Contents
Amateur gardeners successfully grow varieties and hybrids of apple trees intended for cultivation on an industrial scale in their backyards. In them, summer residents are attracted by the taste of fruits, their external presentability, large-fruitedness and high yields. All these criteria are met by the Jonagold apple tree, which is deservedly popular all over the world.
History of breeding
Jonagold (Jonagold) – an apple tree native to the United States, specifically – from the Geneva breeding station in the state of New York. It was created in 1943, the result of crossing the very famous “industrial” varieties Jonathan (Jonathan) and Golden Delicious (Golden Delicious).
For some reason, the achievement of local breeders was not immediately appreciated at home. Variety tests were completed by the mid-50s, but the Jonagold apple tree did not cause much enthusiasm. But when in the 60s she came to Europe, she made a splash. The first “plantations” appeared in Belgium and Holland.
The apple tree was brought to the USSR in the mid-70s. However, all attempts to adapt it to a temperate and more severe climate have failed. It entered the domestic State Register of Breeding Achievements only in 2016 at the request of Sad-Gigant JSC.
Description of the Jonagold apple tree with a photo
Everyone knows what Jonagold apples look like – they are often found on store shelves. But the tree itself does not have any “unique” features; it will not be possible for a non-specialist to “recognize” it.
tree appearance
The apple tree is a tree characterized by rapid growth and a powerful root system. The crown is not too dense, quite compact, almost independently takes a shape close to round-oval. The branches extend from the trunk at almost a right angle. The leaves are large, noticeably elongated.

Depending on the type of rootstock, the height of the tree varies between 3-6 m.
Description of fruits
Apples are one-dimensional, symmetrical, regular round-conical shape. The mass varies between 170-210 g, the average value is 185 g, the “record” is 240-250 g. Sometimes there is a slight “ribbing” of the surface.
The skin of apples is thin, but quite strong and elastic. This provides them with good keeping quality and transportability.
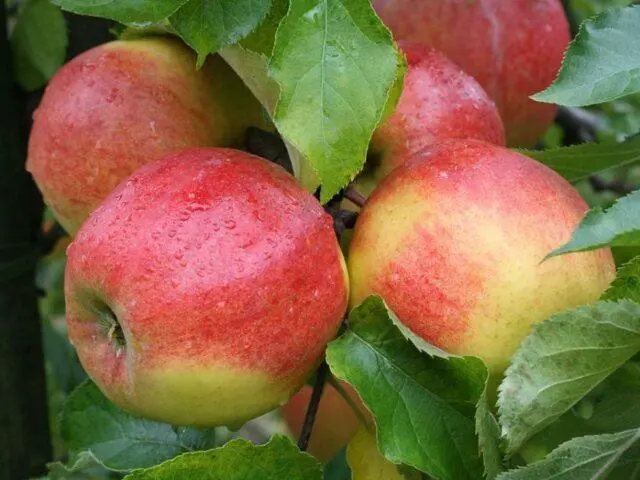

The skin of apples is smooth to the touch, a glossy sheen appears in the sun
Characteristic of the variety
Jonagold apples are very tasty. But this is not the only characteristic that provides them with sustainable popularity.
Jonagold apple flavor
The pulp is yellowish-creamy, fine-grained on the cut, highly juicy, dense, even “rough”. Ripe fruits are characterized by a rich-sweet taste with a slight balancing acidity and “wine” notes.
The taste qualities of Jonagold apples are estimated by professional tasters at 4,6-4,8 points. And in the State Register, the maximum for this indicator is generally indicated – 5 points out of five possible. This is a variety from the dessert category.
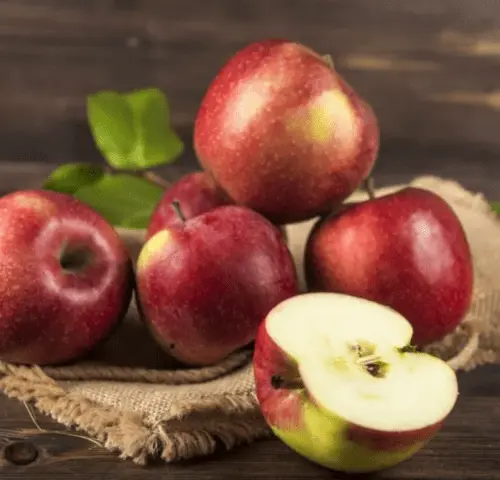

