Contents

Magnesia is a magnesium salt of sulfuric acid, it is also known under the names “magnesium sulfate” and “epsom salt”. Magnesia has been used in medical practice for several decades and has been successfully used in many areas: in neurology, cardiology, gastroenterology, obstetrics and gynecology. Magnesia is very popular for weight loss and body cleansing.
Magnesium sulfate is also featured in the sports industry. All aspects of the use of Magnesia, reviews on the effectiveness of this drug, detailed and reliable information about the price, forms of release, dosage, possible side effects and contraindications are presented further on this page.
Instructions for the use of magnesia
Pharmacological action magnesium
The drug Magnesia (magnesium sulfate) has the following types of effects on the human body (in descending order of severity):
Laxative;
Choleretic;
Spasmolytic;
Tocolytic;
Vasodilator;
Analgesic;
Anticonvulsant;
Antiarrhythmic;
Diuretic;
Hypnotic.
The speed of the onset of the therapeutic effect, its type and duration depend on the method of taking Magnesia:
Orally – laxative and choleretic effect of the drug begins after three hours and lasts for six hours;
Intramuscularly – relaxation of smooth muscles occurs after one hour and lasts up to four hours;
Intravenously – the antispasmodic effect occurs almost instantly, but disappears after half an hour.
The laxative effect of magnesium sulfate is due to its ability to thin and increase the volume of feces, as well as promote an increased flow of water into the intestines. The choleretic effect is achieved due to a decrease in the muscle tone of the duodenum and simultaneous irritation of the mucous membrane lining it.
Since Magnesia is partially evacuated from the body by the kidneys, it has time to cause an influx of fluid to them and serve as a weak diuretic. There is a practice of using Epsom salts for poisoning with heavy metals and poisons: arsenic, mercury, lead. In this case, the ability of Magnesia to enter into chemical interaction with dangerous substances, bind them and quickly remove them from the body is useful.
Magnesium sulfate is actively used in physiotherapy for therapeutic baths and electrophoresis. Such procedures have a pronounced antispasmodic, analgesic, vasodilating and calming effect on the patient’s body. Topical application of Epsom salts as compresses and lotions helps to eliminate warts, heal wounds, and reduce psoriatic manifestations.
Sports magnesia is a special powder for treating the hands of athletes interacting with various equipment: barbells, crossbars, bars, spears, discs, rings. The fact is that magnesium sulfate has a pronounced anti-slip effect when applied to the skin of the hands, due to which sports equipment is securely fixed.
Indications for the use of magnesium
Magnesia is used to treat the following diseases and pathologies:

In neurology – epilepsy, cerebral edema, increased nervous excitability, encephalopathy, convulsive syndrome;
In cardiology – hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia (deficiency in the body of potassium and magnesium), ventricular arrhythmia, tachycardia;
In therapy – poisoning with salts of heavy metals, bronchial asthma, excessive sweating, urinary retention, warts, wounds and infiltrates;
In gastroenterology – biliary dyskinesia, constipation, cholecystitis;
In obstetrics and gynecology – preeclampsia and eclampsia, the threat of premature birth.
Contraindications magnesium Acute conditions: appendicitis, dehydration, intestinal obstruction, rectal bleeding, depression of the respiratory center, prenatal period in women. Chronic diseases: severe renal failure, hypotension (low blood pressure), bradycardia (decreased heart rate), atrioventricular blockade (impaired conduction of nerve impulses from the atria to the ventricles). |
Side effects of magnesium From the nervous system: depression or confusion, headache, muscle spasms, fatigue, irritability, anxiety, insomnia, depression. From the side of the cardiovascular system: hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmia, redness of the face, decrease in body temperature, sweating. From the gastrointestinal tract and excretory system: nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, polyuria, thirst. |
Interaction of magnesium with other drugs
Magnesia may interact with some other drugs, especially when injected or dripped:
Muscle relaxants – enhances their effect;
Anticoagulants, cardiac glycosides, phenothiazine – weakens their impact;
Nifedipine – causes severe muscle weakness;
Tobramycin and Streptomycin – reduces their antibacterial effect;
Ciprofloxacin – enhances the action of this antibiotic;
Tetracyclines – reduces absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and reduces their effectiveness.
Magnesium sulfate is absolutely incompatible with the following substances:
Arsenic salts;
Phosphates, carbonates and bicarbonates of alkali and alkaline earth metals (potassium, barium, strontium);
Tartrates (salts and esters of tartaric acid);
Salicylates (salts of salicylic acid);
Antibiotics of the lincosamide group (Lincomycin and Clindamycin);
Novocaine;
Hydrocortisone.
Magnesia treatment
How to take Magnesia inside?

