Contents
- Klacid – general characteristics of the drug
- Klacid – composition and action of the drug
- Klacid – indications for the use of the drug
- Klacid – contraindications to the use of the drug
- Klacid – precautions
- Klacid – dosage and method of use
- Klacid – side effects
- Klacid – interactions with other drugs
- Klacid and pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Klacid – scene
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Klacid is a macrolide antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It is available only by prescription in 3 different forms: granules for oral suspension, film-coated tablets and powder for concentrate for solution for infusion. The active substance of Klacid is clarithromycin, a bacteriostatic antibiotic. What are the indications for the use of Klacid? Are there any contraindications to the use of this preparation? How to properly dose it? Can its use cause side effects?
Klacid – general characteristics of the drug
Klacid is macrolide antibiotic showing a broad spectrum of activity. It can be purchased in pharmacies only upon presentation of a valid prescription. It is available in three different variants, and their choice in treatment depends on the patient’s age and the form of treatment:
- granules for oral suspension – indicated for use in children from 6 months to 12 years of age;
- coated tablets – indicated for use in adults and children 12 years of age and older;
- powder for concentrate for solution for infusion – indicated for use in adults and children aged 12 years and older only in inpatient treatment.
The active substance of the antibiotic is clarithromycin. It is a compound that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and multiplication. Thanks to this, it stops the development of infection and belongs to the group of bacteriostatic antibiotics.
The appearance of the drug also depends on the chosen variant:
- granules for oral suspension – granules which, when mixed with water, form a suspension. Properly prepared suspension may contain small, undissolved lumps that resemble sugar crystals. This is due to the properties of the drug and should not be alarming. The bottle with the granules is made of HDPE. The capacities of 50 ml, 60 ml or 100 ml are available. The package includes a dispenser in the form of a syringe;
- coated tablets – these are yellow and oval tablets. The package may contain 10 tablets, 14 tablets, 20 tablets or 42 tablets;
- powder for concentrate for solution for infusion – the powder is white to off-white. The package containing the drug is a 15 ml type I Ph.Eur. Colorless glass vial, sealed with a gray halobutyl freeze-dried silicone stopper.
The entity responsible for the distribution of Klacid is Mylan Healthcare Sp. z o. o. The Mylan concern was established in 1961. Mylan initially operated as a pharmaceutical wholesaler that supplied drugs to customers in smaller towns. Today, Mylan is a leader among pharmaceutical companies, and their products are available in 145 countries and territories.
In addition, there are other preparations available on the pharmaceutical market under the name Klacid, the manufacturer or distributor of which are:
- PharmaVitae Sp. z o. o. sp. k. – the offer of tablets with modified release. PharmaVitae is a company dealing with parallel import on the Polish pharmaceutical market. Since 2011, the company has been building a leading position, cooperating with business partners from the European Union, as well as expanding the portfolio of imported medicinal products, private labels and logistics services. The company’s head office is located in Warsaw;
- InPharm Sp. z o. o. – the offer includes extended release tablets and modified release tablets. InPharm is a company that has been dealing with parallel import and distribution of medicinal products, medical devices and cosmetics since 2006. The company has an extensive network of suppliers throughout the European Union. The company’s head office is located in Warsaw;
- Delfarma Sp. z o. o. – the offer includes extended release tablets and modified release tablets. Delfarma is a leader in parallel import. This company supplies the Polish market with cheaper drugs and thus significantly contributes to the reduction of health care costs. The Delfarma company was established in 2004 and offers over 500 drugs. The company’s head office is located in Łódź;
- Medezin Sp. z o. o. – modified release tablets on offer. Medezin is a company that offers a wide range of services in the area of distribution, storage, manufacturing in the field of repackaging, import, labeling for clinical trials, transport, marketing and sales for manufacturers and a selection of medicinal products for wholesalers and pharmacies;
What are bacteriostatic antibiotics and what are the indications for their use? Read: Macrolides
Klacid – composition and action of the drug
Klacid is an antibiotic used against bacterial infections. The main ingredient and active ingredient of this preparation is clarithromycin.
Clarithromycin belongs to the macrolide antibiotics and is a derivative of erythromycin. Macrolides are bacteriostatic antibiotics that act by inhibiting protein biosynthesis in bacterial cells by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and interfering with protein chain elongation. This means that the bacteria are not killed, but only cell growth is inhibited.
Clarithromycin has a broad spectrum of activity, which means that it is effective against many species of bacteria. In some infections, it has better antimicrobial properties than erythromycin. In addition, clarithromycin, when used in combination with other drugs, plays an important role in the treatment of infections caused by mycobacteria, e.g. mycobacteria, including atypical mycobacteria.
