Contents
Cucumbers are very demanding on the composition of the soil. They need many minerals in a balanced amount. Excess or lack of trace elements is reflected in the intensity of plant growth, yield, taste of vegetables. A competent gardener will always be able to identify the problem by external signs that appear on the leaves and fruits of the plant. For beginner farmers, we will try to determine in more detail the symptoms of cucumbers with a lack of fertilizers and their excess, as well as ways to solve the problem.

Essential Substances
The micronutrient requirements of cucumbers depend on the growing season. In general, the plant needs all the minerals in one quantity or another. Cucumbers are intolerant only to chlorine.
Nitrogen
This microelement is necessary for all plant crops, including cucumbers. Nitrogen allows plants to rapidly grow green mass. That is why cucumbers especially need nitrogen at an early stage of vegetation in order to form a sufficient number of leaves. Seedlings and young plants planted in the ground are fed with nitrogen after rooting.

In the future, the use of nitrogen can negatively affect crop yields. Cucumbers with an excess of this substance begin to “fatten”, increasing an excess amount of greenery, without the formation of ovaries. The leaves of the plant turn dark green. You can correct the situation and reduce the amount of nitrogen by washing out the soil (regular abundant watering).
The lack of nitrogen in the soil can be understood by the following signs:
- new shoots on cucumbers do not form, existing ones grow weakly;
- the leaves formed on the main stem are small in size;
- old leaves become light green, and then light yellow in color, eventually they fall off;
- the number of flowers and ovaries is reduced;
- ripening cucumbers of small sizes with insufficient filling.
Observing such symptoms on cucumber plantings, care should be taken to apply root or foliar fertilizers with a high nitrogen content.

Phosphorus
Phosphorus in plants is primarily responsible for the growth and development of the root system. Without phosphorus, cucumbers cannot absorb other micronutrients from the soil, which leads to a general “starvation” of plants. This microelement is necessary at all stages of growing cucumbers, and especially after planting seedlings in the ground. That is why during the period of soil preparation, care should be taken to introduce phosphorus. Phosphate fertilizers should also be used during flowering, the formation of ovaries and the ripening of cucumbers. The amount of trace element should be moderate.
Signs of a lack of phosphorus in cucumbers are:
- discoloration of existing, mature leaves. They take on a bluish tint or turn red;
- the young, forming leaves become smaller;
- the growth of new shoots slows down;
- the number of ovaries decreases, and the existing cucumbers ripen slowly.
It should be noted that the lack of phosphorus in cucumbers is extremely rare. As a rule, this happens when growing cucumbers on depleted soils with a high level of acidity.
Excess phosphorus also negatively affects the growth and yield of cucumbers. Signs of an excess amount of this trace element are:
- accelerated plant growth with insufficient leaves and side shoots;
- cucumber leaves acquire a light yellow tint, necrotic spots can be observed on their surface;
- untimely watering of the culture leads to a sharp wilting.

An excess of phosphorus does not allow proper absorption of potassium. Therefore, signs of a lack of potassium can also indicate an excess amount of phosphorus.
potassium
For cucumbers, potash fertilizers are of particular importance. This micronutrient allows micronutrients to move from the roots to the leaves and fruits, while speeding up the ripening of cucumbers. That is why potash fertilizers are applied to the soil before planting seedlings and in the process of fruit ripening. Without potassium, normal growth and development of a plant at all stages of the growing season is impossible.
A sufficient amount of potassium in the soil is the key to a tasty harvest. Cucumbers in this case are tasty, sweet, crispy. In addition, potassium makes the crop more resistant to adverse weather, diseases and pests.
To determine the lack of potassium in the soil can be on a number of grounds:
- the leaves of the plant acquire a dark green color;
- the lashes of the plant are strongly drawn out;
- cucumbers practically do not form an ovary;
- a dry yellow border forms on the leaves of the plant;
- mature cucumbers are filled with excess water and have a bitter taste.