The pulp has a strong aroma and a pronounced spicy-tart aftertaste.
Terms of maturation
In terms of ripening, the Jonagold apple tree is one of the late-ripening ones. Fruits are harvested at the stage of technical ripeness, around the 20th of September. It takes 3-3,5 months to ripen, after which they can be eaten.
Productivity
When grown on an industrial scale, the yield of adult Jonagold apple trees is about 225 centners / ha. Trees begin fruiting at the age of 3-4 years. The first harvest is small – 5-7 kg.
They reach their “peak” by the age of 12-15. An amateur gardener can count on 40-50 kg of apples per season. Professional farmers raise this figure to 60-70 kg. Weather conditions have little effect on the yield.
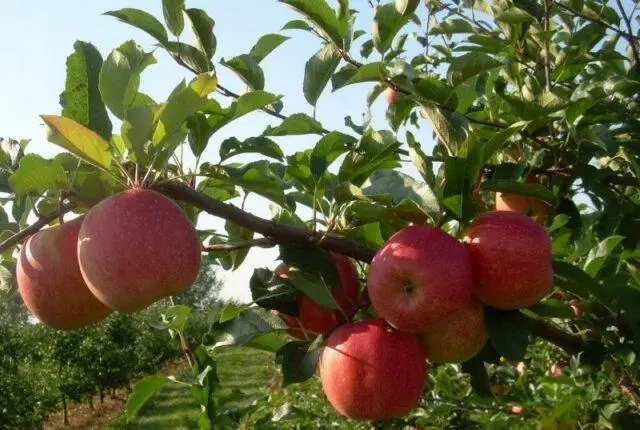

Jonagold apple trees bear fruit almost annually, the “rest” seasons for them are an extremely rare occurrence.
Frost resistance of the apple tree Jonagold
The cold resistance of the Jonagold apple tree is below average. It is able to overwinter without damage at about -10 ° C. Even worse, it reacts to sudden changes in temperature, its strong fall, sudden thaws.
Apple tree pollinators Jonagold
Jonagold is an apple tree from the triploid category. This means that without the presence of pollinating trees, 10-20% of flowers turn into fruiting ovaries. The best “companions” for her are other well-known “industrial” varieties:
- Idared;
- Champion;
- Gloucester;
- Spartan;
- Melrose;
- Jonathan;
- Elstar.
Each Jonagold apple tree needs at least two pollinator trees. The distance between them is no more than 20 m.
Growing regions
According to the results of variety trials, the Jonagold apple tree is recognized as the most suitable for planting in the North Caucasus and the Kaliningrad region. With a high degree of probability, she will not survive winters in other regions. Of the former Soviet republics, the Jonagold apple tree has adapted best in Moldova and Ukraine.
Resistance to diseases
Resistance to fungal diseases in Jonagold apple trees also leaves much to be desired. Especially often they become infected with scab and powdery mildew. Pests do not show any particular “objective” interest in them, but in the event of a “mass” invasion of the site, these apple trees will not bypass either.
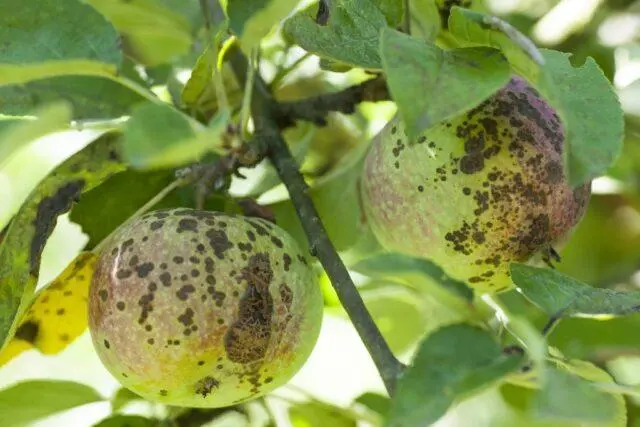