After oral administration, clarithromycin is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, the maximum concentration in the blood is reached 2-3 hours after taking the drug. Then it is metabolized in the liver. The biological half-life of clarithromycin is approximately 4,6 hours and that of the active metabolite is approximately 8 hours. This substance is excreted in urine and feces.
In addition, the drug Klacid includes auxiliary substances. The correct composition depends on the variant selected for treatment:
- granules for oral suspension – carbomers (Carbopol 974P), povidone K90, hypromellose phthalate (HP-55), castor oil, colloidal anhydrous silica, maltodextrin, sucrose, xanthan gum, flavor “Fruit Punch”, potassium sorbate, acid lemon anhydrous and titanium dioxide (E 171);
- coated tablets – sodium croscarmellose, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, povidone (K29-32), stearic acid, magnesium stearate, talc, hypromellose, sorbitol monooleate, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide, vanillin, quinoline yellow (E 104) (aluminum lake) , hydroxypropyl cellulose, sorbic acid, hypromellose, propylene glycol, sorbic acid and vanillin;
- powder for concentrate for solution for infusion – lactobionic acid and sodium hydroxide to the appropriate pH.
What are antibiotics, how do they work and when are they worth using? Check: Antibiotics – types, action, use and side effects [EXPLAIN]
Klacid – indications for the use of the drug
Klacid is an antibiotic that is used in cases of infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to clarithromycin. Your doctor may recommend this medication, especially for the treatment of:
- upper respiratory tract infections – e.g. streptococcal pharyngitis, sinusitis;
- lower respiratory tract infections – e.g. bronchitis, pneumonia;
- acute otitis media;
- skin and soft tissue infections – e.g. contagious impetigo, folliculitis, cellulitis, abscesses;
- disseminated or localized mycobacterial infections.
In HIV-infected patients, Klacid is indicated for the prevention of disseminated infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).
How do you recognize an upper respiratory infection? Read on: The first symptoms of a respiratory infection that must not be ignored
Klacid – contraindications to the use of the drug
Klacid, despite its effectiveness in the treatment of bacterial infections, cannot be used by every patient struggling with this type of ailments.
Contraindications to the use of Klacid are:
- allergic to clarithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics such as azithromycin, erythromycin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine;
- your use of ergot alkaloids such as ergotamine or dihydroergotamine (medicines used to treat migraines, for example) or oral midazolam (a medicine for anxiety and insomnia);
- use of drugs that can cause serious heart rhythm disturbances;
- the use of astemizole or terfenadine (medicines for allergies), cisapride or domperidone (a medicine for digestive disorders), pimozide (a medicine for mental disorders), as their simultaneous use with Klacid can cause serious heart rhythm problems;
- the use of ticagrelor (a drug that inhibits platelet aggregation) or ranolazine (a heart drug);
- too little potassium or magnesium in the blood (hypokalaemia or hypomagnesaemia);
- use of lovastatin, simvastatin (drugs from the group of statins, used to lower blood cholesterol);
- severe liver failure with concomitant renal failure;
- abnormal heart rhythm (ventricular arrhythmias including torsade de pointes) or an electrocardiogram (ECG, recording of electrical activity in the heart) known as ‘long QT syndrome’;
- the use of colchicine (a medicine to treat gout);
- taking medicines containing lomitapide.
What should you know about drug hypersensitivity? Check: Drugs are also allergenic
Klacid – precautions
Before and during the use of Klacid, follow the precautions included in the package leaflet.
The warnings and precautions contained in the package leaflet refer mainly to the use of the drug by:
- pregnant women and women who suspect pregnancy;
- patients with renal or hepatic impairment;
- patients with diagnosed coronary artery disease, severe heart failure or slow heart function.
In addition, special care should be taken if unusual symptoms occur during the use of the drug:
- severe hypersensitivity reactions such as maculopapular rash, urticaria, ecchymosis, laryngeal edema, bronchospasm. You should immediately contact a doctor who will administer appropriate treatment;
- diarrhea, especially if it is acute or prolonged. Please tell your doctor as soon as possible. If necessary, your doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. Antidiarrheal drugs should not be used;
- osymptoms of liver dysfunction such as anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, itching or sore stomach. Discontinue treatment and consult a physician;
- new infection (superinfection) Clarithromycin-insensitive bacteria or fungi, especially during long-term use of the antibiotic. Your doctor will recommend appropriate treatment.
