Contents
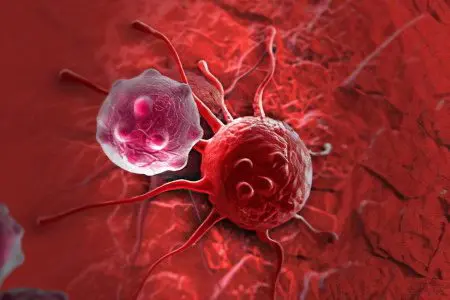
Malaria – This is a disease of an infectious nature, the causative agents of which are parasites, namely, malarial plasmodium. The infection spreads through the blood, and its carriers are female malarial mosquitoes. A person becomes infected when he is bitten by this insect.
In a patient with malaria, the body temperature rises, he is very chilly. Sweating is very intense.
In developed countries with a temperate climate, this disease is rare. Cases of infection are recorded in the tropics and subtropics. And often the disease becomes the cause of death of a person. Not only residents of these climatic zones can become infected, but also tourists. The leadership of states from the risk group directs efforts to combat the disease, but it is not possible to completely get rid of it. Malaria kills about 660 people every year. That is why it is so important to know the symptoms of malaria. This will allow you to start treatment on time and save a person’s life.
What is malaria?
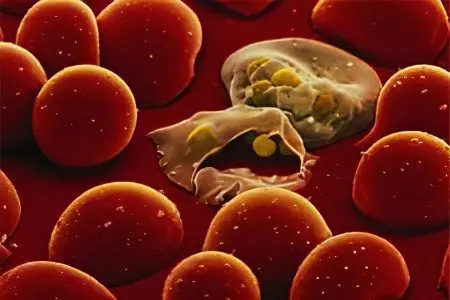
Malaria is an infectious disease that affects red blood cells. They are damaged by intracellular parasites of the genus Plasmodium.
The spreader of the infection is the female malarial mosquito. Parasites are transmitted to humans during an insect bite, that is, through the blood.
There are three possible routes of infection with tropical malaria:
Transmission type. Infection occurs during the bite of an Anopheles mosquito.
parenteral. The infection is transmitted through blood, during its transfusion or during transplantation of donor organs. There is also a risk of contracting malaria during surgery if the instruments used by the surgeon are infected.
Transplacental. The disease is transmitted to the child from the mother.
Malaria is a seasonal infection. Its outbreaks are recorded during the hot and humid season. People living in high-risk areas are regularly tested for malaria. When cases of the disease are detected, treatment is prescribed.
Types of malaria
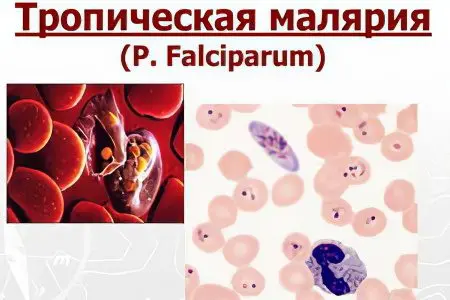
Although scientists know more than 4000 species of protozoa of the order Coccidiida and the genus Plasmodium, it has been established that only five of them can become a spreader of malaria:
Plasmodium falciparum This is the most formidable parasite that causes a severe form of malaria – tropical. It will be difficult to cope with the disease, as the infection does not respond well to therapy.
Plasmodium vivax. This parasite causes malaria as often as Plasmodium falciparum, but it is not as dangerous to the human body. Mostly from the disease affects the inhabitants of India, Central and South America. Once in the human body, the parasite causes symptoms of the disease, which, thanks to treatment, can be eliminated. However, this does not mean that it was possible to get rid of the infection. The “home” of the parasite is the liver. After recovery, the disease may reappear after a few years.
Plasmodium ovale. This parasite is common in African countries. It can also live in the liver, causing a recurrence of the disease after a few years. Experts call this infection “oval-shaped malaria”.
Plasmodium malaria. This parasite is not so common, but it provokes the development of a disease that can be difficult to identify. There are few plasmodium circulating in the patient’s blood, so such malaria (four-day malaria) can last for several years.