Fruit affected by scab should not be eaten.
Advantages and disadvantages
Breeders are willing to experiment with the Jonagold variety. Now there are more than a hundred of its “clones”, which differ mainly in the color of the fruit. This is evident from the description and photo of one of the most popular varieties – Jonagold Decosta apple trees.
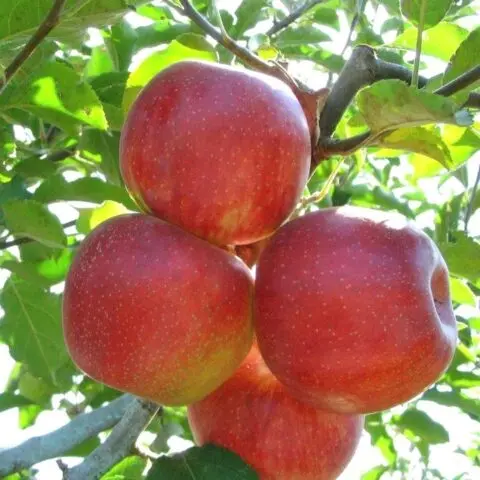

Jonagold apples are mainly consumed fresh.
Pros:
- comparative unpretentiousness in care;
- precociousness;
- consistently high yields, practically independent of the vagaries of the weather;
- annual fruiting;
- high keeping quality and transportability;
- external presentability, large size of apples;
- excellent taste of fruits, versatility of their purpose.
Cons:
- relatively low cold resistance;
- insufficiently high resistance to fungal diseases;
- the need to plant nearby apple pollinators.
Planting an apple tree Jonagold
Both autumn and spring planting of the Jonagold apple tree is practiced. The climate in the regions where it is grown is quite mild, so it all depends on the preferences of the gardener.
The procedure follows a standard algorithm. However, it is impossible to get good yields if you choose the wrong place for planting the Jonagold apple tree. It must meet the following criteria:
- good illuminance;
- regular access to fresh air in the presence of protection from drafts and sudden gusts of wind;
- fertile, but at the same time relatively loose and “light” substrate;
- neutral or slightly acidic soil pH (5.5-6.5);
- lack of prerequisites for permanent waterlogging of the soil.
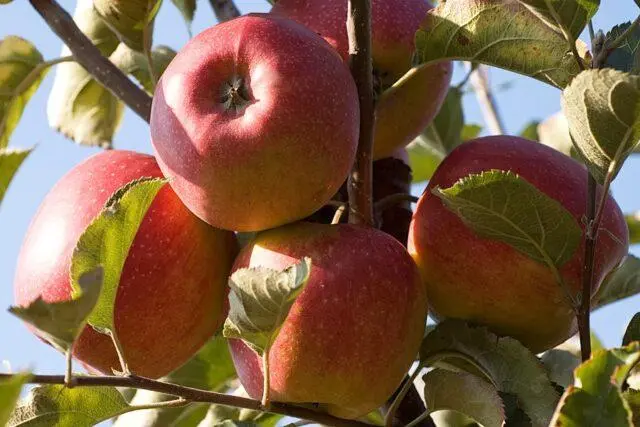

