Contents
The inability to smell is called anosmia. This violation can indicate serious diseases and significantly reduce the quality of life of a person.
One of the dangers of anosmia is that when harmful substances enter the nose, a person does not have a natural protective reaction of the body in the form of sneezing. This leads to the fact that toxins penetrate further and cause serious damage to health. To find out the cause of the loss of smell, you need to visit a specialist.
Description of the disease

Lack of smell is a problem that affects the state of the body as a whole. So, the pleasant aromas of food stimulate the activation of the digestive tract, start the production of gastric juice. If a person does not smell the dishes, then the digestive system as a whole suffers.
With anosmia, the nasal receptors stop responding to stimuli. The brain does not receive impulses and does not recognize odors. When the problem lies in diseases of the central nervous system, then the receptors, on the contrary, send signals to the brain, but it refuses to perceive them. The third mechanism for the implementation of anosmia is that the receptors of the nose recognize odors, send them to the brain, but on the way to it they are blocked.
Types of disease

There are several types of olfactory impairment:
Hyposmia. In this case, the sense of smell is preserved, but it is very weak. A person has the ability to recognize only some smells.
hypersomnia. In this case, the sense of smell will be heightened.
Cacosmia. With this type of disturbance, a person considers pleasant odors unpleasant.
Anosmia. This violation is characterized by a complete loss of smell. Pathology develops against the background of ARVI or after a stroke.
In a person with impaired olfactory function, the quality of life in general suffers. This leads to the fact that he becomes irritable, may become depressed.
Complete or partial loss of smell can be either congenital or acquired. If a violation occurs in a person from the moment of his birth, then the reason is reduced to the underdevelopment of the respiratory system. Most often, the baby will be diagnosed with other pathologies of the skull and nose.
Acquired anosmia can develop due to damage to the central nervous system, or after a negative impact on the nasal area.
Reasons for the lack of smell
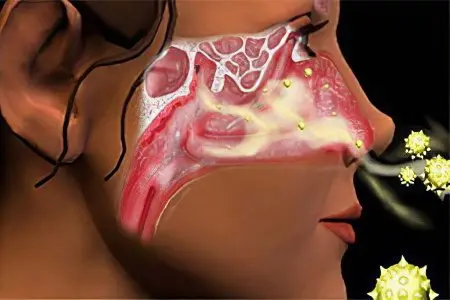
Causes of peripheral anosmia can be as follows:
Respiratory causes. A person inhales air with aromatic molecules, but they do not reach the receptors of the nose. A similar situation is observed in people with hypertrophy of the tissues of the nasal cavities, with curvature of the nasal septum, with polyps and adenoids. In general, any neoplasms growing in the nasal cavity can lead to a violation of the sense of smell.
functional reasons. These include infectious and allergic rhinitis. A person does not feel odors due to swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose. Sometimes a similar situation develops in people suffering from hysteria or neurosis. After treatment, the sense of smell is completely restored.
Aging of the body. Smells are felt by older people worse, as they have a gradual atrophy of the mucous membranes of the nose. Therefore, most aged patients complain to doctors about dryness in the nose.
Pathology of the analyzer of smell (essential anosmia). The reasons for its development: a burn of the nasopharynx, atrophy of the epithelium of the nasal mucosa, inflammation of the mucous membranes, intoxication of the body.
Peripheral anosmia is indicated by the simultaneous deterioration or disappearance of not only smell, but also taste.
Central Anosmia can develop against the background of the following diseases:
Cerebral circulation disorder.
Received TBI.
Encephalomyelitis.
Meningitis.
Arachnoiditis.
Alzheimer’s disease.
Etmoiditis.
When anosmia develops due to disturbances in the work of the cortical centers of smell, the person feels the smell, but cannot understand its nature.
Why does the sense of smell disappear with a cold?

Viral infection. The sense of smell is always reduced in people with a respiratory infection. Symptoms include runny nose, sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion.
Causes of impaired sense of smell:
Mucus envelops the walls of the nose and does not allow them to contact normally with air.
Viruses themselves are capable of blocking the work of nasal receptors.
Sinusitis. This disease is manifested by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the sinuses. Most often, it develops against the background of an untreated cold. A person’s body temperature rises, the nose remains stuffy, severe headaches occur. If treatment is not started in time, then the multiplication of bacteria will lead to the development of a purulent process. Bacteria have a destructive effect on the epithelium in which olfactory receptors are located, so a person ceases to smell.
Overdose of nasal drops. It is not recommended to use vasoconstrictor drops more than 4 times a day. The interval between their introduction into the nasal passages should be at least 4 hours. This rule is true for the acute stage of the disease. However, not all people with a runny nose adhere to this recommendation. Frequent use of nasal drops leads to the fact that the muscular layer of the vessels of the nose ceases to work normally, tissue nutrition deteriorates and the person loses his sense of smell.
Hormonal disorders. Sometimes hormonal fluctuations in the body become the cause of a violation of the sense of smell. Anosmia can develop during pregnancy, menstruation, and when taking oral contraceptives. After stabilization of the hormonal background, everything returns to normal.
Allergy. With the development of allergic rhinitis, a person loses his sense of smell. This phenomenon is temporary and after the allergy symptoms can be stopped, the ability to recognize odors will return. To cope with an allergic reaction, you will need to take antihistamines.
Anatomical changes in the nasal cavity
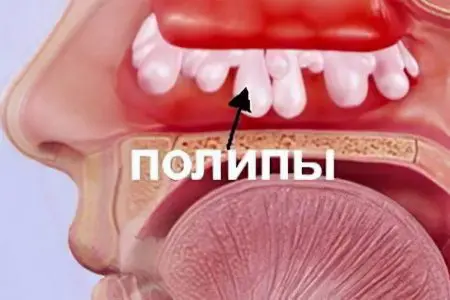
The sense of smell can significantly deteriorate or even disappear with such violations as:
Growth of polyps or adenoids.
Curvature of the nasal septum.
Tumor neoplasms.
Nasal hypertrophy.
To bring the sense of smell back to normal, you need to eliminate the existing defects. Most often, these patients require the help of a surgeon.
Poisons and chemicals. Problems with smell occur in people who, due to professional duties, are forced to come into contact with toxic substances. These include: paints and varnishes, products of the oil industry, acid fumes, etc. Working in hazardous industries threatens with a complete loss of smell.
Symptoms of a lack of smell