It should also be remembered that Klacid should not be used after the expiry date which is stated on the box. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. The drug should also not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. It’s best to ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines you no longer use.
What should you know about proper drug storage? Check: Medications that are stored wrongly are poisonous
Klacid – dosage and method of use
Always use Klacid antibiotic exactly as described in the package leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
The correct dosage as well as the method of using Klacid depend on the form of the drug selected for the treatment.
Klacid granules is a form of the drug intended primarily for children from 6 months to 12 years of age. If the drug is used in children, it is usually used the dose of Klacid suspension is 7,5 mg / kg body weight twice a day. The maximum dose of the drug is 500 mg twice a day. The duration of treatment is usually 5 to 10 days, depending on the type of bacteria and the course of the disease. Take the drug twice a day (preferably in the morning and evening) with or without food. The drug is administered orally and can be administered with milk.
The table below shows the dosage of the suspension (125 mg / 5 ml) in children according to their body weight:
| DOSAGE IN CHILDREN depending on body weight | ||
|---|---|---|
| The child’s body weight | The child’s body weight | The child’s body weight |
| 8 11-kg | 8 11-kg | 8 11-kg |
| 12 19-kg | 12 19-kg | 12 19-kg |
| 20 29-kg | 20 29-kg | 20 29-kg |
| 30 40-kg | 30 40-kg | 30 40-kg |
| Children weighing less than 8 kg are given a dose based on body weight (7,5 mg / kg body weight twice a day). | ||
It should be remembered that pharmacies also offer a variant of the 250 mg / 5 ml suspension, in which the doses are correspondingly lower.
When Klacid granules are used in adults, the recommended dose of clarithromycin is 250 mg, i.e. 10 ml of suspension twice a day. In severe infections, the dose of clarithromycin may be increased to 500 mg or 20 ml of suspension twice daily.
Aby properly prepare the granulate suspension, boil the water, then cool it to room temperature. Pour the boiled and cooled water into the bottle with the drug, up to the line marked on the label, and shake it vigorously. If necessary, top up with water up to the line marked on the label. Before each use, the suspension should be shaken until the particles are uniformly dispersed. Properly prepared suspension may contain small, undissolved lumps that resemble sugar crystals. This is due to the properties of the drug and should not be alarming. The prepared suspension should not be stored in a refrigerator.
In the case of Klacid film-coated tablets the correct dose depends on the condition being treated, the patient’s age and the concentration of the active substance in one tablet (250 mg and 500 mg are available).
Treatment of infections of the respiratory tract, skin and soft tissues, acute otitis media:
- 250 mg tablet – one 250 mg tablet twice a day (every 12 hours). In severe infections, your doctor may increase the dose to two 250 mg tablets (i.e. 500 mg) twice a day (every 12 hours). Usually treatment duration is 5 to 14 days, except for pneumonia and sinusitis, where treatment duration is 6 to 14 days;
- 500 mg tablet – in severe infections, one 500 mg tablet twice a day (every 12 hours). Treatment usually lasts for 5 to 14 days, except for pneumonia and sinusitis, where treatment duration is 6 to 14 days.
To treat infections of the teeth and mouth:
- 250 mg tablet – one 250 mg tablet twice a day (every 12 hours). Treatment usually takes 5 days.
Treatment of a mycobacterial infection:
- 250 mg tablet – the recommended adult dose is two 250 mg tablets (i.e. 500 mg) twice a day. Treatment of disseminated infection in AIDS patients should be continued for as long as prescribed by the doctor. Klacid should be used simultaneously with other drugs active against Mycobacterium. Treatment of other non-tuberculous infections with Mycobacterium should be continued as directed by your doctor.
- 500 mg tablet – the recommended dose in adults is one 500 mg tablet twice a day.
To prevent MAC infections:
- 250 mg tablet – the recommended adult dose is two 250 mg tablets (i.e. 500 mg) twice a day;
- 500 mg tablet – the recommended dose in adults is one 500 mg tablet twice a day.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection:
- 250 mg tablet – in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori infection, clarithromycin can be administered for 7 to 14 days at a dose of 500 mg twice a day;
- 500 mg tablet – in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori infection, clarithromycin can be administered for 7 to 14 days at a dose of 500 mg twice a day.
The drug is administered to the patient orally. Swallow the Klacid tablet whole with a drink of water. You should not chew or suck the tablet. The tablets can be taken with food or on an empty stomach.
In the case of Klacid powder for concentrate for solution for infusion the recommended daily dose of clarithromycin for infusion is 1 gram divided into two doses of 500 mg.