Thus, without a sufficient amount of potassium, a good crop of cucumbers cannot be obtained. The fruits will set in small quantities, and their taste will be of poor quality.
Excess potassium in cucumbers is rare. Its symptoms are:
- discolored, pale leaves;
- plant growth slows down;
- internodes become long;
- on the surface of leaf plates with a strong potassium “starvation” mosaic spots can be observed. Over time, damaged foliage falls off.
Excess potassium stops the flow of nitrogen, causing the plant to slow down its growth. The intake of other trace elements also slows down.
You can determine the deficiency of minerals not only by the leaves and the intensity of plant growth, but also by the cucumbers themselves. With a lack of one or another microelement, they show ugliness of a certain nature.
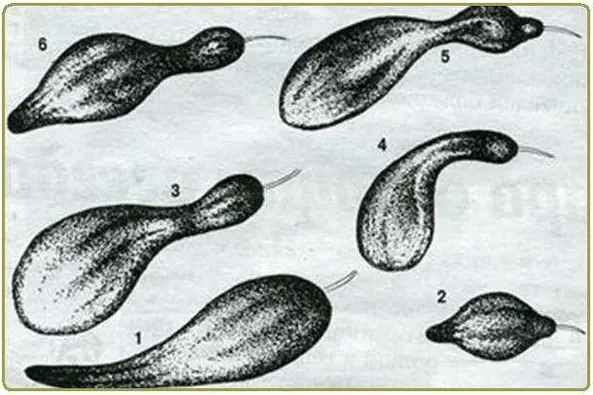
In the figure, in the first and second cases, nitrogen deficiency is displayed. The shape of the third cucumber signals a lack of potassium. The ovaries of cucumbers numbered 4 and 5 were incorrectly pollinated and therefore the fruits acquired such forms. The shape of the sixth cucumber indicates a lack of a whole complex of substances.
Deficiency and excess of other trace elements
It is nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium that play the most important role in the process of growing cucumbers. Fertilizers containing these trace elements in a balanced amount should be chosen for plant nutrition. However, in some cases, on depleted soils, cucumbers may lack other nutrients:
- With a lack of boron, yellow frames appear on the leaves.. Flowers and ovaries, not having time to appear, wither and fall. A characteristic light groove appears on the formed cucumbers. The shape of the fruit is curved. Excess boron causes the edges of the leaves to dry out, curling down like a dome.
- Magnesium deficiency is manifested by uneven coloring of the leaf of the plant.. Light and dark spots can be observed on it at the same time. With an excess of magnesium, the color of the leaves becomes dark, they begin to curl up.
- If the veins on the leaves protrude and become dark green in color, but the leaf itself becomes pale, then it is worth talking about a lack of manganese.. An excess of this trace element stains the veins on the leaves red. The space between the veins is also covered with brown dots. Severe manganese poisoning leads to stunting, and then the complete death of the plant.
- A yellow, dry border on the leaves that turns brown over time is a sign of calcium deficiency.. At the same time, the cucumber leaves themselves are pale, sluggish, twisted up. Excess calcium leads to chlorosis. Pale, necrotic rounded spots appear on the leaves of cucumbers. Boron and manganese cease to enter the plant, which means that over time, symptoms of a deficiency of these substances can be observed.

When one of the signs of “starvation” appears, it is necessary to immediately introduce the missing microelement. The source in this case can be mineral fertilizer, organic matter or other improvised means. Top dressing can be done by watering under the root or spraying. When choosing a method of fertilizing, it must be remembered that when spraying, the consumption and synthesis of substances is much faster, which means that the effect of such activities will be noticeable almost immediately. To prevent the occurrence of a deficiency of a particular substance, it is necessary to regularly feed cucumbers with complex fertilizers.

Variety of fertilizers
Many gardeners prefer to feed cucumbers exclusively with organic fertilizers. Mullein, manure infusions and bird droppings are the main raw materials for the creation of top dressings for them. However, in the case of cucumbers, such fertilizers are not enough, since organic matter contains a lot of nitrogen and an insufficient amount of other trace elements. That is why even when using organic matter, you should not neglect mineral additives.

