Contents
Distant expeditions to exotic parts of the world are the dream of many travelers. Tropics is not only about beautiful views and travel adventures. Deadly diseases lurk in the heart of the jungle.
Shutterstock See the gallery 8
- Diet for hypertension
Doctors recommend a diet that saves you from premature death. It is not complicated, but requires consistency. The consequences of hypertension are …
- Put two fingers together. A simple test can reveal heart disease, liver disease, and lung cancer
Bring the fingernails of the index fingers together with the highest joints (as if you were placing your palms in the sign of the heart). What you see? If you see a crack in the shape of …
- Parkinson’s disease – causes, symptoms, treatment
Neurodegeneration, the progressive degeneration of nerve cells, underlies many diseases of the nervous system that lead to the death of neurons. IN…
1/ 8 Viruses
New, previously unknown to medicine, pathogenic microorganisms are characteristic of tropical areas of Africa and South America. This phenomenon is related to human interference in previously virgin ecosystems. Some scientists believe that hitherto unknown viruses that kill humans exist in the depths of the Amazonian forests.
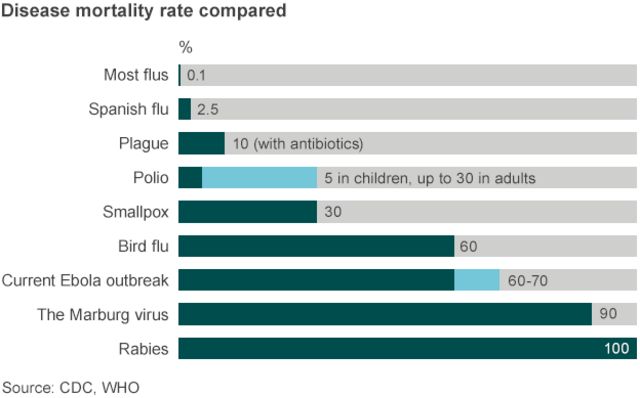
2/ 8 Marburg and Ebola viruses
The initial symptoms of infection are similar to flu infection, i.e. headaches, high fever, general weakness and breakdown, diarrhea and vomiting. This condition lasts for about a week. Then symptoms of hemorrhagic diathesis develop, i.e. a tendency to numerous minor and major bleeding, mainly from the mucous membranes of the mouth, conjunctiva, nose, gastrointestinal tract and lungs. The process is triggered by a reduction in the level of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia). Mortality can be 25-90 percent. Death occurs within a dozen or so days, usually as a result of shock caused by blood loss. These viruses destroy various organs, but wreak the greatest havoc on the liver and spleen. Infection spreads through the bloodstream.
3/8 Arenawirusy
Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever can also be caused by Arenaviruses. One of them is the Lassa virus, the reservoir of which is the rat found in West Africa. Infection occurs as a result of contact with rat faeces, which can take place, for example, during agricultural work in the areas where this rodent lives. While working, agricultural machinery can spray an aerosol of soil manure or even the blood of rats that have entered the combine during harvesting. The aerosol particles are inhaled and deposited in the bronchi. Symptoms are similar to those of Marburg or Ebola viruses. Machupo arenavirus is also similar. Again, the disease spreads through the excreta of rodents.
4/ 8 HIV virus
It is possible that there are viruses somewhere more deadly than all known so far, waiting only for contact with humans. The known HIV virus probably comes from monkeys. They described a very similar virus, SIV, being a “relative of HIV”. It is likely that the SIV mutation resulted in HIV attacking humans.
5/8 Fever and malaria
Another disease caused by viruses is yellow fever. Occurs in Africa and South America. It begins with malaise, headache, and an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees Celsius. Chills may appear. After a few days, jaundice develops, and in some cases, renal failure and symptoms of bleeding disorders. The disease may also be mild. The most common in the tropics is an infectious parasitic disease – malaria. A few days after the mosquito bite, fever with chills, weakness, muscle and joint pain, but also diarrhea, nausea, or disturbed consciousness may appear. Unfortunately, it happens that the disease is severe and violent, and even fatal, especially in people suffering from the disease for the first time in their life.
Yellow fever is the only disease listed against which you can be vaccinated. The vaccine costs about PLN 100 and is valid for 10 years. There is no immunization against malaria, but you can protect yourself against the disease or its severe course by taking prescription anti-malarial drugs (before, during and after departure). There are no vaccinations or medications for diseases caused by Ebola, Marburg and Lassa viruses.
7/ 8 The Yellow Book is required in many African and South American countries
International Certificate of Immunization, i.e. The “yellow book” concerns mainly vaccinations against yellow fever, but it is worth entering all vaccinations made before departure. Proof of vaccination is required for entry into many African countries. Some countries require such proof if you come from countries where the disease occurs or even from those who are transiting through these zones. For example, if we are going from Poland to Venezuela, we do not have to vaccinate, but if we go from Venezuela to Brazil, we must be vaccinated because the Brazilian authorities have introduced such a regulation.
8/ 8 Report any symptoms after returning from the tropics to the doctor
These diseases raise legitimate fear because there is no effective medicine or vaccine for them. Symptoms can be nightmare – in extreme cases, we deal with a patient bleeding simultaneously from the nose, eyes, anus, mouth, lungs, in whom a slight touch of the skin causes bleeding. If, after returning from the tropics, you feel even the slightest discomfort, you should immediately see a doctor and tell us where we have been and how long we have returned to the country. Viral hemorrhagic fever can be ruled out three weeks after the alarming symptoms appear, but even then, for example, malaria cannot be ruled out – not so spectacular, but equally dangerous.