The powder in the vial is dissolved and then diluted with a suitable solvent. The dose is given into a vein as an infusion over a period of at least 60 minutes. The drug should not be given as a single, rapid injection or by the intramuscular route. Depending on the severity of the infection, the administration of clarithromycin by intravenous infusion is limited to 2-5 days, and the oral formulation should be started as soon as possible.
How to take medication correctly? Check: How to take medications effectively?
Klacid – side effects
Klacid, like any other drug, may cause side effects in patients. It is important to report any suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product so that the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product can be monitored.
The frequency classification of adverse body reactions (ADRs) is based on the following principles: very common (≥1 / 10), common (≥1 / 100 to
Side effects that may occur and require immediate discontinuation of the drug and consultation of your doctor include:
- anaphylactic shock – acute life-threatening allergic reaction with symptoms including confusion, pale skin, drop in blood pressure, sweating, low urine production, rapid breathing, weakness and fainting
- allergic reactions Rash (common), itching, hives (uncommon), angioedema of the face, tongue, lips, eyes and throat, difficulty breathing
- severe skin reactions – Acute generalized pustular eruption – a red, scaly rash with lumps under the skin and blisters, bullous erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) with sudden onset of fever and pustules that resolve quickly and spontaneously upon discontinuation of treatment, severe disease such as blisters and erosions on the skin, mouth, eyes and genitals, fever and joint pain, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), DRESS syndrome;
- severe or prolonged diarrhea possibly with blood or mucus in the stools (pseudomembranous colitis). Diarrhea may occur up to two months after stopping treatment with clarithromycin;
- yellowing of the skin (jaundice), skin irritation, light-colored stools, dark-colored urine, abdominal tenderness or loss of appetite. These may be signs of liver failure;
- severe upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and fever. These could be symptoms of acute pancreatitis.
Due to the frequency of side effects, the following are indicated:
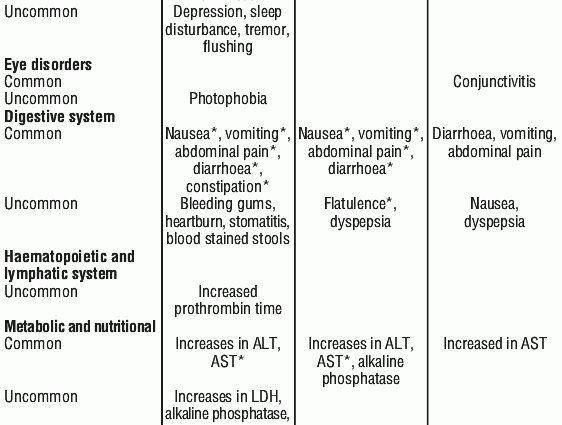
- common side effects after taking Klacid (affects 1 to 10 patients in 100): insomnia, dysgeusia, headache, diarrhea, vomiting, indigestion, nausea, abdominal pain, abnormal liver function tests and excessive sweating;
- uncommon side effects after taking Klacid (affects 1 to 10 out of 1000 people): infection, candidiasis (mycosis), vaginal infection, decreased white blood cells, increased platelet count, anorexia, decreased appetite, restlessness, nervousness, dizziness, sleepiness, tremors, balance disorder, Hearing loss, tinnitus, palpitations, ECG changes (QT prolongation), gastritis, stomatitis, glossitis, constipation, dry mouth, belching, flatulence, increased levels of liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase activity, maculopapular rash, muscle spasms, fever, asthenia (weakness, lack of strength);
- the frequency of side effects is unknown after the use of Klacid: erysipelas, agranulocytosis (decreased number of blood granulocytes), thrombocytopenia (decreased number of blood platelets), acne, psychotic disorder, confusional state, depersonalization, depression, confusion, hallucinations, abnormal dreams, mania, convulsions, lack of taste, sense of smell, loss smell, paresthesia (numbness, tingling), deafness, torsade de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, haemorrhage, tongue discoloration, tooth discoloration, myopathy (muscle disease with muscle weakness), kidney failure, interstitial nephritis, change in diagnostic test results (increase in the value of the international normalized ratio (INR), prolonged prothrombin time, abnormal color of urine)
In addition, the package leaflet indicates that in adult patients with immunosuppression, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, changes in taste, constipation, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gas, dry mouth, headache, hearing impairment, rash, shortness of breath, insomnia, laboratory abnormalities: increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increase in blood urea nitrogen and decrease in platelets and white blood cells.