Plasmodium knowlesi и Plasmodium cynomolgi. These parasites cause infection in monkeys. However, scientists have data on human infection. A person recovers immediately after infection, recurrence of the infection does not happen. Malaysians are predominantly affected by this form of malaria.
Depending on the period of malaria, there are:
primary infection.
Malaria in the period of early relapse (recurrence of symptoms occurs less than six months after the first case).
Distant relapses of malaria, which may be several.
Period of latent malaria.
Depending on the severity of the course of the disease, there are:
Mild malaria.
Malaria of moderate course.
Severe malaria.
Malaria of a malignant course.
Development of the disease
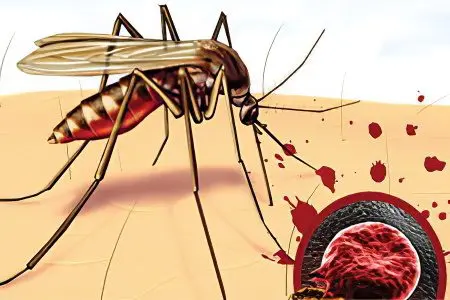
Once infected, the parasites enter the general circulation. This happens during an insect bite, when it feeds on the blood of its victim. Then comes the incubation period. At this time, the person does not know that he is infected, since there are no symptoms of the disease. The latent period can last for several days. It all depends on the specific type of pathogen.
Plasmodium falciparum is detected faster than others, it makes itself felt on 6-8 days. Longer than others does not cause symptoms of Plasmodium malariae disease. The incubation period stretches to 14-16 days.
When the prodromal period begins, the patient feels the first signs of infection. At this time, he has a deterioration in general well-being, chills, headaches may occur. The average duration of the prodromal phase is 5 days.
Then malaria makes itself felt in full force. There is an acute stage of the disease. At this time, the body temperature rises greatly, a series of febrile attacks occur. Each of them can last from 3 to 10 hours. After that, the person becomes easier. The symptoms of the disease are on the decline.
Potentially dangerous regions
Malaria is a common infection. The disease occurs in the West Indies, Mexico, Central America. The inhabitants of the northern regions of South America suffer from the infection, especially the population that lives in the Amazon Valley. For Africans, illness is also a problem. Cases of malaria are recorded among the inhabitants of the Red and Mediterranean Seas, in Ukraine and in the Balkans. Every year, data comes in about infected residents of Southeast Asia, India and northern Australia.
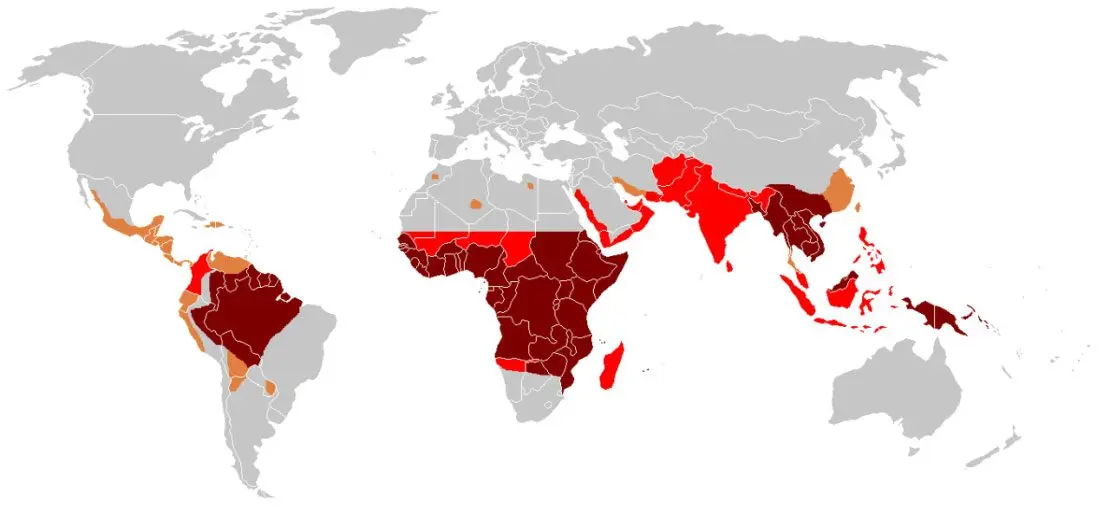
Plasmodium falciparum is the most common parasite that causes malaria in Africa. It is from him that most people die in the whole world.
