Contents
What is joint dysplasia?
The human musculoskeletal system begins to form in the prenatal period, at the fourth week of fetal development, and the end of this process occurs after childbirth, when the child takes its first steps. But the formation process is not always successful: at any stage, various violations of the growth and development of tissues are possible. It is these violations that are dysplasia.
Joint dysplasia is a phenomenon when certain disorders occur in the formation and development of the connective tissue, as a result of which it becomes weak, and this, in turn, leads to pathological joint mobility (hypermobility).
Causes of joint dysplasia
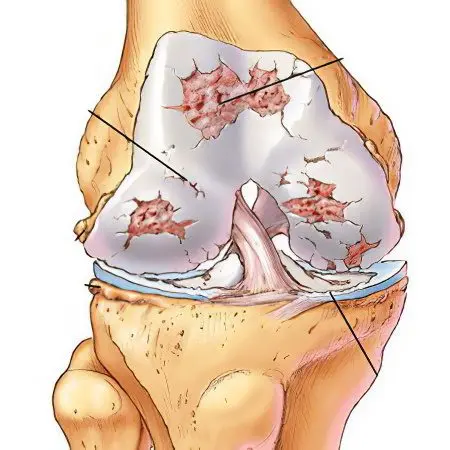
Disturbances in the development of connective tissue are possible at any stage, but joint dysplasia is predominantly a genetic pathology and often occurs in several representatives of different generations of the same genus. Improper formation of bones, ligaments and muscles can also occur during an unfavorable course of pregnancy – toxicosis, preeclampsia, infectious diseases and endocrine system disorders. Factors that negatively affect the intrauterine formation of the fetus are also a poor ecological environment, occupational hazards, an unhealthy lifestyle of a pregnant woman (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs), eating disorders, and so on. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of vitamins, minerals and proteins. Especially important is calcium, which is directly involved in the development and formation of connective tissue. The cause of dysplasia of the joints of the newborn can also be the advanced age of the parents.
Types of joint dysplasia
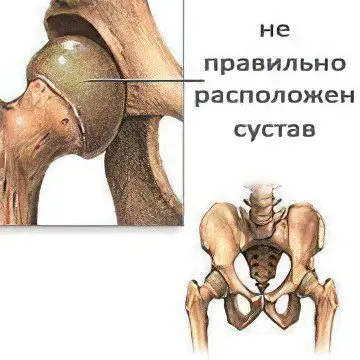
In the vast majority of cases, joint dysplasia affects the hip joint. This pathology belongs to 3 percent of all orthopedic diseases. It is noteworthy that it occurs mainly in girls born in the breech presentation. At the same time, the femoral head is not located in the acetabulum of the pelvic bones, where, it should be noted, it is the place.
However, this is not the only type of joint dysplasia. Common are subluxations and predislocations of the joints, dislocations of the femoral head, shortening the limb and disrupting the function of walking. Another type of joint dysplasia is a false joint that develops in the place where the femoral head was dislocated.
Joint dysplasia can be recognized by the asymmetry of the gluteal and inguinal folds, different lengths of the legs, gait disturbances, clicking of the joint during certain movements.
Treatment of joint dysplasia
Timely diagnosis and proper treatment can almost completely restore the function of the hip joints. For this, the child needs a systematic examination by an orthopedist. Examinations are carried out in the first, third, sixth, ninth and twelfth months of life. Otherwise, the disease will lead to gait and posture disorders, spinal curvature, pain syndrome, and so on.
Treatment consists of fixing the legs in a spread position so that the head of the femur can enter the glenoid cavity. Important in the treatment are also massage and exercise therapy, physiotherapy and drug therapy. But such conservative methods of treatment are effective only for children under one year old. The older the age, the more likely it is that the patient will be recommended surgery. But even several operations do not guarantee the restoration of the functions of the hip joints. Gait disorders most often remain a consequence of dysplasia for life.









