Contents
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is a dangerous disease, it is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. The disease can occur both independently and as a complication of another process.
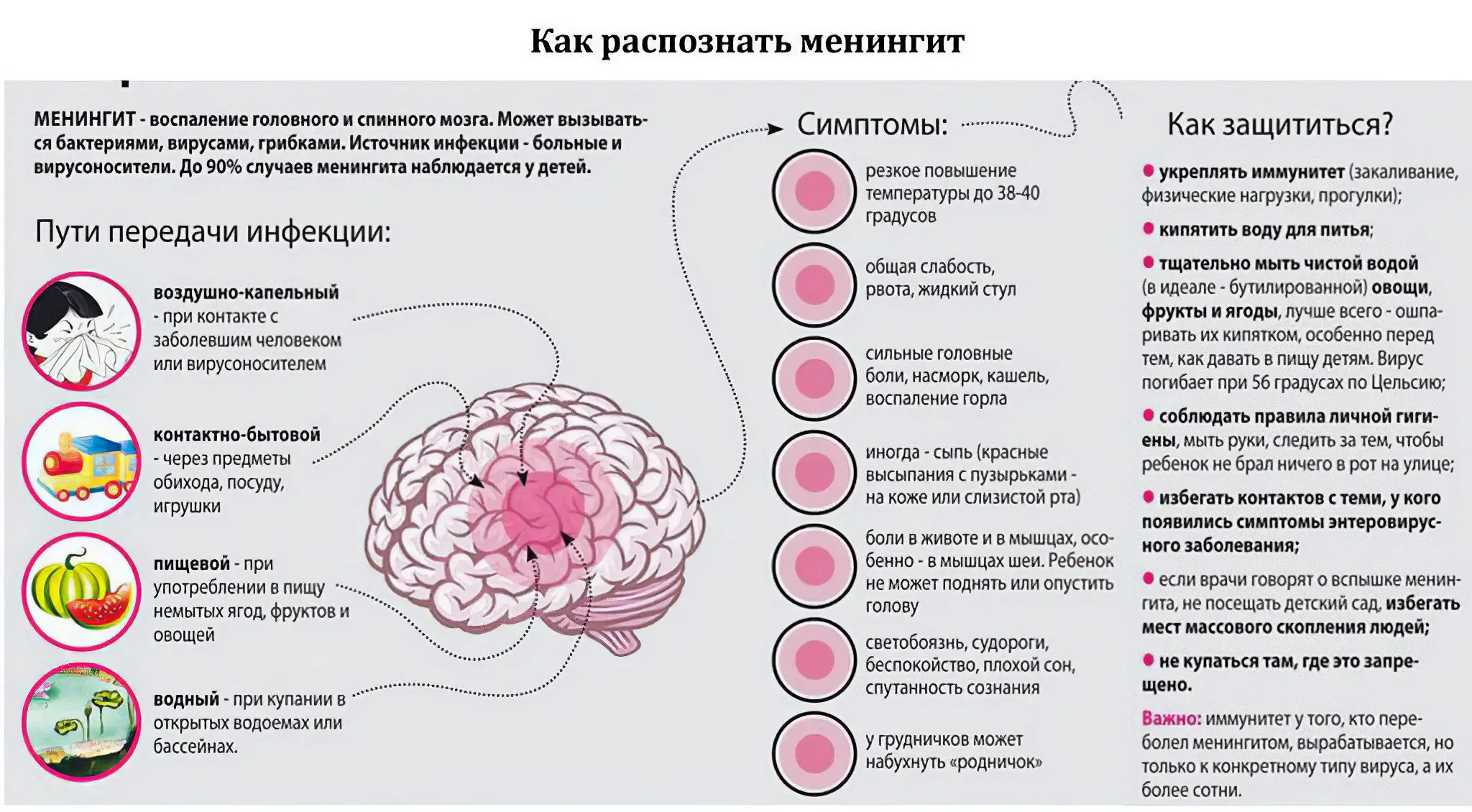
There are several classifications of meningitis. According to the etiology, meningitis can be bacterial, viral, fungal; by the nature of the inflammatory process – purulent and serous (rapid damage to the membranes of the brain, which is characterized by a serous inflammatory process).
The most common symptoms of meningitis are headache, neck numbness, fever, confusion, fear of light, and increased sensitivity to sounds. Nonspecific symptoms include irritability and drowsiness.
Causes of meningitis
The most common causes of meningitis are bacteria or viruses that infect the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid.
In children, the cause of meningitis is mainly enteroviruses that enter the body through food, water, and dirty objects.
In adults, bacterial meningitis predominates, the causative agent of which is the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis. These bacteria do not cause meningitis in the throat and nose, but when they get into the blood, cerebrospinal fluid and soft tissues of the brain, they provoke inflammation.
Sometimes other types of bacteria are the cause of meningitis. Group B streptococcus often causes illness in newborns infected during or after childbirth. Listeria monocytogenes also predominantly affects infants and the elderly.
