Contents
The liver is one of the most important organs in our body. That is why it is so important to care for its proper functioning. It is worth knowing what can threaten it.
Shutterstock See the gallery 8
- The record holder gave birth to a total of 69 children
The most fertile woman in history gave birth to 69 children. This happened in Our Country in the XNUMXth century. Interestingly, all of her pregnancies were multiple.
- Endometrium – structure, endometrial cycle, fertilization, diagnostics, diseases [EXPLAINED]
The endometrium is the mucosa that naturally lines the uterine cavity. It can have a different thickness depending on the age of the woman and the phase of the cycle …
- Thyroid diseases – symptoms, treatment, Karolina’s history
It looks inconspicuous, like a few centimeters long butterfly hidden inside the neck. But when it goes crazy, the butterfly turns into a monster that can destroy your life.
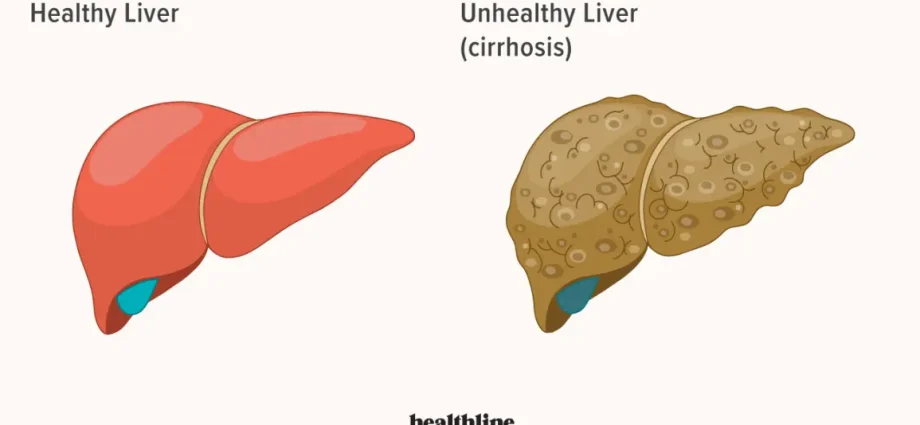
1/ 8 Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease. The essence of the disease is the formation of extensive degenerative changes, necrosis of hepatic cells, as well as excessive growth of connective tissue. As cirrhosis can develop secretly, its initial symptoms are not very characteristic. These include, among others lack of appetite, weight loss, intolerance to fried and fatty foods and alcohol. There may also be constipation alternating with diarrhea, nausea, lethargy and somnolence. The causes of cirrhosis can be different, such as the toxic effects of alcohol, drugs and other chemicals, viral hepatitis or chronic circulatory failure.
2/ 8 Cirrhosis of the liver
The pathogen of this type of infection is the type A virus (HAV). The virus is transmitted through dirty hands and contaminated food. In most cases, however, the infection is mild. The hatching period is about 15-50 days, then dyspeptic symptoms appear (lack of appetite, nausea). There are also low-grade fever and muscle and joint pain. After the next few days, symptoms typical of hepatitis appear.
3/ 8 Hepatitis B
In the case of the B virus, the most common route of infection is associated with the disruption of tissue continuity and the introduction of the virus into the blood. This can take place, for example, through non-sterile needles, as well as at a hairdresser, beautician, or as a result of sexual contact with an infected person. Unfortunately, the disease can lead to carriage and cause cirrhosis and malignant neoplasms.
4/ 8 Hepatitis C
The type C virus is responsible for approx. 20% of acute hepatitis and approx. 70% of chronic hepatitis cases. The infection occurs parenterally as a result of blood or blood products transfusion or through medical procedures using non-sterile equipment, as well as as a result of sexual contact. In infected people, after going through the acute phase of inflammation, recovery most often occurs. However, in about 20-40% of cases, inflammation becomes chronic, which can lead to cirrhosis and cancer.
5/ 8 Fatty liver
Fatty liver disease is a chronic disease in which droplets of fat accumulate in the liver cells (hepatocytes). There can be many reasons: alcohol abuse, drug abuse, diet rich in fat, as well as obesity or diabetes. The disease manifests itself, among others. digestive problems, malaise, fatigue, as well as aches and pains in the right hypochondrium.
6/ 8 Hepatic failure
Liver failure is associated with the impairment of its ability to perform metabolic functions. Failure may be acute or chronic, most commonly as cirrhosis. Initial symptoms are difficult to grasp as the liver does not generally hurt. Only in the course of acute inflammatory diseases does it increase in size, causing pain. It is therefore important to regularly perform diagnostic tests (liver tests) to detect any abnormalities.
7/ 8 Hepatic colic
An attack of severe pains located in the right hypochondrium or epigastric region is called hepatic colic. The causes of colic formation are spasms of the bile ducts (bile ducts or gall bladder) occurring as a result of their irritation, most often caused by disturbed gallstones. If this type of pain occurs in a person suffering from gallstone disease, a doctor should be called.
8/ 8 Abscesses
Liver abscesses are often bacterial in origin. The main pathogens include: colitis, staphylococcus aureus, faecal streptococcus, intestinal bacteria. Initially, the symptoms are not very specific, there is nausea, weight loss, epigastric discomfort, then high fever. The number and size of abscesses may vary.