Plasmodium vivax is common outside African countries. This parasite causes malaria in the southern parts of the Sahara.
Every year, 350-500 million people worldwide suffer from malaria. About 1,3-3 million people die from the disease. Approximately 90% of cases are residents of Africa, located south of the Sahara. Moreover, children under 5 years of age are predominantly infected there.
Symptoms of malaria
After a person is bitten by a malaria-carrying mosquito, it takes about 2 days for the person to develop symptoms of the disease. If the immune system is active and strong, then this period can stretch up to 7 days.
According to the first symptoms, it is impossible to understand that a person develops malaria. They can characterize various diseases.
Early signs of infection include:
Fatigue and weakness.
Lack of desire to eat.
Dizziness.
Headache. This symptom occurs only when infected with Plasmodium falciparum.
Violation of the digestive tract: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
Sometimes blood impurities appear in the feces. This symptom also characterizes Plasmodium falciparum infection.
Muscle pain.
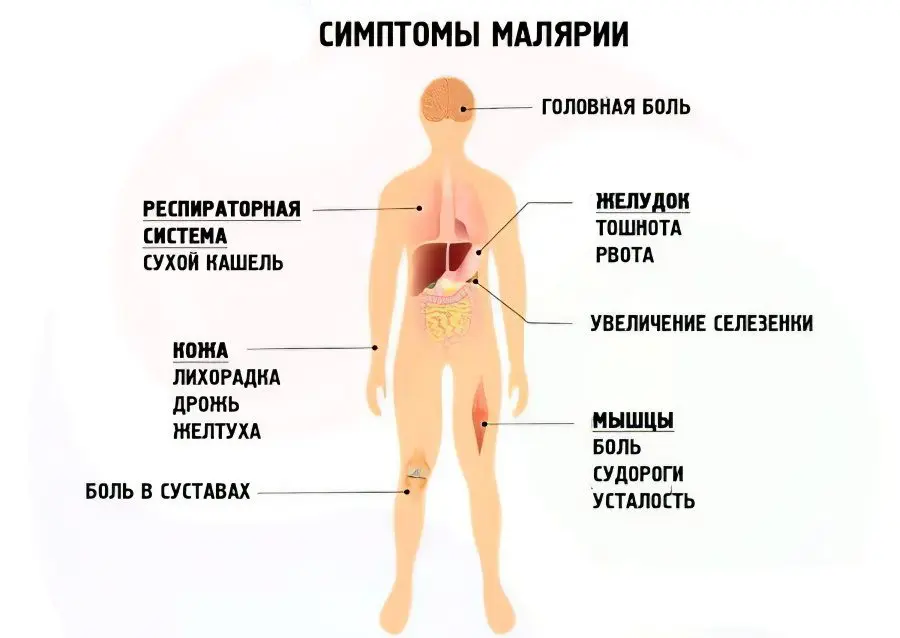
The typical symptoms of malaria occur later:
Cyclic fever. Periods last 3 or 4 days, or permanently.
Tremor of the limbs. It also occurs from time to time.
Joint pain. This feature characterizes Plasmodium falciparum.
Anemia that develops on the background of hemolysis.
Severe Plasmodium falciparum leads to paralysis.
With a malignant form of the disease, a person develops cerebral edema. It grows rapidly and leads to death. This course is characteristic of malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax.
Other symptoms of malaria include an enlarged liver and spleen, a sharp drop in blood sugar levels, and impaired kidney function. If the kidneys are working, then hemoglobin from red blood cells can enter the urine.
Complications

Complications of malaria include:
malarial coma. Most often, women in position, young people and children suffer from it.
Acute kidney failure. Diuresis is reduced to 400 ml per day.
