Contents
Doctors call measles one of the most contagious infections. Those who are close to a coughing and sneezing patient have practically no chance of avoiding infection, infectious disease specialists warn (if the person is not properly vaccinated and has not been ill before). A large stratum of the vaccinated population is now saving our country from a real epidemic, notes vaccinologist, pediatrician Evgeny Timakov. However, cases of importation of measles from abroad are observed more and more often. And the violent activity of anti-vaccinators inside Russia, alas, is also bearing fruit.
Symptoms of measles in adults
Measles in adults begins like a SARS, only the symptoms are usually more severe, that is, more pronounced than in the “common” cold, explains Dr. Timakov. As a rule, the following set of symptoms of measles is observed:
- high temperature – 38 – 40 degrees;
- nasal congestion, runny nose;
- dry hacking cough;
- tearing, redness of the eyes, possibly suppuration (conjunctivitis);
- weakness, loss of appetite;
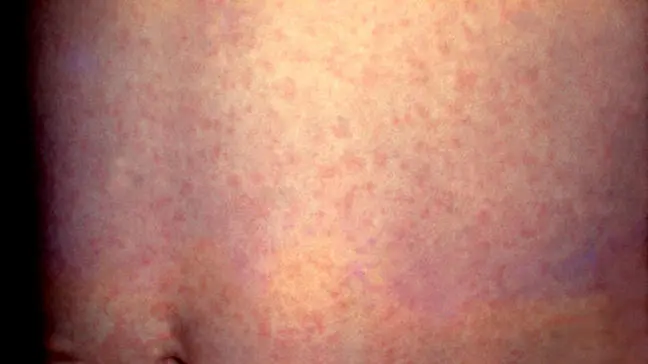
- rash (exanthema), appears on the 4th – 5th day, first on the face, neck, upper body, then goes down, spreads over the arms and legs; the rash does not itch.
After 3-5 days, the exanthema begins to turn pale and gradually disappears. Peeling remains at the site of the rash.
Important! Measles can cause severe complications, affecting the respiratory, cardiovascular and central nervous systems, doctor Yevgeny Timakov told KP. Pneumonia (pneumonia), inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) can develop. Of the most dangerous complications – inflammation and swelling of the brain (encephalitis), blindness and even coma. The risk of complications is highest in smokers, people with diabetes, cardiovascular and other chronic diseases. They need to pay special attention to their condition and in case of deterioration (shortness of breath, dizziness, etc.) immediately call a doctor.
Treatment of measles in adults
Today, there are no drugs in the world that would act directly on the measles virus and fight it. Immunomodulators / immunostimulants have no proven effect either. Therefore, if you are offered such drugs, keep in mind that at best they will not help, and at worst they will create an additional burden on the liver and kidneys.
Treatment for measles in adults is symptomatic medication. That is, drugs that reduce the adverse effects of infection. In particular, the following may apply:
- antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- antihistamines (to relieve swelling);
- vasoconstrictor (for a short time in case of a severe cold).
Patients are recommended bed rest and plenty of fluids, adds Dr. Timakov.
What antibiotics can be used for measles?
By itself, measles, like SARS, flu, is a virus. Antibiotics do not work on viruses, infectious disease specialists remind. Moreover, if you start taking antibacterial drugs when the first symptoms of measles appear (see above), then harm the intestinal microflora, which is largely responsible for our immunity. So it could end up getting worse.
But if measles gives a complication, then the use of antibiotics is already necessary. However, only a doctor can determine whether a complication has begun and select the necessary antibiotic from the appropriate group (depending on the type of complication), emphasizes Evgeny Timakov. In no case do not self-medicate – in the case of measles, it is especially fraught.
Bark graft
In our country, the measles vaccine is included in the National Immunization Schedule (NCV). According to the calendar, the first vaccination is given to the child within 12 months after birth. Then at 6 years – revaccination. For adults, this is important. Because if the first vaccination and / or revaccination was not done, then at the age of 18 – 35 years it is recommended to re-vaccinate against measles. It will be free – you need to contact the therapist of your clinic at the place of residence, and he will issue a referral to the treatment room.
At a later age – from 35 to 55 years old – practitioners recommend vaccinating against measles for those who have not been vaccinated twice during their life (initial vaccination and revaccination) or do not have data on their vaccinations and have not had measles earlier (in in the latter case, lifelong immunity is developed).
Folk remedies
Doctors note that among the folk remedies for the treatment of measles, which definitely do not harm, acidified drinks can be distinguished. Fruit drinks from blackcurrant, cranberry, lingonberry. Rosehip decoction.
Expectorant fees will help relieve coughing – they can be bought at a pharmacy and prepared according to the instructions.
Decoctions of sage or chamomile will help alleviate a sore throat.
If the eyes become inflamed, it is recommended to wipe them with cotton swabs dipped in warm boiled water or chilled tea leaves.
Prevention at home
The measles virus is transmitted by airborne droplets. That is, when the particles of the virus, when coughing or sneezing a sick person, enter the mucous membranes of a healthy person – in the nose, mouth, eyes. Also, for a short time (up to two hours), the virus can persist in the air and on surfaces in the room where the patient coughed and sneezed.
Based on this, for the prevention of measles, doctors recommend that you wash your hands after returning from the street, from public places and premises. Wipe your mobile phone with antibacterial wipes.
The most reliable, effective and safe thing is to get vaccinated. In case of contact with a patient with measles, according to epidemiological indications, a person is urgently vaccinated – within the first 72 hours after contact. If more time has passed (up to 5-7 days), then the introduction of human immunoglobulin, that is, ready-made antibodies to the measles virus, is prescribed. Pregnant women are also prescribed not a vaccination, but the introduction of immunoglobulin.