For oral administration or rectal administration, a suspension is prepared from warm boiled water and magnesium sulfate powder.
The proportions depend on the age of the patient and the goals of treatment:
Magnesia laxative – 10-30 g of powder in half a glass of water (100 ml). Take the entire volume of the suspension once on an empty stomach, in the evening before bedtime or in the morning immediately after waking up. Do not eat anything until a bowel movement (usually after 1-3 hours). To enhance the laxative effect, you can additionally drink 2-3 glasses of warm boiled water;
Magnesia choleretic – 15-25 g of powder in half a glass of water (100 ml). Mix thoroughly and take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day immediately before meals;
Enema with Magnesia – 40-60 g of powder per 200 ml of water. Used to treat severe chronic constipation when oral magnesium sulfate has failed;
Duodenal sounding with Magnesia – 10-50 ml of a solution of 10% or 25% concentration is injected into the duodenum through a probe.
Magnesia intravenously and intramuscularly
If magnesium sulfate is used as a muscle relaxant or a drug that lowers blood pressure and normalizes the heart rate, it is advisable to inject. For injections and droppers, a ready-made 25% solution of Magnesia in ampoules is used. Intramuscular injections do not require a decrease in the concentration of the active substance, and for intravenous and drip administration, the drug is diluted with 5% glucose or saline, since a single entry of undiluted Magnesia into the bloodstream can cause an unpredictable violent reaction of the body and provoke complications.
Intramuscular injection of magnesium sulfate is accompanied by severe pain. Intravenous and drip administration of the drug is characterized by patients as quite tolerable, but at first a burning sensation is usually felt, spreading through the vein and gradually fading away. The medical staff performing the injection is obliged to warn the patient in advance about the need for careful monitoring of well-being after the administration of Magnesia. If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, redness of the face, fading in the chest, you should immediately inform your doctor about them. After removing the dropper with Magnesia, a control measurement of blood pressure and pulse is always performed.
Maximum dosage of Magnesia
For an adult, the maximum allowable single dose of magnesium sulfate for oral administration is 30 g. Under the condition of intramuscular or intravenous administration, the limit is 200 ml of a 25% solution per day.
Magnesia for children
The treatment of constipation with Epsom salts has no age-related contraindications, it is only necessary to correctly calculate the dosage of Magnesia for children. For adolescents over 14 years old, a suspension is prepared from 100 ml of warm boiled water and 15-30 g of magnesium sulfate powder, and to find out how much Magnesia can be given to a younger child, use the following formula.
With severe constipation, a child can be given an enema with Epsom salts. Depending on the age and weight of the baby, you will need 50 to 100 ml of Magnesia solution. A concentration of less than 20 g of powder for such a volume of warm water will not have a therapeutic effect when administered rectally, however, it is not necessary to put more than 30 g per half a glass of water, otherwise irritation of the delicate mucous membrane of the children’s intestines will occur.
Intramuscular or more often intravenous administration of Magnesia to children is used in case of critically high intracranial pressure or suffocation. The drug is even used to treat birth asphyxia in newborn babies, so we can once again say with confidence that Magnesia is safe and has no age-related contraindications.
Magnesia during pregnancy
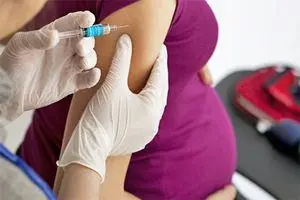
During pregnancy, magnesium is used as an effective muscle relaxant, that is, a means that relaxes smooth muscles and relieves spasms. Uterine hypertonicity is a common cause of spontaneous abortions and premature births. If the muscles of this organ are too tense, and their undulating contractions are observed, which are undesirable for early gestation and can lead to premature shortening of the cervical canal, dilatation of the cervix and fetal expulsion, the doctor may prescribe an intravenous or intramuscular injection of Magnesia to a pregnant woman. Injections are carried out strictly in a hospital under the close supervision of medical staff and with careful monitoring of the patient’s blood pressure and pulse.
Therefore, measures to relieve the increased tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus during pregnancy, including the use of Magnesia, must have good reasons: for example, a miscarriage or a history of premature birth, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, bloody discharge from the genital tract. Any pathological symptomatology during pregnancy should be carefully diagnosed, and almost every expectant mother receives an ultrasound report with the outdated wording “uterine hypertonicity” in our country, and often without any reason.
Another important limiting aspect of the use of Magnesia during pregnancy is that magnesium sulfate enters the placental circulation and can depress the respiratory and cardiac function of the fetus. The later the gestation period, the greater the volume of blood that penetrates through the umbilical cord from the mother to the unborn child, respectively, the stronger Magnesia affects his body. Therefore, magnesium sulfate is used in the last trimester of pregnancy only for special indications, and a few hours before the expected birth, it is completely forbidden to administer this drug to a woman.
Special mention deserves the diuretic effect of Magnesia, which is used by some gynecologists in the treatment of preeclampsia and eclampsia in pregnant women. In this case, the introduction of magnesium sulfate is carried out by drip, very slowly, under constant monitoring of the vital signs of the expectant mother and fetus.
Tubazhi with Magnesia

