Contents
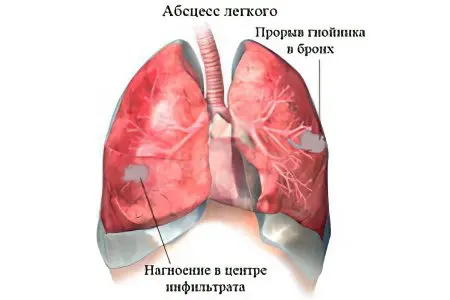
Inflammation of lung tissue of a non-specific nature, provoking its melting in the form of a focus with clear boundaries and the formation of cavities with purulent-necrotic contents, is a lung abscess. It occurs as a result of an infection that causes the formation of necrotic tissue and the accumulation of pus. In most cases, it occurs due to the ingestion of the contents of the oral cavity into the lungs during a person’s stay in an unconscious state.
Treatment of pathology is carried out with antibacterial drugs from the group of beta-lactam antibiotics. In 7-10 patients out of a hundred, after 2 months from the onset of the disease, a lung abscess becomes chronic. Approximately 5% of cases of the acute form of the disease and 15% of all cases of chronic lung abscess are fatal.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
Pathogenic microorganisms enter the lungs through the bronchogenic route. Extremely rarely, an abscess in the lungs is provoked by pathogens that have got there by the hematogenous route through the circulatory system.
Causative agents of the disease:
Anaerobic bacteria – gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli;
cocci (staphylococcus, streptococcus);
Aerobic bacteria – gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli;
Mushrooms;
Parasites (causative agents of echinococcosis, amoebiasis, paragonimiasis).
Causes of an abscess:
Aspiration of secretions from the oral cavity in patients with a history of gingivitis, tonsillitis, periodontal disease, who do not follow the rules of oral care, while taking alcohol, drugs, sedatives, opioids.
Ingestion of oral contents into the lungs in elderly patients and in patients with neurological pathologies that provoke a helpless state.
Complication of necrotizing pneumonia in the form of seeding of the lungs with septic emboli, as a result of purulent thromboembolism, intravenous drug injections. The hematogenous route of infection provokes multiple lung abscesses.
chest injury;
Infection of the lung as a result of its infarction due to a pulmonary embolism.
Aspiration of vomit or foreign bodies.
bacteremia (sepsis).
The presence of a cancerous tumor of the lung, Wenger’s granulomatosis, nodular silicosis in history.
The pathogenesis of the acute form of the disease
At the beginning of infection, the lung tissue undergoes inflammation, a limited infiltrate is formed. With the development of the disease, the infiltrate from the center to the periphery undergoes purulent fusion. A cavity lined with granulation tissue is formed, an area of pneumosclerosis is formed.
The area that has undergone necrosis is transformed into an abscess. If it breaks into the bronchus, the purulent contents of the abscess are coughed up. The remaining cavity is filled with liquid and air. With an unfavorable outcome, when the purulent process becomes chronic, the infection in the cavity is maintained for a very long time, the inflammatory focus is not cleared.
Complications of chronic lung infection:
pyopneumothorax;
sepsis;
pulmonary bleeding;
bacteremic shock;
pleural empyema;
respiratory distress syndrome.
Pulmonary bleeding occurs as a result of damage to the bronchial arteries. In this case, from 50 to 500 ml of blood is released. Signs of pulmonary hemorrhage – coughing or spontaneous sputum with an admixture of foamy scarlet blood. The patient becomes pale, he has a rapid pulse and a decrease in blood pressure. In severe cases, bleeding of the bronchial arteries causes the death of the patient.
Classification of lung abscesses
When classifying a disease according to etiology, attention is paid to the causative agent of the pathology.
According to pathogenesis, they are guided by the ways of infection:
bronchogenic,
Traumatic,
Hematogenous.
According to their location in the lung tissue, they are distinguished:
Central abscess;
peripheral abscess.
In count:
Unit,
multiple abscess.
A lung abscess may be in one or both lungs (bilateral).
Symptoms of a lung abscess

Before the breakthrough of the abscess into the bronchi, the following symptoms of pathology are distinguished:
pouring sweat;
Severe hyperthermia of high values;
Signs of respiratory failure (inability to take a deep breath, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing);
Dry cough;
Pain in the chest when coughing, occurs on the affected side;
When listening with a phonendoscope, weakened hard breathing, muffled heart sounds are distinguished;
With percussion – a shortening of the sound over the abscess area;
skin cyanosis;
The desire of the patient to take a forced position;
Frequent arrhythmic pulse;
Low blood pressure, with shock – a sharp drop in blood pressure.
After the breakthrough of the abscess into the bronchial cavity, the patient begins an attack of coughing, ending with the release of a large amount of purulent sputum with an unpleasant odor. On average, from 100 to 150 ml is released.
Symptoms after an abscess rupture:
Decrease in temperature;
Improvement of the general condition;
When listening – fine bubbling rales;
With percussion – shortening of the sound over the abscess area.
After 1,5-2 months, the symptoms of the disease do not appear. If the drainage of the lung is difficult, the symptoms of the inflammatory process remain. The patient hardly allocates fetid sputum when coughing, he has the following characteristic symptoms:
Dyspnea;
pouring sweat;
Chills;
The last phalanges of the fingers take the form of “drum sticks”;
The nails on the fingers become like “watch glasses”.
Expectorant sputum, when kept in a container, is divided into fractions:
The lower one is a thick dense layer of tissue detritus;
Medium – liquid pus with saliva;
Upper – foamy serous fluid.
During the day, the patient can stand out up to a liter of sputum. Its quantity depends on the volume of the cavity formed by the abscess.
Diagnostics
The most informative method for diagnosing a lung abscess is radiography. Before the breakthrough of the abscess, the image shows an infiltrate in the lung tissue, after the breakthrough of the purulent formation, a bright spot with a horizontal level of fluid is fixed. This study will help to make an accurate diagnosis and differentiate it from other pulmonary diseases.
Additional instrumental methods:
MRI, CT scan of the lungs – is performed if lung cavitation is suspected or if the bronchi are compressed by a large formation;
Spirography;
Bronchoscopy – allows you to exclude malignant tumors of the lung;
Picfluometry;
ECG.
To exclude pleurisy when similar symptoms appear, a pleural puncture is performed.
Laboratory diagnostics – methods and indicators confirming the disease:
Complete blood count – at the first stage, leukocytosis, an increased level of ESR, a shift in the leukocyte formula, at the second stage, the indicators are close to normal, when moving into the chronic stage, there are signs of anemia, the ESR level is stable.
Urinalysis – microhematuria, albuminuria, the presence of protein;
Biochemical analysis of blood – an increase in the amount of fibrin, haptoglobins, ?-globulin.
General analysis of sputum – the presence of atypical cells, fatty acids, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, elastic fibers;
Sputum bacterioscopy – identification of the pathogen;
Bacterial culture of sputum – determination of the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs.
According to the results of the diagnostic examination, the doctor determines the tactics of treatment, focusing on the severity of the patient’s condition.
Treatment of lung abscess
This disease is treated in stationary conditions in the pulmonology department. In the acute stage, the patient is shown bed rest. Several times a day, for 10 to 30 minutes, it is placed in a draining position to stimulate the outflow of sputum.
Possible manipulations and medical procedures:
Treatment with antibiotics that are effective against the type of pathogenic bacteria that have affected the lung – Clindamycin, Ampicillin-sulbactam, Metronidazole, Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, Amoxicillin-clavulalate;
Blood transfusion, autohemotransfusion – activates the patient’s immunity;
Appointment of antistaphylococcal globulin and gamma globulin if necessary;
Bronchoalveolar lavage – washing the abscess cavities with antiseptics;
Transthoracic puncture on large peripheral abscesses;
Tracheotomy and suction of sputum in debilitated patients;
Percutaneous or surgical drainage of abscesses;
Drainage of concomitant empyema;
Resection of the lung with the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, multiple abscesses, gangrenous tissue damage.
The average duration of treatment for a lung abscess is 3-6 weeks, with large formations and multiple lesions, it is extended to 6-8 weeks.
Chronic lung abscess
The causative agents of the chronic form of the disease are the same as in the acute form of the pathology – fungi, gram-negative and gram-positive bacilli, various strains of staphylococcus.
Diagnosing the transition of the disease to a chronic form is not easy, because its symptoms can be minimal, be in remission. Improving the methods of diagnosis and treatment of acute lung abscess led to a decrease in the number of its transitions to the chronic form.
Clinical manifestations of the chronic form:
Symptoms of intoxication (headache, weakness, fatigue);
Frequent cough;
Pain in the chest on the affected side;
Feeling short of breath;
Violation of the work of other organs of unknown etiology.
Reasons for the transition of the disease to a chronic form:
The presence of multiple or too large abscesses;
With ineffective drainage, a fibrous capsule was formed, covered with connective tissue, which makes it difficult to reduce the abscess cavity;
The presence of sequesters in the cavity of the abscess, preventing proper drainage;
After treatment, a dry residual cavity formed;
Reduced immunity, inadequate response of the body to treatment;
The presence of pleural adhesions in the lung that prevent the destruction of the abscess cavity.
The presence of a chronic inflammatory process negatively affects the functioning of the body. Chronic hypoxia and intoxication with the waste products of pathogenic bacteria, imbalance in the activity of the endocrine and nervous systems leads to dangerous consequences:
Formation of pulmonary hypertension;
Violation of microcirculation in the tissues of various organs;
The appearance of immunodeficiency;
Violation of protein and energy metabolism.
Chronic lung abscess can be complicated by pulmonary hemorrhage, development of sepsis, secondary bronchiectasis, parenchymal amyloidosis.
Treatment of chronic abscess. The only effective way of treatment is surgery to remove the cavity with pus from the lung. Since patients are significantly weakened, careful preparation for surgery is required.
Preparation methods:
Sanitation of the purulent cavity with antiseptics;
Fighting the consequences of intoxication;
Correction of the general condition of the patient’s body to increase immunity and reserve capabilities.
After surgery, it is important to pay special attention to the rehabilitation of the patient to prevent postoperative complications.
During resuscitation, special attention is paid to the restoration of blood circulation and respiratory function, the prevention of infection. After straightening the operated lung, restoring normal blood counts, and the patient being able to stand up and walk on his own, we can assume that the operation was completed successfully.
To prevent the formation of a lung abscess, it is necessary to treat diseases of the respiratory system in a timely manner, sanitize the oral cavity and foci of chronic infection.