Symptoms of anosmia are most often mild. Often people completely ignore them, considering the violation of smell as something insignificant and not requiring attention. In many ways, the symptoms of pathology depend on the cause that provoked its development. The main manifestations of the violation can be identified as follows:
Difficulty in nasal breathing, swelling of the mucous membranes, secretion from the nasal passages. These symptoms indicate rhinitis.
If a violation of smell develops after a recent acute respiratory viral infection or a cold, then this indicates the so-called essential anosmia. It is characterized by a violation of the replacement of the olfactory epithelium with the respiratory one.
If a person smells, but cannot verify them, then with a high degree of probability the reason lies in disturbances in the work of the central nervous system.
Temporary loss of smell is observed in trauma. Sometimes the resulting damage to the nasal structures leads to a distortion of the sense of smell.
Dryness of the nasal passages, the appearance of crusts in them and a weakening of the sense of smell indicate atrophic processes. Often this problem occurs in older people.
With the deterioration of the olfactory function of the nose, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the well-being of a person, but also to the pathologies that have recently been transferred.
Diagnosis of anosmia and hyposmia

To find out exactly the cause of the deterioration of the sense of smell, you need to consult a doctor. To begin with, the doctor will conduct a test aimed at recognizing smells and tastes by the patient. To do this, he will offer him to smell various substances that have a bright aroma.
To establish the cause of the violation, a thorough examination of the nasal cavity, clarification of information about previous nasal injuries, diseases of an allergic and infectious nature may be required. Sometimes it is necessary to examine the state of the nervous tissue responsible for the innervation of the maxillofacial muscles and respiratory organs.
Other diagnostic methods include:
Olfactometry. The procedure is carried out using a special device called the Zwaardemaker olfactometer. The study allows you to determine the sensitivity threshold of olfactory receptors and their ability to recognize odors.
Rhinoscopy. This procedure is aimed at assessing the condition of the nasal cavities, nasal septum and mucous membranes of the organ. Diagnostics is carried out using a rhinoscope.
Nasal mucus analysis. Sometimes a chronic infection becomes the cause of a violation of the sense of smell. Its causative agent can be identified with the help of the study.
MRI of the brain. It is done when a severe pathology is suspected, the doctor gets the opportunity to visualize the changes that occur in his lobes. First of all, the specialist is interested in the frontal lobe of the brain. If a violation is detected, the patient is referred for a consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
CT scan of the nasal cavity. This study makes it possible to visualize neoplasms and clarify their nature.
After establishing the cause of the violation of smell, the patient is prescribed treatment.
Which doctor should I go to?
In case of violation of the sense of smell, you need to contact an otolaryngologist. This doctor will interview the patient, perform an external examination, prescribe the necessary tests. After interpreting the data obtained, the specialist will prescribe treatment. If the pathology is hidden in the disruption of the brain, then the patient is referred for a consultation with a neuropathologist and a neurosurgeon.
How to restore the sense of smell?

If a person does not smell for a long time and does not know the cause of the violation, then it is necessary to go to an appointment with an otolaryngologist. You should not try to deal with the problem on your own. Only a doctor will help restore the sense of smell.
The main directions of treatment:
Eliminate the effect of toxins on the body. Lifestyle modification with quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.
Taking drugs that allow you to cope with the existing pathology.
Physiotherapy treatment.
Surgery.
Medications
The right to choose a particular drug remains with the doctor.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
Means for washing the nose. They can be represented by sea water or saline. (more: how and with what to wash the nose?).
Vasoconstrictor drugs – these drugs can reduce the severity of edema and get rid of nasal congestion.
Drugs for relief of allergy symptoms. (more about 1st, 2nd and 3rd generation antihistamines).
Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal agents. The specific drug is selected depending on the type of infectious agent.
If the patient has a pathology associated with the central nervous system, the neurologist selects the drugs on an individual basis.
[Video] If the sense of smell is gone and I do not feel the smells and taste of food. Recovery practice:
Prevention

In order to prevent loss of smell, infectious diseases must be avoided. It is important to maintain the normal functioning of the nervous and immune systems.
The main recommendations of experts:
Maintaining a stable emotional background, avoiding stressful and conflict situations.
Adherence to daily routine.
Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition.
Taking vitamins.
Performing good and regular nasal hygiene.
Moisturizing the mucous membranes with saline solutions and natural oils (peach or almond).
Control of humidity in the room, regular ventilation.
Perform daily wet cleaning.
Refusal to visit places with a significant congestion of people. This recommendation is especially relevant during the period of mass outbreaks of infections.