Meningitis often develops as a complication of various diseases and head injuries.
The disease can be transmitted during childbirth, by airborne droplets, through mucous membranes, dirty water, food, rodent and insect bites.
Symptoms of meningitis
The most common symptoms of meningitis are headache, numbness (rigidity) of the neck muscles, fever, impaired consciousness (up to coma), increased sensitivity to light and sound. The patient has nausea and vomiting, general weakness, heart rhythm disturbance, muscle pain. Meningeal syndrome is expressed by the symptoms of Kernig and Brudzinsky: the patient cannot bend the neck, straighten the leg at the knee joint. Hyperesthesia is manifested in hypersensitivity: a person cannot endure bright light, loud sounds, touches.
An upper respiratory tract infection is often a harbinger of meningitis, but taking antibiotics can smooth out the overall picture of the disease. With a weakened immune system, meningitis can either occur as a mild infection with a mild fever and headache, or quickly develop into a coma.
Meningitis is diagnosed through the study of cerebrospinal fluid, after taking a lumbar puncture.
Bacterial meningitis usually begins acutely, meningeal symptoms are pronounced. Serous tuberculous meningitis has a gradual course.
A variety of chronic diseases often lead to lesions of the meninges: tuberculosis, syphilis, sarcoidosis, toxoplasmosis, brucellosis.
Types of meningitis
Bacterial meningitis usually occurs due to the penetration of pneumococcus bacteria, meningococcus, Haemophilus influenzae into the central nervous system.
1. Haemophilus influenzae provokes the disease mainly in children under 6 years of age, less often in adults. It occurs against the background of diseases such as pneumonia, otitis media, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, traumatic brain injury, sinusitis.
2. Meningococcal meningitis usually proceeds quite hard; a hemorrhagic rash may occur in the form of spots (asterisks) of different sizes. Spots are localized on the legs, thighs and buttocks, mucous membranes and conjunctiva. The patient is disturbed by chills and high fever, intoxication is possible.
3. Pneumococcal meningitis occurs quite often and proceeds with the onset of pneumonia in about half of the patients. The disease is most severely tolerated by people with diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, cirrhosis of the liver. Symptoms are damage to consciousness and cranial nerves, gaze paresis, epileptic seizures. Pneumococcal meningitis can recur and is often fatal.
Bacterial meningitis can lead to complications such as shock, endocarditis, purulent arthritis, bleeding disorders, pneumonia, and electrolyte disorders.
Viral meningitis begin with the symptoms of the infectious disease that caused them. Such meningitis occurs with moderate fever, severe headache and weakness. At the same time, meningeal symptoms are mild in patients. The disease most often proceeds without disturbances of consciousness.
Tuberculous meningitis is now often one of the first clinical symptoms of tuberculosis. Previously, this form of the disease was always fatal, but now, with adequate treatment, mortality is 15-25% of all cases of the disease. Tuberculous meningitis begins with fever, headache, and vomiting. Meningeal symptoms appear, cranial nerves are affected.
Meningitis treatment
Treatment of meningitis should always be comprehensive and carried out in a hospital. The patient is shown strict bed rest, taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Sometimes severe conditions of the disease require resuscitation procedures. With proper and timely treatment, meningitis is completely curable.
For the prevention of certain types of meningitis, a vaccine is given that is valid for about four years, but it is impossible to protect yourself from the disease by 100%. The main thing is to diagnose it in a timely manner and immediately begin treatment.
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to get meningitis a second time? As a rule, no, a person who has been ill with meningitis develops lifelong immunity. However, in rare cases, those people who have a traumatic brain injury and who have post-traumatic liquorrhea (liquor leakage into the nasal passages through a crack at the base of the skull) can get sick again.
I have a temperature of 3+ for 5-7-39 days, my head hurts a lot, I feel sick, is it meningitis? No, if you had meningitis, in 5 days you would already be in intensive care. Meningitis proceeds rapidly, it is inflammation of the meninges, high fever and resuscitation. You most likely have a viral infection, the temperature should start to drop on the 5th day. You can periodically bring down the temperature with ibuprofen. Contact a therapist.
What is the main difference between meningitis and other diseases? Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain. A person cannot walk, buy antibiotics for himself, make an appointment with a doctor, perform any actions at all, he simply lies with an unbearable headache, a high unrelenting temperature of 39+, sometimes unconscious.
How to suspect meningitis in infants? Symptoms of meningococcal infection in children are: severe headache, nausea and vomiting, a sharp increase in temperature, photophobia, lethargy and drowsiness, pale skin, possible loss of consciousness and convulsions. One of the symptoms is also neck stiffness (the baby is almost always with his head thrown back. The fact is that with meningitis, the child is unable to tilt his head forward – so as to touch his chest with his chin, due to strong tension in the neck muscles). Another striking symptom in children of the first year of life is swelling and pulsation of the fontanel, combined with constant monotonous crying.
[Video] TOP 100 DOCTORS – symptoms of meningitis in adults and children, consequences:









