Contents
In nature, there are more than one and a half hundred varieties of loosestrife. These perennials are imported from North America. Purple loosestrife is one of the representatives of the primrose family. The culture is used to decorate landscape design, in group plantings.
Botanical description of the species
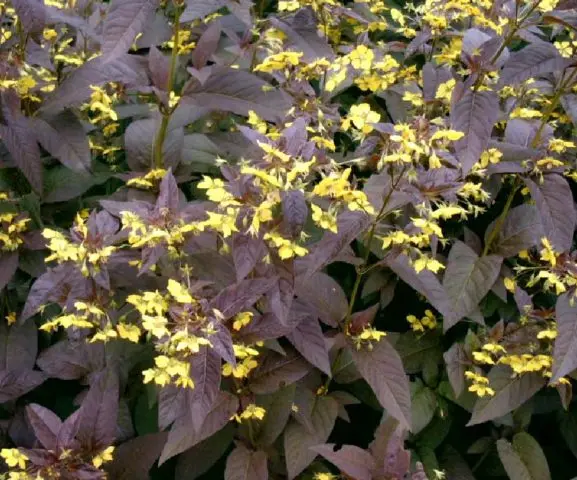
This is an upright, branched culture, the height of which does not exceed 1 m. The leaves and stems of purple loosestrife in the sun are painted in maroon, dark purple, chocolate colors, and in the shade they become brown-green.
Shoots branch from the base, have the shape of a tetrahedron. The leaf plate is back ovoid, up to 12 cm long, the surface is smooth.
Inflorescences are located at the ends of the shoots and in the axils of the apical leaves. Bright, lemon-colored petals favorably emphasize the deep wine color of the ground part of the plant. The flowering period begins in August, ends in September.
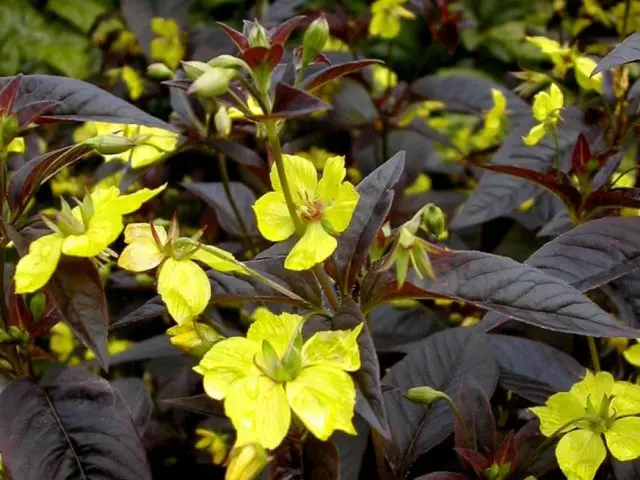

The flowers of the plant are small, their middle is red, the petals are bright yellow, collected in sparse inflorescences.
As soon as the flowers crumble, boxes appear on the shoots, tightly stuffed with small seeds.
The culture grows rapidly, the bushes become lush, densely leafy. They contrast well against the background of green plants.
At present, several new ornamental varieties have been bred on the basis of loosestrife. All of them are used for landscaping open areas.
Popular varieties of loosestrife ciliary:
- Firecracker – the culture is distinguished by bright, purple leaves;

In summer, the ground part of the purple plant turns purple
- Lysimachiaatro purpurea – black-purple loosestrife, blooms with maroon spike-shaped apical racemes;

Wine-colored ears contrast beautifully with silver-green leaves
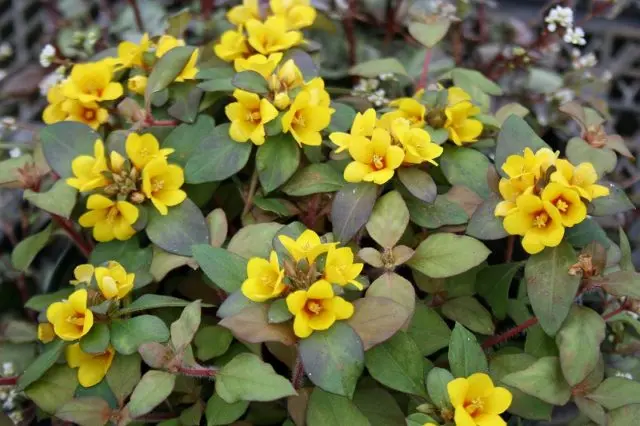
- Lysimachia congestiflora – crowded loosestrife, low culture (up to 30 cm) with light green rounded leaves and yellow flowers.

The flowers have a delicate fragrance that attracts butterflies.
All members of the family grow rapidly, surviving their neighbors. This is taken into account in group plantings, autumn pruning is able to temporarily stop the growth of the culture.
Application in design
Purple loosestrife is one of the most commonly used plants in landscape design. Its popularity is due to rapid survival, undemanding to soil and watering, and rapid growth.
The purple loosestrife has a superficial root system, it can be easily grown in shallow planters, flowerpots, on lawns and decorative stones.
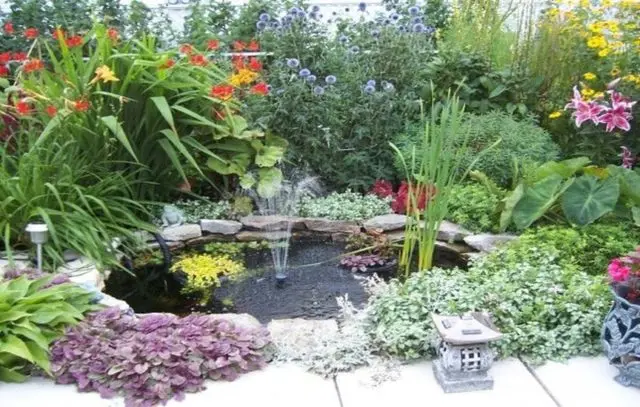

The culture looks good on the banks of artificial reservoirs, the supports of walls and beams are covered with plants
In rock gardens, flowerbeds, lawns, mixborders, purple loosestrife acts as a bright ground cover plant. The plant looks especially good in rocky terrain.

Often the culture is used as an addition to garden paths or a fence for flower beds.
The loosestrife goes well with coniferous crops.
Features of reproduction
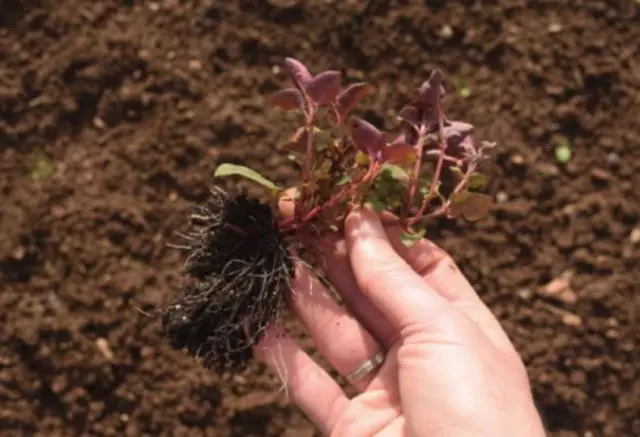
Purple loosestrife reproduces by vegetative and seed methods. To propagate the culture, cuttings are grown, the rhizome is divided, or the shoots are separated.
For reproduction, strong bushes with a strong root system are taken, the height of which is at least a quarter of a meter. A good time for dividing the bushes is early spring or autumn.
The mother bush is dug up, the children are separated from it, the rhizome is divided into 2-3 parts with a sharp knife.
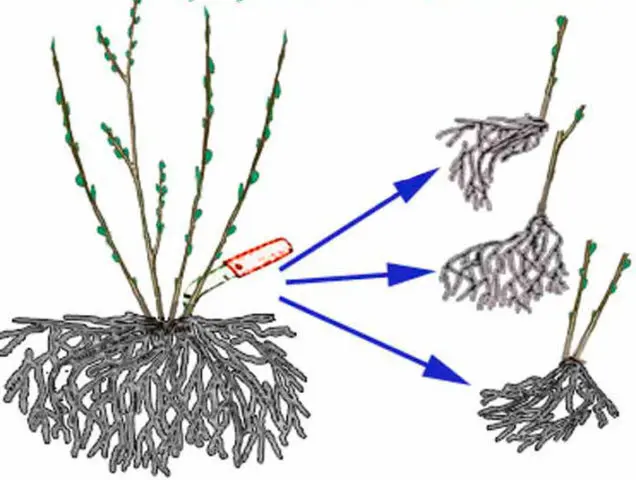
Each such division should have stems and strong root processes.
New plants are planted in holes, half a meter apart. Young seedlings bloom a few months after rooting.
Reproduction of loosestrife by seeds is a laborious method. Seed material requires a two-month stratification before laying in the ground.

