Contents
- Ankylosis
- Arthralgia
- Arthritis
- Arthropathy
- Chondrocalcinosis or pyrophosphate arthropathy
- Bechterew’s disease
- Still’s disease
- Infectarthritis or infectious nonspecific polyarthritis
- Periarthritis
- Gout
- Felty’s syndrome
- Synovioarthritis or synovitis
- Spondyloarthritis
- Arthrosis or osteoarthritis
- Hemarthrosis
- Hydroarthrosis
- Gonarthrosis
- Coxarthrosis
- osteochondrosis
- Pseudo- or neoarthrosis
- Spondyloarthrosis or facet arthropathy
- Epicondylosis
- Hip dysplasia
- Bursitis
- Hygroma
- Synovioma or synovialoma
- Systemic scleroderma or dermatosclerosis
Global computerization is increasingly immobilizing humanity. This adversely affects the musculoskeletal system.
Lack of physical activity destroys it.
Ankylosis
Ankylosis is the immobility of a joint due to fusion of the articulating articular surfaces.
Causes of ankylosis:
infection;
inflammatory arthritis;
arthrosis;
degeneration, prolonged immobilization – immobility due to plaster;
trauma, such as intra-articular fracture.
Ankylosis symptoms:
pain;
immobility in the joint.
The symptoms get worse gradually. At first the pain disturbs only in the mornings. Then the discomfort grows. Suddenly the pain disappears. This is an indicator that the deformation of the joint is completed. It is fixed in a bent, half-bent or straightened state.
Treatment of ankylosis
Conservative treatment may be used:
gymnastics;
massage;
manual therapy;
physiotherapy;
medicines: anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, hormones.
Otherwise, the operation is carried out:
redressing;
osteotomy;
arthroplasty;
endoprosthetics.
Arthralgia
Arthralgia is pain in the joint. This is a harbinger of the disease or the disease itself. Appears before the onset of organic damage. Occurs as a result of irritation of the neuroreceptors of the synovial bag. Polyarthralgia covers more than 5 joints at once. There is controversy about whether arthralgia can be considered a separate disease.
Causes of arthralgia:
infection;
tumor (paraneoplastic syndrome);
immune system disorders.
Symptoms of arthralgia:
pain of a different nature, localized or “wandering” through the joints;
myalgia – discomfort in the muscles;
ossalgia – a feeling of ache.
The symptoms of this disease are very variable.
Treatment of arthralgias
Reception or application of analgesics and elimination of the causes of diseases. Exercise therapy also helps to relieve pain – a physiotherapy complex, physiotherapy.
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation of the joint. Polyarthritis affects several joints at the same time.
Causes of arthritis:
metabolic disorder;
injury;
infection;
avitaminosis;
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or the genitourinary system.
Arthritis symptoms:
edema;
persistent pain syndrome;
stiffness in the morning;
inflammation;
hyperemia – redness of the skin;
fever.
arthritis treatment
Anti-inflammatory (Acetylsalicylic acid, Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Brufen) and painkillers (Capsaicin, Tylenol, Oxycodone, Methadone, Tramadol), hormones – corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Triamcinolone).
Arthropathy
Arthropathy is a type of arthritis, a secondary inflammatory disease. It is included in the triad of signs of Reiter’s syndrome or disease along with urethritis and conjunctivitis.
Causes of arthropathy:
changes in the level of pituitary and hypothalamus hormones;
allergy;
infection;
endocrine diseases;
disorders of nervous regulation.
Symptoms of arthropathy:
arthralgia – pain;
asymmetry of the lesion;
swelling in the periarticular region.
Treatment of arthropathies
The disease always occurs a second time, against the background of other diseases. Therefore, treatment is directed mainly to the underlying ailment. After getting rid of the underlying cause, arthropathy usually disappears.
Chondrocalcinosis or pyrophosphate arthropathy
Chondrocalcinosis is a type of arthropathy, accompanied by the deposition of salts in the articular cartilage.
