Contents
What is mastitis
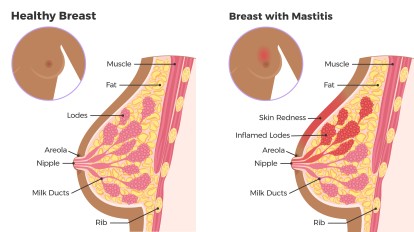
Mastitis is an inflammatory condition that causes tenderness and tenderness in the breast tissue. The specialist notes that mastitis occurs more often in primiparas due to the lack of skill and experience in breastfeeding. Less often – in those who give birth not for the first time.
Mastitis in lactating women is caused by a bacterial infection of the milk ducts that enters through cracks, due to irritation of the nipple, or in the presence of a nipple piercing. Breastfeeding mastitis is dangerous because it can cause pain while breastfeeding, interfere with the bonding process between mother and baby, or even interfere with milk production.
To protect the health and comfort of mother and child, as well as the mother’s milk production, this problem must be addressed urgently. The sooner a breastfeeding woman sees a doctor, the better.
Causes of mastitis in women
Mastitis can develop in a new mother at any time, but more often it occurs within the first two to three weeks after childbirth. A common cause of this disease is long breaks between feedings – for example, when the baby begins to sleep through the night.
There are other possible causes of mastitis:
- improper grip of the breast during feeding;
- incomplete outflow of milk from the mammary glands, for example, due to blockage of the milk duct;
- breast engorgement, left unattended;
- regular pressure on some part of the mammary gland, wearing tight clothes;
- chest injury caused by injury or impact.
“Inflammation is promoted by stagnation of milk and cracked nipples, which leads to the penetration of infection into the breast tissue,” says Olga Diveeva.
Symptoms of mastitis in women
The doctor identifies several symptoms:
- pain in the mammary gland;
- swelling;
- breast augmentation in volume;
- redness, thickening;
- chills;
- increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees;
- weakness;
- headache;
- possible enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
Treatment of mastitis in women
If mastitis in a nursing woman was diagnosed on time and was not allowed to develop, then conservative therapy can be limited. It includes antibiotic therapy, the use of antispasmodics, UHF therapy.
If the process is already running and the condition is only getting worse, then there is a need for surgical treatment. It consists in removing pus from the focus with washing it with antibiotics.
Diagnostics
With mastitis, jokes are bad, with the slightest symptoms, a nursing woman already needs to run to the doctor. The doctor makes a diagnosis of mastitis based on the patient’s complaints, the clinical picture and the results of the examination.
The doctor may prescribe studies:
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- bacteriological and cytological examination of discharge from the nipples;
- breast ultrasound;
- mammography;
- taking a biopsy if necessary, differentiation from a cancerous tumor.
Therapies
- Antibiotic therapy – taking antibiotics;
- Taking antispasmodics – these are drugs that weaken or completely eliminate spasms of smooth muscles of internal organs and blood vessels;
- UHF therapy – a physiotherapy technique based on the impact on the patient’s body of a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a frequency of electromagnetic oscillations of 40,68 MHz or 27,12 MHz;
- Operation. Surgical intervention is prescribed already because of advanced purulent mastitis. The operation must be performed in a hospital under general anesthesia. Depending on the situation, the location of the seals, the prevalence of the process, the anatomical and functional features of the breast, doctors will choose where to make the incision.
Prevention of mastitis in women at home
– The main preventive moment is the correct attachment to the breast and the complete emptying of the mammary glands. It is important to avoid nipple cracks, if there are difficulties with catching the nipple (flat nipples, or the baby is very small and cannot fully latch on to the nipple), you need to use special pads. In the event of cracks, it is necessary to temporarily limit feeding to this breast in order to avoid infection, but do not forget to pump at the same time. It is important to monitor the complete emptying of the breast. The most difficult period when lactostasis and mastitis can occur is the first weeks after the birth of the baby, when lactation is established, and more milk comes in than necessary. Already after 2-3 weeks, a feeding regimen is formed, and milk is produced on demand, and exactly as much as the baby needs at the moment. Do not give your baby a pacifier or a bottle during this period, as this may interfere with lactation! It is important to prepare in advance for the breastfeeding period, study the literature, watch educational videos in order to be prepared for possible difficulties, and to know and be able to cope with them. At the first signs of lactostasis, it is necessary to express, (correctly!) And apply it to the diseased breast. A child is the best assistant for lactostasis.
It is important not to miss the disease and, at the first sign, seek help from a doctor, a breastfeeding specialist who will help you cope with the problem, so you can avoid the inflammatory process and, most importantly, preserve such an important process in the life of mom and baby – breastfeeding. After all, there is no more complete nutrition for newborns than mother’s milk. Moms, do not be afraid to ask for help, be patient, keep breastfeeding to give your child only the best! — said gynecologist Olga Diveeva.
Popular questions and answers
Olga Diveeva, gynecologist-endocrinologist, nutritionist, head of the integrated medicine clinic in Novorossiysk Diva clinic answers: