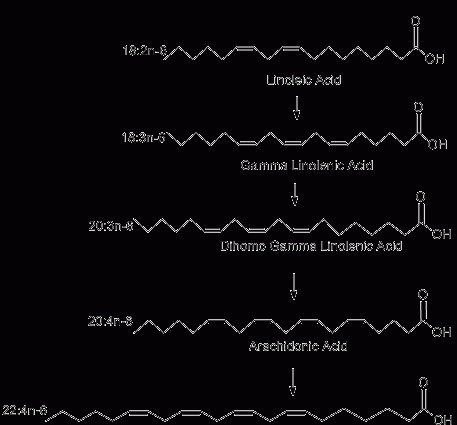
Linoleic acid is an unsaturated acid belonging to the omega-6 group, included in the so-called exogenous fatty acids. This means that it is an essential component of the diet and must be supplied to the body with food, as it is not produced by the body itself.
The main sources of linoleic acid are vegetable oils, especially grape seed oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, and soybean oil.
Action
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs), which include linoleic acid, play important functions in the body: they participate in many biochemical changes and in the regulation of physiological functions. Linoleic acid can also have a beneficial effect on the skin, which is used in the production of cosmetics.
Linoleic acid deficiency
Linoleic acid deficiency is rare. It can occur in children who are fed skim milk and in patients who are on a fat-free diet. In the case of a deficiency of linoleic acid, disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands and slowing down of skin regeneration processes, including dry and rough skin, disturbances in the keratinization of the epidermis, and increased brittleness of hair and nails are observed. Linoleic acid deficiency can lead to various diseases, including psoriasis, erythema, eczema, ichthyosis and atopic dermatitis.
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
– a derivative of linoleic acid found in cow’s milk and dairy products. Currently, research is conducted on the role of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in the prevention of cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and supporting weight loss and maintaining a healthy body weight. However, their results do not yet allow drawing unequivocal conclusions.