Contents
Lamblia is a parasite that causes a dangerous disease – giardiasis. Contrary to popular belief, we do not get lamblia by eating bananas. Bathing in a river with infected beavers is much more risky.
Lamblia infection
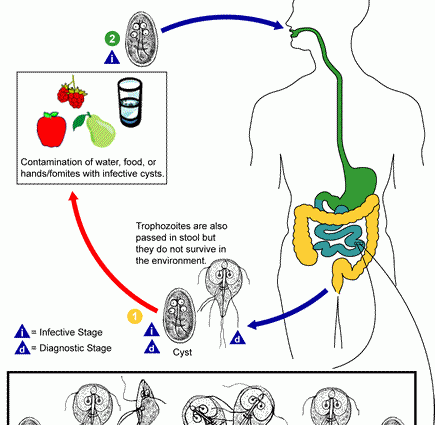
– These organisms, invisible to the naked eye, parasitize the small intestine of many species of animals and humans – explains Połozowski. Their cysts are excreted in the faeces. They are very durable. They can live up to 7 weeks in soil and up to 3 months in cold water. The minimum dose that is able to cause infection in mammals varies from 10 to 100 pcs. Meanwhile, in 1 gram of faeces there may be over a million.
Man becomes infected with lamblia through the food. – All we need to do is eat food or water contaminated with cysts, and trophozoites, i.e. parasitic forms of giardia, will come out of the cyst in our body, which will start to multiply and colonize the walls of the small intestine – warns the parasitologist. Our dog or cat can also infect us. But it is also the other way around – we infect our pet.
Infection with lamblia from food is less common because high temperatures kill the parasites. Hygiene is crucial here when handling food or food products, which unfortunately happens to be washed out in contaminated water, and which may result in the spread of lamblia.
Not only domestic animals are dangerous to humans, but also … beavers. They are very often sowing lamblia cysts, although they themselves do not have any symptoms of the disease. So we just need to rinse our face in the river where infected beavers live, and this can introduce giardia cysts into our digestive tract.
What’s more, parasites can also spread through contact with a sick person through, for example, unprotected anal sex.
People who, for example, work in kindergartens or people who change their baby’s diapers are also at risk of contracting gin. The babies themselves are cornerstone of lamblia contamination through feces while wearing diapers or learning to use the potty.
To find out if you are infected with lamblia, do a Giardia lamblia mailing test.
Lamblia – risk factors
While anyone can become infected with the lamblia parasites, some people are at particular risk:
- people without access to safe drinking water. Lamblia infection can occur especially in places where the water is not suitable for drinking and where the sanitary conditions are significantly abnormal. The most dangerous places due to the possibility of infection are wild areas and rural areas. In places where there is a high risk of lamblia infection, it is recommended to be very careful and watch what you eat and drink.
- kids. Children are most at risk of contracting lamblia because they are more likely to come into contact with faeces, especially if they wear diapers, exercise to use the toilet or are in a nursery. People who live or work with young children should also be alert.
- people who have anal sex. People who engage in anal or oral-anal sex without a condom or other protection are at greater risk of developing lamblia and sexually transmitted infections.
See also: Human parasites: causes, symptoms, treatment
Symptoms of giardiasis
Symptoms of infection with the protozoan giardia lamblia appear after a few days. These are vomiting and diarrhea. In the next stages of the disease appear: weight loss, muscle wasting, excessive sleepiness. Dr. Połozowski explains that although it is not in the interest of the parasite to kill its host, giardias can inhibit psychophysical development in children. – Giardiasis (giardiasis) causes disorders of the absorption of fats and carbohydrates, which, together with the deficiency of vitamins, proteins and micronutrients resulting from long-term diarrhea, lead to malnutrition – says Dr. Połozowski.
One of the methods of diagnosing intestinal diseases is through stool tests. At Medonet Market, you can now buy a stool test for parasites, as well as intestinal microflora tests. It will also be useful to test the level of EPX protein in the stool by mail, which is the protein produced in the event of a parasitic infection.
Diagnosing lamblia infection
To diagnose lamblia infection, stool samples are taken for testing. The laboratory tests stool samples for lamblia parasites. Additional samples should sometimes be taken while the infection is being treated.
In addition, enteroscopy is also performed to diagnose lamblia infection. This test involves the insertion of a flexible tube down the throat and into the small intestine. Thanks to this method, the doctor can examine the digestive tract and take tissue samples.
Also check: Faecal examination for parasites – indications, course, price [EXPLAINED]
Treatment of lamblia infection
The presence of lamblia is detected by examining the stools. Remember that it is also worth doing research on our four-legged companions. — It should be remembered that if this parasite is found in at least one family member, all household members should undergo therapy – says Dr. Połozowski. It is worth consulting your doctor which preparation will be the best and the least harmful. Drug treatment lasts for several days. A stool check should be performed approximately two weeks after the last drug application. All family members should be encouraged to wash their hands properly and frequently, especially after using the bathroom and before eating.
In some cases, lamblia infection resolves on its own. In the rest of the cases, when there is a severe infection or a prolonged infection, the doctor prescribes antiparasitic drugs.
Antibiotics are used to treat giardiasis infection, such as:
- Metronidazole – take this for five to seven days. Side effects that it can cause include nausea and a metallic taste in the mouth.
- Tinidazole – This antibiotic is as effective as metronidazole and often treats giardiasis in a single dose.
- Nitazoxanide – This is a popular option for children because it is available in liquid form and only needs to be taken for three days.
- Paromomycin – Characteristic for this antibiotic is a lower risk of birth defects than with other antibiotics. Still, pregnant women should wait until delivery before taking any medications for giardiasis. This drug is given in three doses over 5 to 10 days.
There are no consistently recommended medications for lamblia infection during pregnancy due to the potential harmful effects of drugs on the fetus. If your symptoms are mild, your doctor may advise you to delay treatment until the first trimester or longer. If treatment is necessary, the woman should consult her doctor about available treatment options.
If you want to prevent parasite contamination, use Tea on lambla, which contains wormwood and thyme herb, walnut and sage leaves, and calamus rhizome. These herbs have a health-promoting effect on the digestive system. As an auxiliary in the treatment of parasitic diseases, it is worth using Na parasites – the Panaseus dietary supplement, which you can buy at Medonet Market.
Complications of giardiasis infection
Lamblia infection is not fatal, but can cause persistent symptoms and serious complications, especially in infants and children. The most common complications include:
- dehydration. Dehydration is a consequence of severe diarrhea. Dehydration occurs when the body has not been supplied with enough water for proper and normal functioning.
- lack of proper development. Severe diarrhea can also lead to malnutrition, as well as abnormalities in the physical and mental development of children.
- lactose intolerance. A very common complication caused by lamblia infection is the development of lactose intolerance. Lactose intolerance is a condition in which the body is unable to properly digest milk sugar (that is, lactose). The problem may persist long after the infection has cleared.
See also: Parasite medications – when to use, types
Prevention of infection with giardiasis
There is no prescribed vaccine to prevent lamblia infection, but measures can be taken to reduce the risk of catching the infection or spreading the infection to others.
- Avoid drinking untreated water. Avoid drinking untreated water from shallow wells, lakes, rivers, springs, ponds, and streams. This should be filtered or boiled for at least 10 minutes at 70 ° C. Being in countries where the possibility of lamblia infection is high, it is advisable not to drink tap water or brush your teeth with it. For this, it is recommended to use bottled water. It is better not to consume ice cream or other drinks that may also contain such water. You should also try not to swallow water while swimming in pools, lakes, or streams.
- Wash the products. Before eating fruits and vegetables, wash them with safe, uncontaminated water. The fruit should also be peeled before consumption. Moreover, it is better to avoid eating raw fruits or vegetables if you are traveling to countries where they may come into contact with unsafe water.
- Wash hands. This is the most obvious of the rules, but very important. Always wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds after using the toilet or changing diapers and before eating or preparing meals. If we do not have access to soap and water, go ahead, we can use alcohol-based disinfectants instead. It should be added, however, that alcohol-based disinfectants are not effective in destroying cysts that have survived in the environment.
- Make sex safer. In the case of anal sex, you should use a condom each time, and wash your hands and intimate places after intercourse. These practices can ensure that we do not come into contact with infected feces. Oral sex immediately after anal sex should also be avoided unless you are fully protected.
Also check: Tap Water – Is It Healthy? Can you drink it? Why is it worth it?