Contents
- What is leptospirosis
- Sources of infection and routes of infection
- Forms of the course of the disease
- Symptoms of leptospirosis in cattle
- Research on leptospirosis in cattle
- Treatment of leptospirosis in KRS
- Pathological and anatomical changes in leptospirosis in cattle
- Prevention of leptospirosis in KRS
- Conclusion
Leptospirosis in cattle is a fairly common infectious disease. Most often, the lack of proper care and feeding of cows leads to the mass death of animals from leptospirosis. The disease occurs with various lesions of the internal organs of cattle and is the greatest danger to young and pregnant cows.
What is leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a contagious disease of humans, wild and domestic animals, has a bacterial nature. For the first time this disease was noted in 1930 in the North Caucasus in cattle.
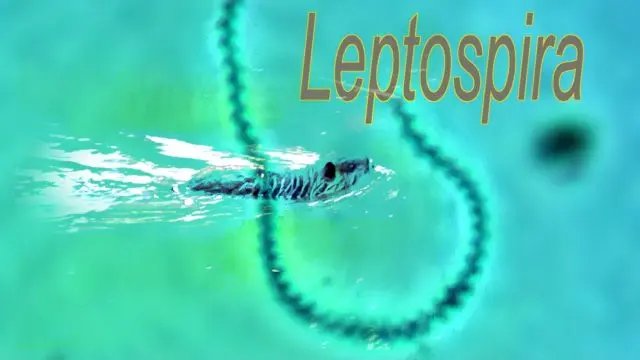
The causative agent of bovine leptospirosis is leptospira
The causative agent of leptospirosis in cattle is leptospira, pathogenic microorganisms. They have a curved body shape and are extremely active when moving. They live in a humid environment, for example, in the soil they can remain viable for about a year. Bacteria get there with the faeces of infected cattle. Leptospira does not form a spore, quickly dies in the external environment. Especially detrimental to her exposure to direct sunlight. Bacteria are also affected by disinfectants.
Leptospirosis causes significant damage to the economy of many farms. In addition to the death of young cattle, leptospirosis provokes spontaneous abortions in adults, the birth of dead calves, the exhaustion of animals, and a significant decrease in milk production. The activity of leptospirosis is most often observed during the beginning of grazing on the pasture, in the spring. Young animals suffer more from the disease, because they have not yet strengthened the immune system.
Sources of infection and routes of infection
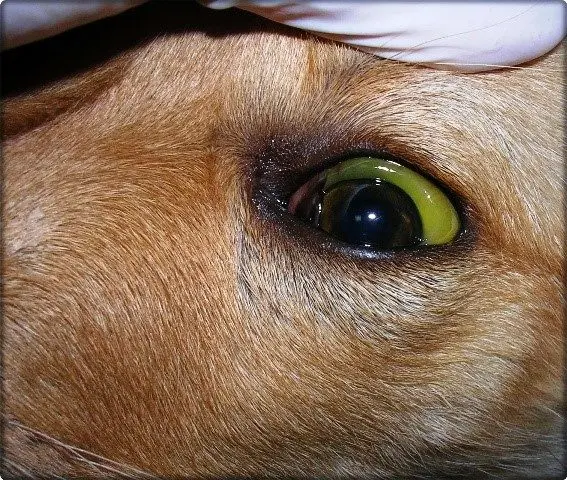
One of the symptoms of leptospirosis is yellowness of the mucous membranes.
The source of infection is the feces and urine of sick individuals, as well as rodents that carry bacteria. Transmission factors include contaminated feed and water, soil and animal litter. As a rule, infection occurs through the alimentary route. In addition, infection is possible:
- aerogenic way;
- sexually;
- intrauterine;
- through open wounds on the skin, mucous membranes.
Outbreaks of infection occur in the warm season. After the penetration of leptospira into the bloodstream of cattle, they begin to actively reproduce. The body of an infected individual, trying to get rid of the pathogen, releases toxins. They are the cause of the pain. After infection of one animal, the infection is rapidly transmitted to the entire livestock with urine, saliva, and feces. Then the disease becomes epidemiological.
Forms of the course of the disease
Leptospirosis in cattle can occur in the following forms:
- acute;
- chronic;
- subclinical;
- manifest;
- atypical;
- subacidic.
Each of these forms of the disease has its own characteristics of manifestation and treatment.
Symptoms of leptospirosis in cattle
Symptoms and treatment of leptospirosis in cattle largely depend on the course and form of the disease. For adults, an asymptomatic course of the disease is characteristic. Young people suffer from the following manifestations:
- fever;
- development of anemia and jaundice;
- diarrhea;
- atrial atony;
- muscle cramps;
- rapid pulse, shortness of breath;
- dark urine;
- loss of appetite;
- conjunctivitis, necrosis of the mucous membranes and skin.
The acute form of the disease causes the death of the animal within 2 days after heart failure or kidney failure. In the chronic course of leptospirosis, the symptoms are not so pronounced, but in the absence of therapy, they also lead to the death of cattle.
One of the first symptoms of leptospirosis in cattle that you need to pay attention to is a sharp hyperthermia, followed by a decrease in body temperature. In this case, the animal may show aggression.
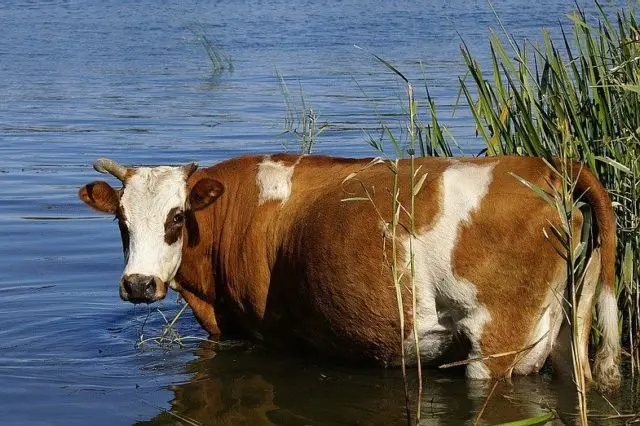

Ponds with dirty water can be a source of infection
The manifest form lasts up to 10 days. Characteristic signs of this form of the disease:
- elevated body temperature up to 41,5 ° C;
- animal oppression;
- lack of gum;
- yellowness of the skin;
- painful urination;
- diarrhea, stool retention;
- pain in the lumbar region on palpation;
- abortions of pregnant cows;
- disheveled wool;
- tachycardia.
With untimely treatment, the mortality rate of livestock reaches 70%.
The chronic form of leptospirosis is characterized by exhaustion, a drop in milk yield and fat content, and the development of mastitis. The prognosis is most often favorable, as well as with an atypical form of the disease, which occurs with blurred clinical manifestations.
The subclinical course of leptospirosis in cattle is usually detected during routine diagnostics.
Research on leptospirosis in cattle
Diagnosis of cattle for leptospirosis involves the use of epizootological data, pathological observations, the identification of symptoms and changes in the blood. In a hematological study in infected individuals, the following is noted:
- low content of red blood cells;
- increased or decreased hemoglobin content;
- drop in blood sugar levels;
- leukocytosis;
- increase in bilirubin and proteins in plasma.
Another clear sign of leptospirosis is the detection of antibodies to the pathogen in a fifth of the entire cattle population. This will require a bacteriological analysis of cow urine. In addition, the diagnosis should be differentiated from listeriosis, chlamydia, piroplasmosis and brucellosis.
The final diagnosis is made after all the necessary studies (microscopy, histology, serological tests). Leptospirosis is established only after culture is isolated. Thus, the diagnosis of leptospirosis in cattle should be complex.
Treatment of leptospirosis in KRS
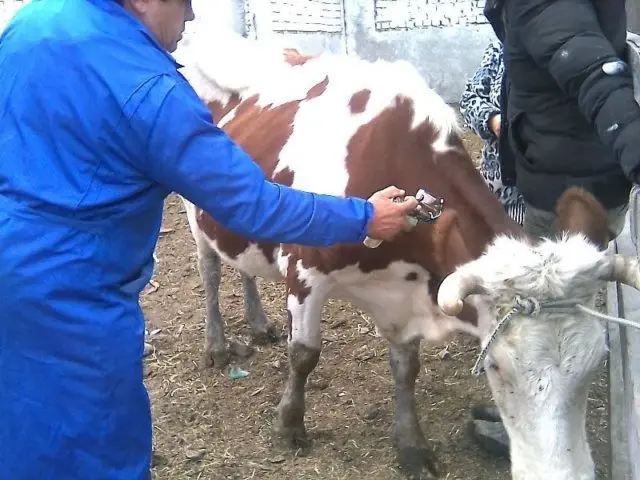

Livestock vaccination
First of all, it is necessary to isolate diseased individuals from the herd in a separate room and create comfortable conditions for them. To combat leptospirosis in cattle, an injection of antileptospirosis serum is performed. Antibiotic therapy and symptomatic treatment of leptospirosis in cows will also be required.
Serum against bovine leptospirosis is injected subcutaneously at a dosage of 50-120 ml for adults and 20-60 ml for calves. The injection should be repeated after 2 days. Of the antibiotics, streptomycin, tetracycline or biomycin are used. The drugs are used for 4-5 days twice a day. To eliminate hypoglycemia, intravenous glucose solution is administered. To normalize the function of the gastrointestinal tract, Glauber’s salt is prescribed. Good results are obtained by taking caffeine and urotropin. If there are lesions of the oral mucosa, you need to rinse with a solution of manganese.
The instruction for bovine leptospirosis provides for the inspection of all animals in the herd if at least one diseased individual is found. Further, the entire livestock is divided into 2 halves: in one, animals with clinical signs of the disease, which are treated according to the scheme, as well as hopeless cows to be culled. Healthy cattle from the second half undergo mandatory immunization.
Pathological and anatomical changes in leptospirosis in cattle
The corpse is emaciated, dry, the coat is dull with bald patches. At autopsy, the following changes are observed:
- yellow tint of the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs;
- necrotic foci and edema;
- accumulation of exudate with an admixture of pus and blood in the abdominal cavity and thoracic region.
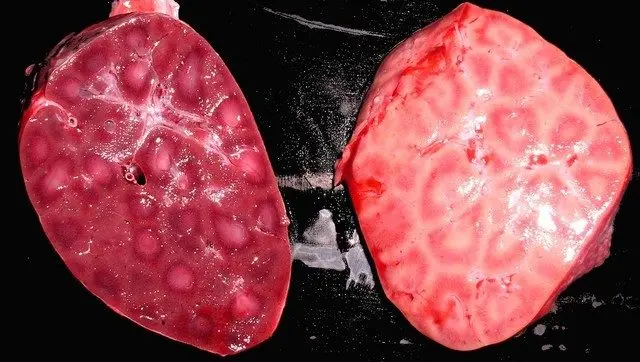
Changes in the animal’s liver
Leptospirosis is especially strongly reflected in the liver of a cow (photo). It is significantly enlarged in volume, the edges are somewhat rounded. At the same time, the color of the organ is yellow, hemorrhages and foci of necrosis are visible under the membrane. The kidneys of the cow are also subject to changes. At autopsy, pinpoint hemorrhages and exudate are noticeable. The bladder is greatly swollen, filled with urine. The gallbladder is filled with brown or dark green contents.
Samples taken from the organs of the corpse and analyzes show changes as a result of invasion.
Prevention of leptospirosis in KRS
One of the most effective measures to prevent disease among livestock is timely vaccination. To do this, use a polyvalent vaccine against bovine leptospirosis, which prevents the development of the disease in unfavorable farms. It consists of various cultures of infectious agents inactivated by artificial means. The drug, getting into the body of a cow, leads to the development of stable immunity for a long time. After a certain time, re-vaccination will be required. The frequency of the procedure depends on the age of the animal.
In addition, the veterinary rules for animal leptospirosis provide for compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules when breeding cattle in farms. Farm owners must:
- perform regular inspection of individuals in the herd;
- feed with high-quality proven food and drink clean water;
- change the bedding in time;
- to fight rodents on the farm;
- perform daily cleaning in the barn and disinfection once a month;
- carry out grazing in areas with a clean reservoir;
- carry out scheduled diagnostics of the herd;
- declare quarantine of cattle in case of suspected leptospirosis and when new animals are imported.
It is also recommended to examine the fetus in a miscarriage in a cow for the presence of bacteria.
When quarantine is introduced on the farm, they prohibit the movement of livestock within and outside the territory, do not use individuals for breeding work during this period, do not sell products from the farm, and prohibit grazing. It is necessary to carry out disinfection and deratization of the barn and adjacent territories and premises. Milk from infected cows is boiled and used only inside the farm. The milk of healthy individuals can be used without restrictions. Quarantine is removed only after all necessary measures and negative tests.
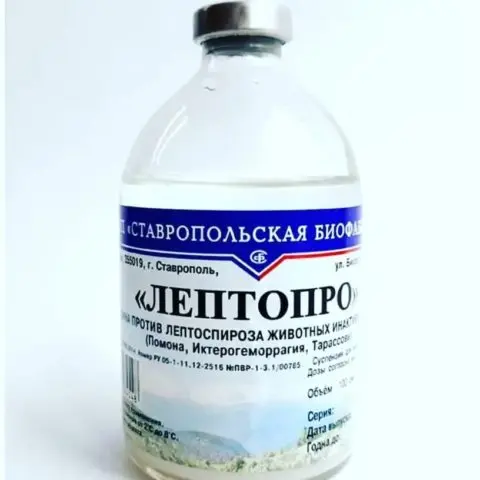
Polyvalent vaccine
Conclusion
Leptospirosis in cattle is a complex infectious disease in which all organs of the animal are affected. It is also quite dangerous for humans, therefore, when a diseased individual is found in the herd, all necessary precautions will need to be taken to prevent further spread of the infection in the herd and among the staff on the farm. It is worth noting that if strict preventive measures are observed, infection can be avoided.