Tubage is a cleansing procedure that is designed to increase the flow of bile through the ducts, eliminate congestion in the gallbladder and prevent the formation of stones in it, that is, the development of cholelithiasis. Tubage can be done not only in a hospital, but even at home on a regular basis, but only as prescribed by the attending physician and after a thorough examination of the body. The indication for such treatment is biliary dyskinesia and bile stasis.
Contraindications for tubage:
Intestinal obstruction;
rectal bleeding;
Appendicitis;
Stones in the gallbladder;
Dehydration of the body;
low blood pressure;
hypermagnesemia;
Exacerbation of any chronic disease;
An infectious process in the body, accompanied by a febrile syndrome.
For tubage, Magnesia is used in powder form: 1 tablespoon in a glass of warm water. The mixture must be thoroughly stirred and drunk as a whole, and then lie on your right side, put a heating pad under the liver area and lie there for about an hour and a half. The procedure is considered successful if, after tubage, the first stool is greenish, that is, it contains bile. Treatment with Magnesia in the form of tubes can last up to 15 weeks in a row – one procedure every week, unless otherwise prescribed by the doctor.
Before starting therapy, you need to adjust your diet: exclude fatty, spicy, pickled, smoked and canned foods. The basis of the menu should be cereals (except for semolina, millet and pearl barley), soups, stewed vegetables, boiled or baked chicken or low-fat fish, in a word, easily digestible and healthy dishes. It is recommended to follow a sparing diet throughout the course of treatment, but especially carefully on the day when the tubage procedure is performed. After it, doctors advise eating a little grated carrot with an apple or a salad of boiled beets with vegetable oil.
Magnesia for colon cleansing

Colon cleansing with Epsom salts is another popular home procedure. However, it can be done, like tubage, only after consulting a doctor. As we mentioned above, magnesium sulfate is irritating to mucous membranes and is not suitable for regular use. Therefore, it is impossible to clean the intestines with Magnesia more than once a month. Strictly speaking, two or three series of such procedures per year are enough for a person to maintain the intestines in a normal state with a tendency to constipation.
With age, in all people, even those who do not have problems with stools, hard stones – fecal stones – stick and accumulate on the walls of the colon and rectum. They impede the passage of feces through the intestines and serve as a constant source of toxic substances and decay products that enter the bloodstream. All this leads to the development of allergies, spoils the complexion and provokes constipation. To eliminate fecal stones, they need to be softened, and magnesium sulfate is the best suited for this, which foams the shaft, increases it in volume and quickly removes it from the body.
Bowel cleansing Magnesium is carried out using an enema: 100 g of powder is taken per 30 ml of warm boiled water, mixed thoroughly and the resulting solution is injected into the anus, and then lie on your side, bending your legs under you, until the urge to defecate becomes expressed. Complete emptying of the bowels occurs about an hour after the enema with Magnesia. Purification is carried out in a short course, 2-5 procedures per week (the exact amount is determined by the doctor based on the diagnostic data of the patient).
If we consider the effectiveness of cleaning the intestines with Magnesia, the reviews are mostly positive – the state of health improves, the stool normalizes, there are no side effects. But as for the safety of this method of cleansing the body, doctors disagree: representatives of the “old school” actively recommend Magnesia as a laxative and an agent for enemas, and young specialists talk about the too aggressive effect of magnesium sulfate on the intestinal walls and offer other, more modern and sparing drugs.
Magnesia for weight loss

