Birthmarks, moles, or, in medical terminology, nevi, are benign growths on the skin. Usually they appear during the prenatal development of the child and can be of different sizes. It is widely believed that such formations are absolutely safe for human health. However, it is the nevi, under the influence of a number of certain factors, that often become the basis for the development of a dangerous disease – melanoma.
Melanocytic nevus
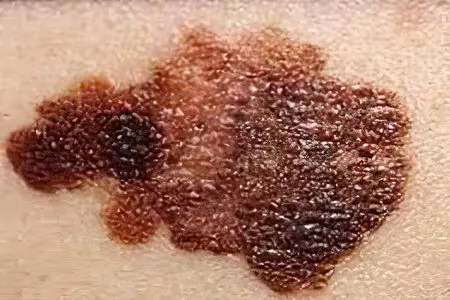
Melanocytic nevi are benign formations formed by three different types of cells, among which there are dermal, nevus and epidermal. They can be located anywhere on the skin. Most melanocytic nevi appear already during life, and with age they become more and more. Very rarely they are congenital. Their maximum number is noted at the age of 15 to 20 years.
The following types of melanocytic nevi are distinguished:
epidermal origin. They have a smooth surface, have a rounded or oval shape. Hairs often grow on the surface of nevi of epidermal origin. They are most often darker and tougher than those that form the rest of the hairline. In light-skinned people, there may be from 10 to 15 such benign formations. If there are many more of them and they protrude strongly above the surface, this indicates a high risk of melanoma. Nevi of epidermal origin are classified into intradermal, borderline and complex. For children, the most characteristic are borderline. They are formed on the soles, palms, genitals and have a rich gray or brown color, less often black. With age, borderline nevi are transformed into intradermal and complex. Intradermal is also called a birthmark. Their shape is hemispherical. They can be identified by their characteristic dark brown or black color. Complex nevi are of the transitional type.
dermal origin. Unlike epidermal, these nevi are congenital. They have a characteristic flesh color and are plaques and solitary papules. Sometimes they can be covered with a small amount of hairs or completely devoid of hair. Nevuses of dermal origin are less likely to cause other diseases. Therefore, experts recommend removing them only for cosmetic reasons.
mixed dermal and epidermal origin.
Causes of melanocytic nevus
Benign formations of this type appear under the influence of several factors. When disturbances appear in the movement of melanoblasts from the neuroectodermal tube to melanocytes, they can accumulate in one place. This is how nevi appear. This reason is congenital. However, benign formations in a child are not immediately noticeable. It is possible to determine their presence only with age. The risk of degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant one is higher, the larger the area that they occupy on the body.
Acquired nevi appear for various reasons. The main one is changes in the hormonal structure of the body or pregnancy. No wonder doctors warn that prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays is harmful to health. After all, sunlight contributes to the formation of birthmarks. Frequent skin diseases also lead to the appearance of nevi.
Melanoform nevus
Melanoform nevus is a benign formation formed from special cells. They serve as a source of melanin, so the formations have a brown tint of varying degrees of saturation. Melanoform nevi are congenital but difficult to find in young children. Moles appear during adolescence. During life, they can both appear and disappear. Their size also changes.
Diagnosis and treatment of nevi
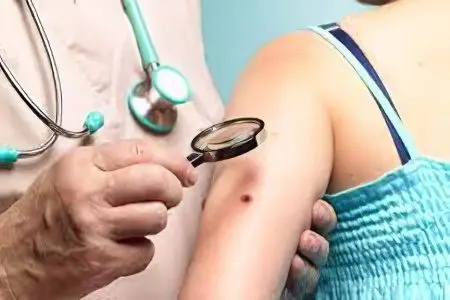
The presence of a large number of nevi does not mean that this will lead to the development of melanoma. Despite this, it is necessary to regularly carefully examine all birthmarks and, if external changes occur, immediately contact a specialist. Also, deviations are indicated by itching or pain in the area of nevi. The doctor will be able to reliably determine whether the formation is malignant.
Diagnosis is made by various methods. First of all, the specialist examines the nevus. If there is a noticeable release of fluid or blood on its surface, then a smear is taken. His laboratory study allows you to determine the malignancy of the formation and the risk of developing melanoma. This diagnostic method also has a drawback. Taking a smear can lead to the transformation of the formation into a malignant one due to the microtrauma that is applied during the procedure.
Examination is also carried out using a dermatoscope. The device works like a microscope. Oil is applied to the examined area of the skin, then the nevus is illuminated with a dermatoscope. This method is called fluorescence microscopy. No less effective is computer diagnostics, which requires expensive equipment. Laboratory methods are used only when there are sufficient grounds to assume the presence of malignant tumors.
After determining the degree of danger of the nevus to the health of the patient, the specialist prescribes treatment.
In modern medicine, resort to the following methods:
surgical intervention. It is necessary when the formations grow and occupy a large area on the body, cause irritation or are in hard-to-reach places. During the surgical intervention, not only the nevus itself is removed, but also part of the skin. In children, the operation is performed under general anesthesia; for adults, local anesthesia is sufficient. The main disadvantage of this method of treatment are the scars and scars that remain on the body.
Electrocoagulation. This procedure consists in exposing the nevus through high temperature. When cauterized, the formation does not exude blood, and there is no need to remove the skin around it as in a surgical operation. But electrocoagulation is accompanied by tangible pain for the patient. In addition, using this procedure will not be able to get rid of a large nevus.
Cryodestruction. With the help of carbonic acid, liquid nitrogen or ice, the affected area is frozen. As a result, a dense crust appears on the surface of the nevus, and under it – new skin. After cryodestruction, no traces remain. During the procedure, patients do not experience discomfort and pain. But often this method is ineffective or several sessions are required.
laser therapy. Also, as with cryodestruction, when exposed to a laser, there is no pain and no scars remain. But the skin area at the site of the nevus can become white and stand out noticeably due to the lack of pigment. With laser therapy, it is important to completely remove the formation. Otherwise, various complications and an increase in the size of the nevus are possible.
radiosurgical methods. Began to be used quite recently. The impact on the nevus is carried out with the help of a radio knife, which serves as a source of radiation. This method is suitable for malignant and benign formations, but will be ineffective for large nevi.