In agricultural stores, gardeners are offered complex preparations and certain nutrients. Depending on the task at hand, one or more of them should be selected:
- Nitrogen sources are ammonium nitrate and urea, which is sometimes called urea. For a single application to the soil, these substances are diluted in a bucket of water in the amount of 10-20 g and 20-50 g, respectively. The concentration of top dressing largely depends on the age of the plant and its condition.
- Superphosphate is more often used to feed cucumbers with phosphorus. This trace element is applied to the soil at the rate of 40-50 g/m2.
- You can compensate for the lack of potassium in cucumbers using potassium sulfate or potassium magnesia (a combination of potassium and magnesium). These substances do not contain chlorine harmful to cucumbers. Prepare a nutrient mixture of them at a concentration of 1-3%. A large amount of potassium is found in wood ash, which can be used in dry or liquid form (infusion) to feed cucumbers.
- The lack of boron can be compensated either with boric acid or with a special preparation Biochelate-Bor. The concentration of boron in top dressing should not exceed 0,02%. For example, only 1 g of the substance is added to 0,2 liter of water. Boron is toxic and, if the dosage is exceeded, can adversely affect the growth and development of cucumbers.
- You can saturate cucumbers with magnesium using potassium magnesia. This substance for the season, in several stages, should be applied in the amount of 15-20 g for every 1 m2 soil. Dolomite flour and wood ash also contain a large amount of the trace element. Consumption of these substances per season per 1 m2 soil should be 20-50 and 30-60 g respectively.
- Manganese for cucumbers can be obtained by diluting a weak, light pink solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate).
- Calcium can be added to the soil with calcium carbonate in the amount of 5-7 kg per 10 m2 soil. Also, the trace element is found in chalk, dolomite flour, wood ash. To feed cucumbers at home, you can make eggshell flour.

To feed cucumbers, you can use a specific substance or prepare a complex mixture of trace elements in the required concentrations. When preparing fertilizers for young plants, special care must be taken, since they are very sensitive to overdose.
On sale you can find combined fertilizers that combine the necessary trace elements in a certain amount. The most widely used of them is ammofoska – a three-component fertilizer that contains nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. You can prepare such a mixture yourself by mixing ammonium nitrate (10 g), superphosphate (30 g) and potassium sulfate (15 g). Substances must be diluted in water and used to fertilize plants per 1 m2 soil.

Top dressing of cucumbers
Top dressing of cucumbers must be carried out from the moment 2 true leaves appear. For such seedlings, a whole complex of microelements is needed, including nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus. You can fertilize young plants with complex preparations, for example, Agricola, Bio-master, Topers.
An example of the use of such complex fertilizers is shown in the video:
Before planting cucumber seedlings, the soil must be fertilized so that it contains all the necessary trace elements for normal plant growth. So, in the fall, organic fertilizers with a high nitrogen content should be added to the soil. It can be rotted or fresh manure, humus. In the spring, just before planting cucumbers in the ground, it is necessary to add fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. These trace elements will allow plants to take root better in new conditions.
A week after planting, cucumbers must be fed with nitrogenous fertilizers. They activate the growth of cucumbers and allow the plants to grow green mass. During flowering and the formation of ovaries, a fertilizer complex containing a large amount of potassium, phosphorus, boron and a little nitrogen should be applied. Such combined fertilizers should be used until the end of the growing season.

For the entire period of growing cucumbers, 3-4 basic top dressings should be carried out. In the intervals between them, it is recommended to additionally apply micronutrients by spraying and watering with low concentrated solutions.
To summarize
Deciding to get a good harvest of delicious cucumbers, you need to stock up on certain knowledge. So, according to the leaves and fruits of cucumbers, you need to understand and determine the lack of a particular substance. This will allow timely elimination of problems and prevent the further development of microelement starvation, because the lack of one substance can cause a cessation of the intake of other substances, which will lead to stunting and possible death of the plant. During the entire growing season, a caring farmer must repeatedly apply complex top dressing, which will not only prevent starvation, but also guarantee high yields and good taste of cucumbers.