For hardening, the seeds are placed in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf.
After they can be germinated in the ground. The resulting seedlings bloom only 3 years after planting in the ground.
If autumn planting is planned, it is not necessary to stratify the seeds. They are immediately embedded in the ground, where in winter they will naturally harden.
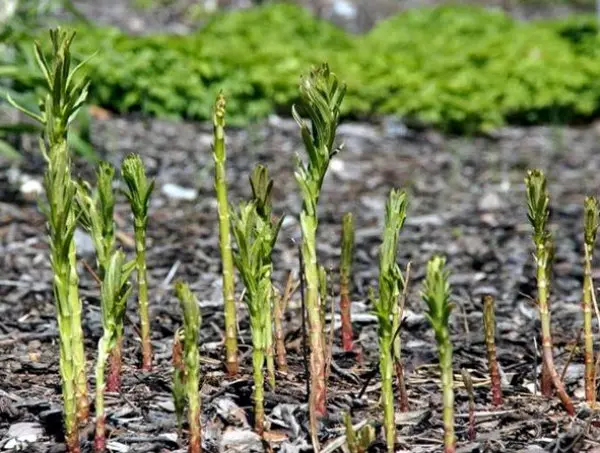

In the spring, friendly young shoots of purple loosestrife will appear
Planting and caring for loosestrife
This is an unpretentious plant, the main condition for good growth of which is an abundance of sunlight. This important factor is taken into account when preparing seedlings for planting.
Recommended dates
The seeds of the plant are sown in the ground, starting in June and before the onset of cold weather. Young growth or rhizome is separated from the mother bush and rooted in the summer, as soon as the plant gets stronger.
Site selection and soil preparation
Purple loosestrife grows well in open, well-lit areas. The land should be fertile, well loosened. The close occurrence of groundwater is only welcome.
The composition of the soil does not matter, only a high content of clay in the soil is undesirable.
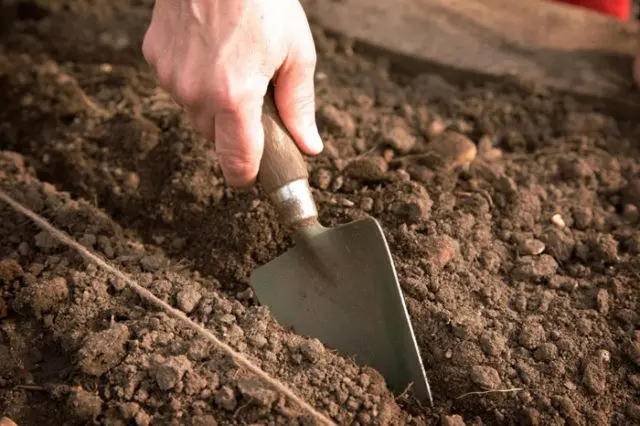

Before planting, the soil is dug up, loosened
After loosening, rotted manure is introduced, fertilizer is evenly distributed.
Landing algorithm
After preparing the soil, proceed to planting. To do this, dig shallow holes (about 10 cm), the distance between them is 50 cm.
Landing:
- A thin layer of humus is laid out at the bottom of the planting hole.
- The seedling is placed in the center.

Root processes are straightened in the hole, covered with loosened soil
- Then the earth is rammed, the seedling is watered abundantly.
After planting, the soil moisture is monitored, as soon as the water evaporates, the plant is watered again.
Peculiarities of growing
Purple loosestrife is a culture that grows well without human intervention. In order for the flower to retain its decorative qualities, it needs additional care.
Watering in the summer should be frequent and plentiful. The soil near the stems should not dry out. Watering is especially important on dry days.
You can determine the lack of moisture by dry, yellowing leaves. Such a plant is watered often and plentifully. An excess of moisture does not harm this culture.
Purple loosestrife requires regular weeding and loosening of the soil. Weeds are removed often, after pushing the soil. Do this carefully, since the rhizome of the plant is located almost on the surface.
If the bushes grow on fertile soil, they do not need fertilizers. When planting a flower on depleted soils, various complex compositions are used for flowering crops. They are watered with purple loosestrife 2 times a month, during the entire growing season. In late autumn, humus is introduced into the soil in a flower bed.
Flower pruning is carried out several times a season. Remove dry, broken stems, prevent the growth of culture. This plant in a short time can fill the entire flower bed. If there is no such goal, plastic or metal limiters are dug around each bush.
In autumn, the purple loosestrife is cut off completely, leaving only a few lower shoots. The procedure stimulates the growth of young shoots in the spring.

After autumn pruning, purple loosestrife bushes are covered with dry foliage.
Purple loosestrife does not need additional shelter for the winter – it is a winter-hardy crop. The roots of the plant can be sprinkled with humus.
Purple loosestrife grows in one place for about 10 years. But after 2 years, you can transplant, as the soil is depleted. Bushes are transferred in early spring or autumn. They are dug up, the children are separated and planted in a new place.
Diseases and pests
The culture is not attacked by harmful insects. If fruit crops grow near the flower bed, the flower may suffer from aphids. Spraying with special chemicals will help from pests: Aktara, Decis, Fitoverm.
Conclusion
Purple loosestrife is an unpretentious ornamental plant that is widely used in landscape design. The flower is easy to propagate on its own, and it grows not badly. To preserve the decorative qualities of the shrub requires good lighting and abundant watering. It is important to consider that in the shade the leaves of the flower fade, turn brown.