Fighting excess weight with laxatives is not a good idea. When the food eaten leaves the body earlier than it is envisaged by physiology, a person not only does not extract energy from it, but also loses the most important useful substances: vitamins, minerals, amino acids – they simply do not have time to be absorbed in the intestines. Therefore, Magnesia for weight loss, reviews of which can often be found on the net, is one of the dubious, and sometimes simply dangerous methods of correcting excess weight. Especially given the duration of this process and the detrimental effect of magnesium sulfate on the mucous membranes.
However, when obesity is accompanied by severe constipation (and this happens very often), the use of Magnesia for weight loss and solving problems with stool is fully justified, since these two aspects are closely interconnected. The solution of magnesium sulfate in this case is prepared in exactly the same way as described above in the section “Treatment with Magnesia”. But the limitations of this therapy are the same: it should not be carried out on a regular basis.
There is another way to use Magnesia to combat extra pounds – therapeutic baths. Such procedures have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin, promote the evacuation of water molecules from subcutaneous fat, have a calming effect on the nervous system and simply improve mood.
To prepare a therapeutic bath, you will need:
Magnesium – 4 packages of 25 g each;
Table salt – 0,5 packs;
Sea salt – 500 g.
Dissolve the listed ingredients in a bath of hot water (but not more than 42 ° C) and lie there for 25 minutes, then dry yourself dry and apply a moisturizing lotion to the skin. You can repeat these procedures 2-3 times a week. As an independent weight loss technique, baths with Magnesia are ineffective, but in combination with diet and exercise they give a good effect (mainly cosmetic, as a means of combating cellulite).
Contraindications to taking therapeutic baths with Magnesia:
Arterial hypertension of the 3rd degree;
Heart failure;
oncological diseases;
Infectious and inflammatory processes;
Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and other endocrine disorders;
Epilepsy and some other nervous pathologies;
Any chronic disease in the acute stage.
Physiotherapy with Magnesia
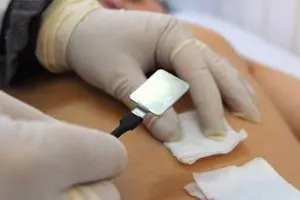
Magnesia in physiotherapy is used in the following medical procedures:
Electrophoresis – a solution of magnesium sulfate is used at a concentration of 20-25%. Methods can be different, depending on the diagnosis, while the drug penetrates deeply into soft tissues and blood vessels, increases blood flow, neutralizes congestion, lowers blood pressure, relaxes muscles and normalizes the psycho-emotional background;
Compresses – sterile gauze is impregnated with a 25% solution of Magnesia and applied to the sore spot for 6-8 hours, and then a greasy cream is applied to the skin to eliminate the drying effect of the drug. Such compresses promote wound healing, resorption of subcutaneous infiltrates after injections, elimination of warts and a decrease in the intensity of psoriatic manifestations on the skin;
Healing baths – magnesium sulfate powder is dissolved in warm water and the patient is placed there for 15-20 minutes, while the heart area should not be immersed in the bath. The scope of this technique is very wide: it is hypertension and tachycardia to increased nervous excitability and post-traumatic syndrome. Baths with magnesia eliminate spastic phenomena and may be useful even for convulsions in pregnant women.
Mineral water “Magnesia”

Such water is natural, it is extracted from wells, like many other types of medicinal table mineral waters. “Magnesia” is characterized by a high content of bicarbonate and magnesium sulfate, which is why it is called so. It is recommended to drink it to people who have a deficiency of magnesium in the body.
In addition, mineral water “Magnesia” is indicated for the following categories of patients:
With gastrointestinal diseases – gastritis, pancreatitis, constipation, dysfunctions of the liver and biliary tract;
With nerve problems – convulsions, insomnia, chronic fatigue syndrome;
With diseases of the genitourinary system – pyelonephritis, nephropathy, urinary retention;
with endocrine disorders – for example, with obesity;
With bone pathologies – osteoporosis, demineralization of bone tissue, caries.
It is possible to take Magnesia mineral water regularly for therapeutic purposes only after consulting a doctor and passing tests, because if a person has hypermagnesemia (an excess of magnesium in the body), drinking such water in large quantities will aggravate the situation and result in serious complications. There is a long list of diseases of various etiologies in which Magnesia mineral water is not recommended or is completely contraindicated, so if you have any health problems, be sure to consult your doctor before drinking any medicinal mineral water.
Sports Magnesia