In the shade, the yield of the Jonagold apple tree drops noticeably, the taste of the fruit deteriorates.
The approximate dimensions of the landing pit are 50-60 cm in depth and in diameter. They always dig it in advance, apply organic and mineral fertilizers in the required volumes. Then, depending on the chosen landing time, the pit is left to “stand” for 3-4 weeks or for the whole winter.
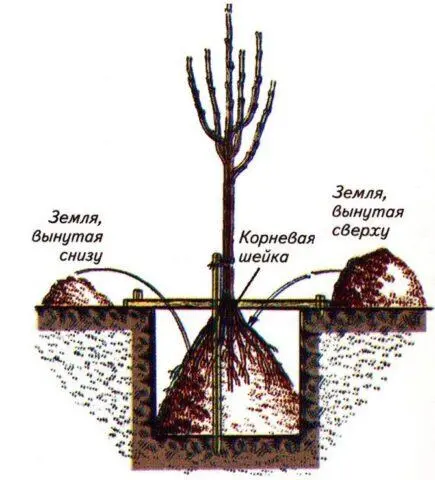
The main thing when planting is not to “bury” the root collar
Jonagold apple tree care
Growing an apple tree Jonagold does not require particularly complex actions from the gardener, deep knowledge and specific skills in the field of agronomy. However, time and effort to care for the tree will have to be devoted regularly. It includes the following activities:
- Watering. The Jonagold apple tree has a fast growth rate, so it needs regular watering. In the absence of natural precipitation, the soil in the trunk circle is moistened every 15-20 days, in the heat – weekly. In the first year after planting, seedlings are watered every 4-5 days. The approximate norm for adult trees is 70-80 liters of water, for seedlings – 10-15 liters.
- Loosening and weeding. If the trunk circle is not mulched, the soil is loosened the next day after each watering, while weeding out. Mulch allows you to abandon these activities, as well as watering the apple tree less often.
- Top dressing. During the first season, the tree has enough nutrients introduced into the planting hole. Further, the Jonagold apple tree requires regular feeding: abundant annual fruiting greatly depletes it. Fertilizers are applied according to the standard scheme: nitrogen and humus at the beginning of the active growing season, complex products for fruit trees before and after flowering, phosphorus and potassium in preparation for winter.
- Pruning. The crown of the Jonagold apple tree is not particularly dense, so it is quite possible to limit yourself to sanitary pruning twice a year. It is also recommended to get rid of the least well-located branches in the fall – deformed, intertwining, thickening the crown, directed downwards.
- Preparing for winter. It should not be neglected even in regions with a mild climate. It is imperative to carry out water-charging irrigation, clean the near-trunk circle from debris, renew the mulch layer, whiten and “insulate” the base of the trunk.
- preventive treatments. During the season, they are held regularly, once every 2-3 weeks, especially if the weather is conducive to the activation of pathogens. Folk remedies are quite suitable for prevention; at the first suspicious symptoms, biological products and agrochemicals are used.

It is recommended to feed the Jonagold apple tree with specialized fertilizers with a balanced composition.
Collection and storage periods
Apples are harvested starting from the 20th of September. However, they reach consumer maturity only by December. Therefore, Jonagold is a winter apple tree.
To keep the crop as long as possible, you need to consider the following nuances:
- choose a dry day for fruit picking;
- remove apples by hand, along with the stalks;
- use air-permeable containers for storage;
- “isolate” each fruit, for example, by wrapping it in paper, sprinkling it with sawdust, shavings;
- provide optimal conditions.
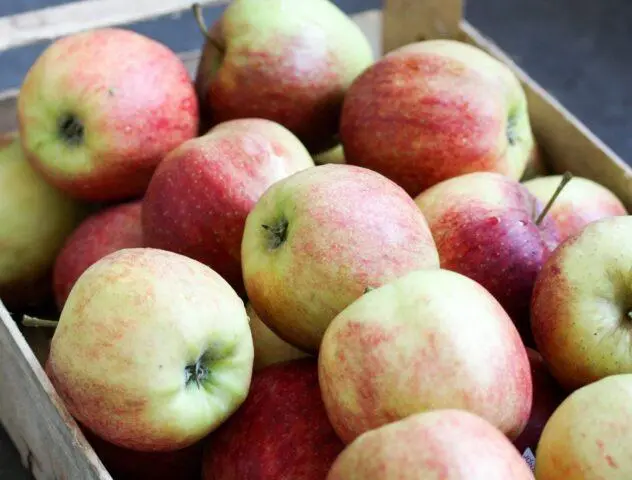

Fruit must be carefully sorted before storage.
Conclusion
The Jonagold apple tree is a popular “industrial” variety all over the world. When grown on personal plots, it also performs well: only insufficient frost resistance prevents widespread distribution in Our Country. In suitable conditions, apples are distinguished by outstanding taste and presentation.









