the form of a red-purple skin rash.
Types of meningitis in children
Serous
Serous meningitis is usually caused by a viral infection and has a more favorable course. Such meningitis is characterized by muscle pain, fever, conjunctivitis, redness of the throat, rash. As a rule, the patient complains of a sharp headache, vomiting.
Purulent
The cause of the development of purulent meningitis is bacteria – meningococci, streptococci, staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, etc. The infection enters the child’s body through the mother’s placenta, if she has such diseases as pyelitis, cystitis, etc. Purulent meningitis is the most dangerous and in 50-60% cases lead to death. Newborn babies do not fully recover. Often the nervous system is so affected that the child has a mental retardation, paralysis of the limbs and other serious complications.
Viral
Viral meningitis usually proceeds more favorably. Its causative agents can be viruses of various types. At the same time, along with a headache, neck muscle tension, and vomiting, the child has signs of a viral infection, such as redness of the throat, conjunctivitis, lacrimation, etc.
Treatment of meningitis in children
In order to make an accurate diagnosis of meningitis, it is necessary to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid. The diagnosis of meningitis can be confirmed if there are certain changes in it. Additionally, a bacteriological examination of blood, a smear from the throat, etc. is carried out.
After confirming the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. It allows:
- Eliminate bacterial, viral infection;
- Reduce cerebral edema and normalize intracranial pressure;
- Reduce body temperature;
- Eliminate oxygen starvation, convulsions, reduce headache.
Aftermath
With untimely and inadequate treatment of meningitis in children, severe consequences can develop. There may remain disorders of the psyche, speech, hearing, lesions of the facial nerves (paresis and paralysis), dementia. After the illness, the child may still have headaches, increased intracranial pressure, intellectual retardation, strabismus, etc.
Is it possible to treat at home
Treatment of meningitis is possible only in a hospital. The child is shown bed rest.
Prevention of meningitis in children
The most effective measure to prevent meningitis in children is vaccination. There are the following types of vaccines:
- Meningococcal vaccine – for children aged 10-12 years. Recommended for people who often visit other countries, recruits;
- Haemophilus influenzae vaccine – for children aged 2-5 months;
- Vaccines for other childhood infectious diseases (measles, rubella, mumps, chicken pox), as meningitis can develop as a complication of these diseases.