If we talk about Magnesia in sports, then this is not at all a drug for ingestion or injection, but a special powder for anti-slip hand treatment. Magnesium sulfate is perfectly distributed over the skin and forms the thinnest layer that quickly absorbs sweat and prevents sports equipment from slipping out of the hands or falling of an athlete hanging on a projectile (for example, on a bar or rings). These properties of Magnesia are very relevant for gymnasts, weightlifters, tennis players and representatives of many other sports, as well as for mountaineers who make long mountain climbs.
Sports magnesia is either a ready-made powder in bags, or rectangular briquettes or balls that are easily crushed in your hands. It should be understood that this product may contain additional components that enhance the anti-slip effect, extend the life of use, or hold the magnesium sulfate in a given form. Therefore, it is unacceptable to take sports Magnesia inside for therapeutic purposes.
Reviews about Magnesia

The opinion of doctors about the use of Magnesia as a laxative and choleretic agent is currently predominantly negative, since many more gentle drugs suitable for regular use have appeared in the medical arsenal. The bad reviews of doctors about Magnesia are centered around its detrimental effect on the mucous membranes in case of ingestion or rectal administration. However, as an antispasmodic, antiarrhythmic, hypotensive and sedative, Magnesia is still relevant, but for such purposes it is administered intramuscularly, intravenously or drip.
As for the impressions of patients from treatment with Magnesia, the reviews about the drug are mostly positive, since magnesium sulfate is very effective for constipation and bile stasis, while it compares favorably with an affordable price from other laxatives and choleretic agents. Preparing a solution of magnesium sulfate is very simple, which cannot be said about the process of drinking – Magnesia has a very specific bitter-salty taste, because of which, according to many people, taking Magnesia inside becomes torture. Sensations in the abdomen may also not be the most pleasant: sometimes there is a burning sensation and cramping pain.
Good reviews about magnesia for weight loss should be considered only as a subjective opinion of people who deliberately harm their health in order to improve their appearance (moreover, they do it to no avail). The same applies to baths for weight loss with Magnesia – women’s reviews confirm that such procedures in themselves do not allow you to get rid of extra pounds. In addition, a solution of magnesium sulfate dries the skin very much, and in some girls it even causes irritation, redness, peeling and a rash.
Most people who search the web for reviews of Magnesia do this in order to understand if they will have to experience discomfort from intramuscular injections, and is it true that magnesium sulfate can almost pass out when administered intravenously? We answer: if the dosage and concentration of the solution are chosen correctly, and the injection is performed professionally, there can be no “fire” in the veins, sudden dizziness or fainting. Does it hurt to give an injection with Magnesia in the ass? Yes, this is a rather painful procedure.
Magnesium: price and release form
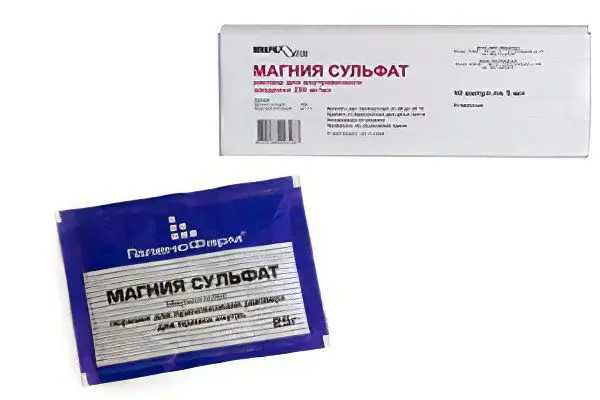 Through the pharmacy network, magnesium sulfate is sold in several medicinal forms at the following price:
As for sports Magnesia, the price depends on many factors: the form of release (powdered, briquettes, balls), the country of origin, the weight of the package. Domestically produced Magnesia powder will cost an athlete 200-250 rubles for a 150 g container, about the same is the cost of a plastic jar with three balls. |