The causes of chondrocalcinosis have not been precisely established, but an association with the following pathologies has been identified:
hyperparathyroidism
hemolytic anemia;
primary hyperparathyroidism;
hemochromatosis;
hemosiderosis;
hypothyroidism;
gout;
neuropathic arthropathy;
kidney stone disease;
Forestier’s syndrome;
ochronosis;
diabetes;
Wilson’s disease;
heredity;
injury;
surgical intervention.
Symptoms of chondrocalcinosis:
destruction of the surface of the articular cartilage;
pain syndrome;
edema;
limited mobility, morning stiffness;
hyperemia;
fever;
persistent increase in ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
dysfunction of the joints.
Treatment of chondrocalcinosis
Do intra-articular injections of corticosteroids. Crystals of calcium pyrophosphate salts provoke the development of inflammation. Therefore, the synovial fluid is washed to remove dangerous crystals. Physiotherapy and a course of massage are shown.
Bechterew’s disease
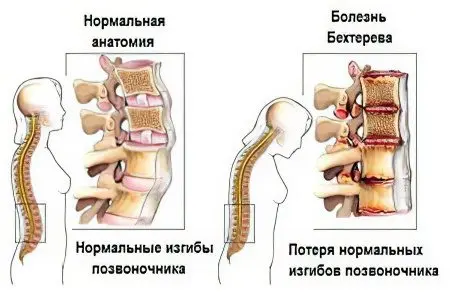
Bechterew’s disease is ankylosing spondylitis or Strumpell-Bechterew-Marie disease.
The causes of Bechterew’s disease have not been precisely established. A connection with heredity and some chronic infectious diseases has been revealed.
Symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis:
girdle pain radiating to the spine;
back muscle tension;
slouch;
stiffness;
ankylosing of intervertebral joints;
stop the growth of the chest;
irites;
iridocyclitis – inflammation of the eye;
aortitis – inflammation of the wall of the aorta;
insufficiency of aortic valves;
pericarditis – inflammation of the lining of the heart;
arrhythmia;
amyloidosis of the kidneys – a violation of protein metabolism.
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
Healing is impossible. The suffering of the patient is alleviated with the help of pain relief and reduction of inflammation. Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, manual therapy are also used. It is advisable to reduce physical activity and use an orthopedic mattress.
Still’s disease
Still’s disease is a type of arthritis. It appears in children under 16 years of age, and is accompanied by systemic inflammation.
The causes of Still’s disease have not been identified.
Symptoms of the disease:
multiple arthritis;
inflammatory changes in the synovial fluid;
internal edema of soft tissues;
accumulation of intra-articular effusion;
periarticular osteoporosis;
erosion or ankylosis of bones;
eye damage;
temperature increase;
pain;
intoxication syndrome;
the appearance of contractures;
stiffness;
hyperemia of the skin with subsequent pigmentation;
allergic rash;
hyperplasia of the lymph nodes;
enlargement of the liver and spleen;
progressive exhaustion;
lag in physical development;
amyotrophy;
tachycardia;
arterial hypotension;
sweating;
blood leukocytosis.
Treatment of Still’s disease
Medical methods are used. Additional measures are taken in accordance with the course of the disease.
Infectarthritis or infectious nonspecific polyarthritis

Infectarthritis is a type of arthritis, a common infectious-allergic disease.
The causes of infectarthritis are presumably established:
infection;
autoimmune tissue destruction;
heredity.
Symptoms of infection:
fever;
chills;
sweating;
weakness;
weight loss;
decrease in working capacity;
acute synovioarthritis;
enlargement and deformity of the joints;
soreness and limited movement;
temperature increase at the site of edema;
muscles in the affected area atrophy;
neutrophilic leukocytosis;
hypochromic anemia;
increased ESR;
fibrinogenemia;
globulinemia;
increased capillary permeability;
swollen lymph nodes;
subcutaneous “rheumatoid” nodules appear;
osteoporosis;
narrowing of joint spaces;
marginal bone growths.
