Medical treatments for preterm (pre-term) labor
Preventive treatment of preterm labor
Women who have already had a premature child (less than 37 weeks gestation) may receive, as a preventive measure, a progesterone supplement (PrometriumMD) by injection or vaginal gel. Progesterone supplements are usually given between 16 and 26 weeks of pregnancy until the 36e week. These supplements are not effective in women who are pregnant with twins and have not been shown to be effective in women without a history of preterm labor.
Strapping of the cervix
In some women at risk or with too large an opening in the cervix, the cervix is sometimes banded. This operation consists of tightening the opening of the cervix with a thread. The thread is removed when the baby is seen full term, around the 37e week of pregnancy.
Treatment to slow or stop preterm labor
Treatments given to slow or stop preterm labor are intended to allow the fetal lungs to develop to full maturity (usually after 34e week of pregnancy). They also allow time for the pregnant woman to travel to a hospital or to a professional center that can provide the necessary care for the premature child.
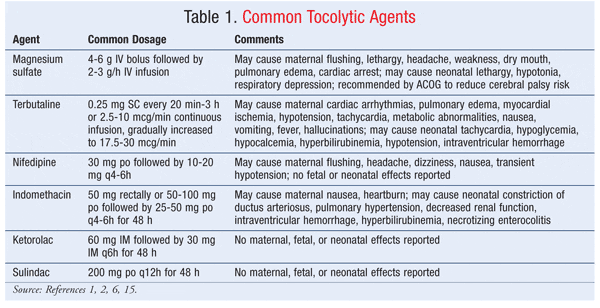
Medicines such as tocolytic agents (= terbutaline, magnesium sulfate, nifedipine indometacin and atosiban) are given to relax uterine muscles and stop contractions. These drugs are usually given if the pregnant woman is less than 34 weeks pregnant. They can stop the contractions and allow a delay of several hours, up to 48 hours.
These medicines are usually given in combination with an injection of glucocorticoids (betamethasone) which can speed up the maturation of the lungs of a premature baby and prevent certain complications of the circulatory system.