Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Lactation is the process of milk being secreted from the mammary glands in the breasts during pregnancy and afterwards. Lactation continues as long as the woman feeds her little one naturally. There are situations when the lactation process should be supported externally or stopped, when for some reasons the mother cannot breastfeed her baby. Read what is lactation and how can you help it with home remedies?
Lactation – milk production
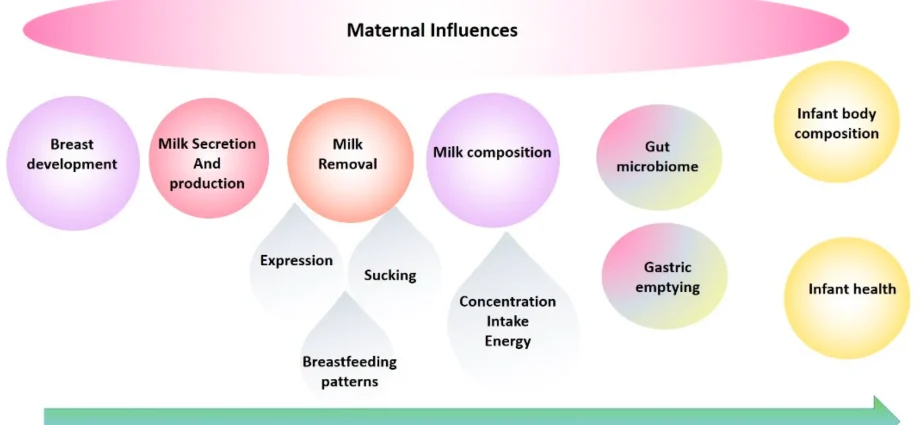
Breastfeeding is the recommended and preferred method of feeding infants up to 2 years of age. The process of breastfeeding begins right after giving birth, but milk production itself begins much earlier – usually between 16 and 22 weeks of pregnancy. The main influence on food production is progesterone, produced in the placenta, which has a direct impact on the development of the so-called milky vesicles. Estrogen, the second of the female hormones, is responsible for the formation of the milk ducts.
Thanks to lactation, a woman can breastfeed her baby after giving birth. However, problems with physiological food shortage appear more and more often – they affect about 3-5% of women after childbirth. To stimulate lactation, it is worth using home methods – they can also be used to stop lactation.
Read also: You give them to your baby every day. How to choose the best one to strengthen its immunity?
Lactation – stages
Breast development begins in adolescence, and the development of nipple functions is completed only in pregnancy. In the first half of pregnancy, the nipple ducts proliferate and group together to form large lobules. The secretory activity of the breast begins as early as the 16th week of pregnancy.
The ability of the mammary gland to secrete milk during later pregnancy is called lactogenesis, this is stage 1. During this time, the size of the breast increases and fat droplets accumulate in the secretory cells. The onset of copious milk secretion after delivery is stage 2, and usually occurs between the second or third and eight days after delivery. During this time, the milk matures to meet the baby’s needs. Without the hormone prolactin, lactation would not have happened.
During pregnancy, prolactin helps to increase the weight of the breast, but it does not cause lactation because it is inhibited by the hormone progesterone, which is produced by the placenta. Prolactin levels rise and fall in direct proportion to the frequency, intensity, and duration of nipple stimulation by suckling the infant.
In the first week after birth, prolactin levels in breastfeeding women drop by about 50 percent. If the mother is not breastfeeding, prolactin levels typically reach pre-pregnancy levels up to seven days postpartum. After milk ‘enters’ or rapidly expands, lactation is no longer driven by the hormone prolactin. It transfers control to a process based on milk removal, i.e. the suckling stimulus.
The initiation of lactation is not driven by breastfeeding, but breastfeeding is necessary to continue lactation.
Lactation – the composition of milk
The breast is not a passive milk container. It is an organ that actively produces milk under the influence of the infant’s suckling stimulus – removing milk from the breast results in a continuous production of milk. It is a supply and demand response that regulates milk production to accommodate infant consumption. The composition of breast milk changes to meet the specific needs of the growing infant. In response to suckling, the hormone oxytocin triggers the milk ejection or “let go” reflex.
Milk ejection is the rapid ejection of milk from the alveolar openings. The secretion of oxytocin is also a natural way of causing the woman’s uterus to contract after delivery to control postpartum bleeding and support uterine involution. These contractions can last up to 20 minutes after feeding and may be painful in the first few days. The advantage of this, however, is that it makes the uterus involution faster.
The colostrum (starting milk) is thick and creamy yellow compared to mature milk which is thin and white. Compared to mature milk, colostrum is richer in protein, vitamins and minerals. The high concentration of total protein and minerals in the colostrum gradually changes to meet the infant’s needs during the first two to three weeks until lactation is stabilized. A key ingredient in colostrum and breast milk are immunoglobulins or antibodies that are used to protect the baby from infections or viruses.
Breast milk also helps the baby develop its own immune system so that it can mature faster. As a result, it is believed that breastfed babies do not get sick as often as formula-fed babies and that they suffer less from allergies, diarrhea and vomiting.
To support nursing mothers, a preparation FOR THE NURSING WOMAN was created – herbal tea, which has a relaxing effect and supports lactation. You can buy tea at Medonet Market.
Breast milk is rich in proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, hormones, enzymes, growth factors, and many types of protective agents. It contains about 10 percent solids for energy and growth, with the rest being water, which is essential to keep your baby hydrated. Therefore, a breastfed baby does not need any additional water. Babies digest breast milk much faster than formula. Contrary to breast milk, it takes about 30 minutes longer to digest the formula.
Breastfeeding is also associated with a lower risk of breast and ovarian cancer. For every year of life spent breastfeeding, a woman’s risk of developing breast cancer drops by 4,3 percent.
Mother’s milk is always with the mother. Mothers don’t have to keep it. It always has the right temperature. It is free. It does not require sterilization. In fact, it prevents disease and has protective factors, resulting in healthier children and lower healthcare costs. It saves money as there is no need to buy formula, bottles and teats.
- Formula milk – what are its types? Indications and contraindications for use
Lactation – common problems
What causes lactation problems? The main reason is the mother’s mental state and her well-being. Problems with lactation cause stress and exhaustion, so it is important to care for the mental comfort of mum. Problems can also arise from attaching the baby incorrectly or too infrequently to the breast.
In addition, young mothers may experience the following symptoms during lactation:
- breast swelling: breasts that are too full may prevent your baby from sucking because they cannot be grasped. Expressing milk by hand or with a breast pump can reduce this problem.
- nipple pain: temporary soreness may occur in the first week after birth and is usually temporary. The nipples are soothed with air and rubbed with colostrum or breast milk and lubricated with lanolin,
- infection: soreness and inflammation on the surface of the breast or a fever in the mother may indicate a breast infection (mastitis). If it is just getting started, the mother should drink plenty of water and feed the diseased breast frequently. If the infection persists, antibiotic therapy may be necessary.
- automatic flow of milk from the breast. With such a problem, it is worth using the Neno Claro Milk Collector Set, which helps to collect breast milk, ensuring that not even a drop is wasted. On the other hand, during one breastfeeding, the flowing milk from the other can be collected in the Magic Neno Leite bottle – a milk collector available on Medonet Market at a favorable price.
There are no rules on when to stop breastfeeding. Babies need breast milk for at least the first year of life, and solid food should not be given for at least the first six months to prevent allergies.
See: Purulent mastitis
Lactation – home remedies
The lactation process normalizes around 2 months after delivery – this is when the breasts, although still producing milk, are not swollen. However, in the so-called during the toddler’s developmental jumps, there are temporary and most often temporary food deficits. It is at this point that lactation should be supported with home methods to ensure that the baby receives the optimal amount of food.
The basic home lactation treatment is frequent latching on to the breast. It’s best to do it every hour during the day and even every 3 a.m. – that’s when the food has the highest calorific value. You should feed from both breasts at each feeding, so that lactation is stimulated in both breasts at the same frequency. It is important to monitor that your little one is properly grasping the nipple. Proper suckling stimulates food production, which allows you to stave off a lactation crisis fairly quickly.
The second way to stimulate lactation is to use the breast pump right after feeding your little one. In such a case, a small amount of food should be sucked out using a breast pump, which will stimulate the mammary glands to work more intensively within a few days. Electric breast pumps are the best solution as they ensure constant suction power. At Medonet Market you can buy breast pumps at attractive prices. We recommend, for example: the Neno Bella electronic breast pump or the Neno Bella Twin double, two-phase wireless breast pump.
You don’t have to give your baby the expressed milk right away. You can refrigerate them or freeze them. Use the Neno food storage and freezing bags for this. Then just heat them up. So you will need the Neno Vita 2-in-1 Sterilizer and Bottle Warmer, which you can find now at a promotional price on Medonet Market. You can also try Neno feeding bottles with different capacities that can be adapted to the age and needs of the child. Click and check the offer.
Another popular method for lactation among mothers is consuming barley malt. Malt is one of the byproducts in the beer production process that stimulates the production of prolactin, a hormone that is responsible for the production of milk. However, it should be remembered that pregnant and breastfeeding women cannot consume alcohol, and even “free alcohol” products contain trace amounts of it.
In addition, the expectant mother and nursing mother should pay special attention to a balanced diet and an adequate amount of fluids – at least 2 liters per day. You can also try herbal teas, such as fennel. It turns out that some spices also have a positive effect on lactation, e.g. anise. So let’s add it to your food.
Ways to stop lactation
After the baby is born, doctors and midwives recommend that the mother breastfeed her baby naturally. However, it is a matter of choice: mom may choose to breastfeed, but she does not have to. This decision has no effect on milk production, so it is worth stopping lactation in such situations. How to do it?
The first way is to stop latching your baby to the breast. If the mammary glands do not receive external stimuli for food production for a long time – lactation will cease, but it is a long process lasting from several days to even several weeks.
Shortly after giving birth, food is often produced in large quantities – then the breasts swell, become swollen and often hurt. To alleviate these symptoms, it is worth using cabbage leaf compresses or a massage with lukewarm water in the shower. Sage infusion, drunk several times a day, also helps to stop lactation. However, you must not limit the amount of absorbed fluids – this may cause electrolyte disturbances and even the formation of inflammation of the urinary system. However, if weaning the baby from the breast does not bring results – pharmacotherapy should be administered after consulting a doctor.