Treatment of infectious arthritis
Pain is relieved by analgesics:
Acetylsalicylic acid;
Paracetamol;
Codeine.
Of the anti-inflammatory drugs, adrenosteroids and NSAIDs are used – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These include:
Benorilate;
Ibuprofen;
Naproxen;
Piroxicam;
Indomethacin;
mefenamic acid.
If there are problems with the immune system, immunosuppressants are prescribed, for example, Azathioprine. Physio- and occupational therapy is recommended. Deformities that greatly complicate the patient’s life are removed by surgery. Often artificial implants are inserted.
Periarthritis
Periarthritis is a type of arthritis, inflammation of the periarticular tissues:
capsules;
ligaments;
tendons;
the muscles.
Most often there are cases of shoulder or shoulder-blade inflammation.
Causes of periarthritis:
traumatic injuries;
overload;
hypothermia
Symptoms of periarthritis:
pain syndrome;
slight limitation of movement in the joint.
Treatment of periarthritis
Immobilization of the joint with a fixing bandage, physiotherapy, anesthesia help to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis. There is a deposition in the tissues of urate crystals – salts of uric acid. Gouty nodules – tophi – are formed due to impaired functioning of the kidneys. More often “bumps” appear near the joints.
Causes of gout:
malnutrition with excess offal;
drinking alcohol, especially beer;
stress;
heredity;
arterial hypertension;
hyperlipidemia;
an increase in the catabolism of purine nucleotides, for example, in antitumor therapy;
renal insufficiency.
Symptoms of gout:
pain;
redness;
temperature increase;
hyperuricemia – an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the blood;
obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, or hypertension.
Treating gout
The patient is admitted to the hospital. Inflammation is usually relieved with colchicine. The drug is effective, but use it with caution. Overdoses are very dangerous. They can also prescribe Indomethacin, Naproxen, Phenylbutazone, Etoricoxib. Prevention of urolithiasis is also important.
Felty’s syndrome

Felty’s syndrome is a type of arthritis, a complication of rheumatoid arthritis. There is disagreement about whether this syndrome is considered a disease or a symptom.
The cause of Felty’s syndrome is rheumatoid arthritis.
Disease symptoms:
general exhaustion;
increase in spleens – splenomegaly – and livers – hepatomegaly;
portal hypertension;
lymphadenopathy – swelling of the lymph nodes;
anemia;
leukopenia – a decrease in the number of leukocytes;
thrombocytopenia or thrombopenia – a decrease in the number of platelets;
granulocytopenia;
brown skin pigmentation;
the formation of rheumatoid nodules – focal seals of the skin;
“dry” Sjögren’s syndrome – dystrophy of the secretory glandular apparatus, accompanied by pathological dryness of all mucous membranes;
ulcers on the skin of the legs;
polyneuropathy.
Treatment of Felty’s syndrome
To block the process, drugs are administered and plasmapheresis is used. The destruction of cells is stopped with the help of splenectomy – the surgical removal of the spleen.
Synovioarthritis or synovitis
Synovioarthritis is a type of arthritis, inflammation of the synovium.
Causes of synovioarthritis:
getting an infection;
repetitive injury;
neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders;
allergic and chemical factors.
Synovioarthritis symptoms:
edema;
smoothing the contours of the joint;
increase in local temperature;
stiffness;
pain on palpation;
with the progression of the disease, the nature of the inflammatory effusion changes;
purulent form is accompanied by fever.
Treatment of synovioarthritis
The diseased joint needs complete rest, it is immobilized with special means. Apply dry heat. With excessive accumulation of synovial fluid, punctures with lavage are performed.