Hemoglobinuric fever. It occurs due to the massive destruction of red blood cells, which leads to the release of toxins into the blood. With this complication, the patient’s urine output decreases rapidly, which leads to progressive renal failure. Often such cases end in the death of the patient.
Malarial algid. This complication proceeds according to the type of inflammation of the brain, but the consciousness of a person is not disturbed.
Pulmonary edema. Its symptoms grow rapidly, often this complication ends in the death of the patient.
Spleen rupture, which occurs due to torsion of the legs of the organ. If the patient is not provided with emergency medical care, he may die from blood loss.
severe anemia on the background of hemolysis.
DIC syndrome. First, the blood coagulates directly in the vessels, and then the patient develops bleeding.
The consciousness of a person can be disturbed. This process goes through 3 phases:
Somnolence. A person loses motor activity, becomes drowsy, refuses to contact other people.
Sopor. Consciousness slows down. A person reacts only to expressed stimuli. Reflexes are minimal, convulsions often occur. Symptoms of impaired consciousness can proceed according to the type of meningitis.
Coma. The patient is unconscious, there are no reflexes.
Diagnostics
To diagnose malaria, the following blood tests are performed:
Examination of a thick drop of blood.
Thin smear of blood. If the doctor detects changes characteristic of malaria in a thick drop, he prescribes this study. It allows you to clarify the type of pathogen and the stage of its development.
The methods of immunological research include:
Determination of proteins to Plasmodium falciparum. This method allows you to diagnose tropical malaria. It is often resorted to in those countries where the tropical form of the disease is widespread. A person can perform such a test even on their own. For its implementation, blood from a finger is required.
ELISA. This method examines venous blood. It contains antibodies that are produced in response to a parasitic infection. Most often, ELISA is resorted to in countries where malaria is not widespread.
PCR or polymer chain reaction to malaria. For the study, blood is taken from a vein, or a thick drop of blood is taken from a finger. This method allows you to detect the causative agent of the disease. They resort to PCR to detect difficult-to-diagnose forms of malaria.
When the disease has just begun to develop, it can be confused with pneumonia, food poisoning, influenza, meningitis, etc. As the pathology progresses, the symptoms become more specific. However, differential diagnosis is carried out with such diseases as: typhoid fever, yellow fever, tuberculosis, viral hepatitis, leptospirosis, sepsis, leukemia.
Malaria treatment
The main goals to be achieved in the course of malaria treatment are:
Elimination of the parasite in the human body.
Getting rid of the complications of pathology.
Prevention of recurrence of the disease and relief of pathological symptoms.
Enhance immunity.
Types of treatment:
Carrying out specific therapy. The patient is prescribed drugs that can destroy the causative agent of the disease.
Carrying out symptomatic therapy. It is necessary to stop the symptoms of the disease in the case when they have a vivid manifestation.
Compliance with patient care.
Antimalarial drugs
You can cope with malaria with drugs that contain quinine, mefloquine, chloroquine, fansidar, metakelfin, artemisin, proguanil. Some drugs are used only for prophylactic purposes, others allow you to completely cope with malaria. There is no universal drug for the treatment of infection, as different forms of the disease are recorded in different regions. In addition, some parasites have learned to adapt to ongoing drug therapy and do not respond to it. Therefore, the drug is selected in each case individually.
To cope with the infection, it is increasingly necessary to resort to combination therapy with the inclusion of artemisinin in the treatment regimen.
WHO recommends the use of drugs to get rid of malaria, such as:
Artemether/lumefantrine (Artemether/lumefantrine). Trade name of the drug Coartem. In a number of countries it can be found under the brand name Riamet. The drug is used to treat an infection.
Artesunate/amodiaquine – used for prophylactic purposes.
Malaron both for treatment and prevention. Its other name is Malanil. The main active ingredient in this drug is Atovaquone/proguanil.
Quinine (Quinine). Used to treat sickness
Chloroquine (Chloroquine). Trade name of the drug Delagil. It is used for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes.
Cotrifazid – used to prevent and treat malaria.