The occurrence of side effects after the use of Klacid can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring Adverse Effects of Medicinal Products, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw.
What causes an antibiotic rash? Read on: Antibiotic rash – is it an allergy symptom?
Klacid – interactions with other drugs
Before starting treatment with Klacid, please inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you are taking or have taken recently. You should also inform what medications the patient plans to take in the near future.
The active substance of Klacid may interact with other drugs or substances contained in medical products, which was mentioned in the contraindications to the use of this antibiotic. Contraindicated drugs or substances include:
- ergot alkaloids such as ergotamine or dihydroergotamine – medicines used for migraine treatment, among others;
- astemizole or terfenadine – drugs for allergies;
- cisapride or domperidone – a drug used in gastrointestinal disorders;
- pimozide – a drug used to treat mental disorders;
- ticagrelor, ranolazine – drugs used in diseases of the heart and circulation;
- colchicine – a drug for gout;
- statins – lovastatin, simvastatin, i.e. drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels;
- Oral midazolam – a drug for anxiety or insomnia.
In addition, you should inform your doctor if you are taking any of the medicines listed below, as special care is required when using them with Klacid, or the indicated dosage has to be changed:
- rifampicin, rifapentine, rifabutin – antibiotics used to treat tuberculosis;
- fluconazole, itraconazole – antifungal drugs;
- atazanavir, efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine, ritonavir, saquinavir, zidovudine – used to treat HIV infection;
- digoxin, quinidine, disopyramide, verapamil, amlodipine, diltiazem – used to treat abnormal heart rhythms or high blood pressure;
- alprazolam, triazolam, midazolam administered intravenously or onto the oral mucosa – drugs used in anxiety or insomnia;
- warfarin or any other oral anticoagulant;
- quetiapine or any other atypical antipsychotic medicine
- carbamazepine, valproate, phenytoin – antiepileptic drugs;
- methylprednisolone – an anti-inflammatory drug;
- omeprazole – a drug that reduces the secretion of gastric acid;
- cilostazol – a drug used in intermittent claudication, which is manifested by pain in the muscles of the lower extremities during exercise and disappears after a short rest;
- cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus – drugs used, inter alia, after transplants;
- sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil – drugs used in erectile dysfunction;
- ibrutinib or vinblastine – drugs used in cancer chemotherapy;
- theophylline – a drug used in bronchial asthma;
- Tolterodine – a drug used in urinary incontinence;
- phenobarbital – an anticonvulsant drug;
- St. John’s Wort – a herbal remedy used for mild depression;
- sulfonylurea, nateglinide, repaglinide, insulin – drugs used in diabetes;
- ototoxic drugs (damaging hearing), especially aminoglycosides, e.g. gentamicin.
Which drugs should never be combined with each other? Check: Dangerous interactions
Klacid and pregnancy and breastfeeding
The use of any medications or dietary supplements during pregnancy requires consultation with the attending physician. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking Klacid.
The safety of clarithromycin for use during pregnancy and lactation has not yet been established. Klacid may be used during pregnancy only when, in the doctor’s opinion, the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. As clarithromycin passes into breast milk, special care should be taken by breastfeeding women when taking this antibiotic.
What is worth knowing about proper supplementation during pregnancy? Check: Conscious choices. Diet and supplementation in pregnancy
Klacid – scene
The price of the drug Klacid may differ depending on the city in which the antibiotic will be purchased or the pharmacy chosen by the patient. The price of the product also depends on the selected form of the drug and the content of the active substance.
Price of Klacid granules for oral suspension:
- 100 ml of the drug, 25 mg / ml (125 mg / 5 ml) – approx. PLN 28-30, reimbursement price approx. PLN 15;
- 60 ml of the drug, 25 mg / ml (125 mg / 5 ml) – approx. PLN 18, reimbursement price approx. PLN 10;
- 100 ml of the drug, 50 mg / ml (250 mg / 5 ml) – approx. PLN 54, reimbursement price approx. PLN 27;
- 60 ml of the drug, 50 mg / ml (250 mg / 5 ml) – about PLN 34, the price after reimbursement is about PLN 17.
Price of the drug Klacid in coated tablets:
- 10 tablets of 250 mg – about PLN 15, the price after reimbursement is about PLN 10;
- 14 tablets of 250 mg – about PLN 20, the price after reimbursement is about PLN 14;
- 14 tablets of 500 mg – about PLN 40, the price after reimbursement is about PLN 27.
How much money does the average Pole spend on treatment? Check: The Pole is not expected to see a doctor