Doxycycline (Doxycycline). Appoint with the preventive and therapeutic purpose.
Lariam, containing mefloquine (Mefloquine) is used for prophylactic purposes, as well as for the treatment of malaria.
Savarin, containing proguanil (Proguanil) is used only for treatment.
Primaquine used exclusively for prevention.
Fansidar, containing substances sulfadoxine / pyrimethamine (Sulfadoxine / pyrimethamine) is used both for the treatment of the disease and for prophylactic purposes.
In Russia, not all listed medicines are allowed for use.
If a case of malaria was registered on the territory of the Russian Federation, then the patient may be prescribed drugs such as:
Quinine.
Delagil containing Chloroquine.
Plaquenil based on hydroxychloroquine.
Lariam with mefloquine.
Fansidar. It is a combination drug with pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine.
Doxycycline, which is a broad spectrum antibiotic.
To prevent recurrence of the disease, all adult patients (with the exception of pregnant women and children with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency), in addition to therapy with chloroquine or artemisinin, are additionally prescribed primaquine. The course should last 2 weeks.
If malaria has been provoked by such parasites as Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax or Plasmodium knowlesi and has a severe course, then parenteral administration of Artemetrin or Artesunate into the body is necessary. Patients are then prescribed combination preparations containing Artemisinin. WHO recommends emergency care for all patients with severe forms of malaria.
Therapy of malaria in Russia is quite difficult. Not every medical institution has a specialist who can make a correct diagnosis. Even after the confirmation of malaria in the country, there may simply not be drugs to treat it.
After recovery

If the infection was caused by parasites such as Plasmodium vivax or Plasmodium ovale, then it is impossible to exclude the risk of recurrence of the pathology. These infectious agents can exist asymptomatically in the human liver for a long time.
A person who has had malaria cannot donate blood for 3 years. After this period, donation is possible, but medical personnel must be warned that such an infection was transferred 3 years ago.
Malaria during pregnancy
Pregnant women are seriously ill with malaria. This infection can cause miscarriage or early labor. If a woman in position went on a trip to countries with a high risk of infection, or lives there, then efforts should be directed to the prevention of the disease.
If a pregnant woman has contracted malaria, she should seek medical attention as soon as possible. Most of the drugs designed to combat this infection do not harm the health of the child and do not affect his development.
Malaria in children

Malaria for children is dangerous, as it has an aggressive course. If the child does not receive therapy, then he remains at a high risk of developing complications.
Treatment of malaria in childhood is carried out according to the same scheme as in adults, but the dose of drugs is reduced.
Prevention of malaria
If a person goes on a trip to a country where malaria is “raging”, or lives in such states, you need to take care of preventive measures. Preparation should be taken seriously. It is not recommended to go to malaria pandemic countries for people with HIV, as well as children under 4 years old.
Mosquito bite protection
The most reliable way to prevent the disease is to prevent mosquito bites.
It is impossible to protect yourself from insects by 100%, but recommendations such as:
Use of mosquito nets. They are installed in windows and doorways.
Use of network curtains. They need to be tucked into the mattress. In such a bed you can sleep without fear.
The use of repellents. These substances repel insects, but they cannot destroy them. Repellents are applied to clothing or skin. They are available in the form of sprays, aerosols, gels, creams, etc. You need to use such products in accordance with the available instructions.
The use of insecticides. These drugs allow you to destroy insects. They are available in the form of an aerosol. To kill mosquitoes, you need to spray them indoors, apply them to thresholds and mosquito nets. Half an hour after treatment, the room is ventilated.
Medical prevention of malaria
To prevent infection, you can take drugs that are used to treat the disease. However, when infected, an integrated approach is required. For prophylactic purposes, you can take Lariam, Quinine, Primakhin, Malarone, etc.
It must be remembered that these drugs are harmful to human health and have multiple side effects. They are taken 2 times a week, 14 days before the trip and 14 days after it.
Every person who arrives from a dangerous country in terms of infection must be examined. If an infection occurs, then within 3 years the patient will be registered with an infectious disease specialist.