Spondyloarthritis
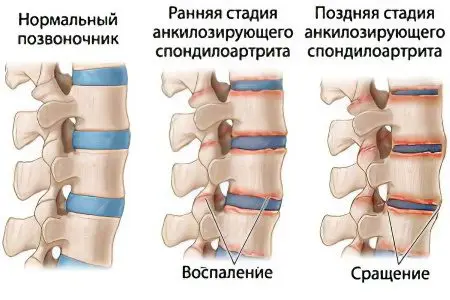
Spondyloarthritis is a type of arthritis, multiple inflammation of the intervertebral joints.
Causes of spondyloarthritis:
infectious nonspecific polyarthritis – “infectarthritis”;
brucellosis;
dysentery;
syphilis;
hypothermia;
injury;
overvoltage.
Symptoms of spondyloarthritis depend on its type:
limitation of mobility of the spine in the morning, and then in the rest of the time;
temperature increase;
anemia;
accelerated ROE – erythrocyte sedimentation reaction;
progressive ossification of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine;
pain radiating to the thigh;
back muscle atrophy;
lordosis of the cervical region;
kyphosis of the thoracic spine;
uneven contours of the sacroiliac joints.
Treatment of spondyloarthritis
The infectious focus is sanitized. Pyrazolone (Butadione, Reopirin, Pirabutol) and hormonal drugs (ACTH – Adrenocorticotropic hormone, Prednisolone, Triamcinolone) are prescribed. Exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy are also needed.
Arthrosis or osteoarthritis
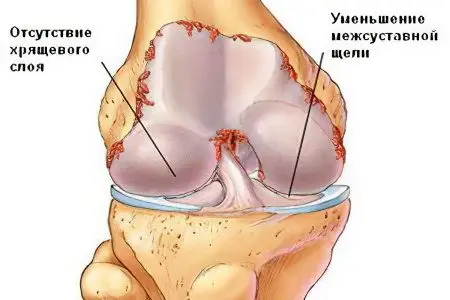
Arthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the joint, leading to its immobility. Synonyms – osteoarthritis, arthrosis-arthritis.
The cause of arthrosis is premature aging, wear and tear of cartilage, for example, due to trauma, inflammation, dysplasia, or metabolic disorders. Not only cartilage, but also other parts of the joint can be affected. The process of formation of cells of cartilage and bone tissue is disrupted.
Arthrosis symptoms:
severe pain during movement due to thinning of the cartilage layer;
tumor;
inflammatory process;
reduced joint mobility – hypodynamia;
atrophy of muscles and ligaments;
joint deformity;
softening, disintegration, ulceration and thinning of the cartilage;
osteosclerosis – pathological hardening of the bone;
synovitis, accompanied by edema.
Treatment of arthrosis
After inflammation is removed, rehabilitation becomes a priority. It is carried out with the help of exercise therapy and physiotherapy. Of the medicines, in addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics and chondoprotectors are prescribed that activate tissue regeneration: Chondroitin sulfate or Glucosamine. In severe cases, endoprosthetics may be required.
Hemarthrosis
Hemarthrosis is a type of arthrosis, internal hemorrhage.
The cause of hemarthrosis is an injury that provokes rupture of blood vessels. In patients with hemophilia, hemorrhage can begin even with minor injuries. This sensitivity is caused by poor blood clotting.
Symptoms of hemarthrosis:
swelling due to internal hemorrhage;
stiffness of movements;
pain;
elevated temperature.
Treatment of hemarthrosis
Provides rest to the joint. If the hemorrhage is small, it is enough to fix the limb. Otherwise, the blood is pumped out of the cavity and a pressure bandage is applied. For rehabilitation, exercise therapy and physiotherapy are prescribed. If, as a result of tissue rupture, free fragments are found in the joint, ligaments or menisci are severely damaged, arthroscopy is performed. This surgical procedure is performed endoscopically. “Articular mouse” – a pathological particle, a fragment – is removed with the help of tools, this requires a second puncture. Sometimes the joint is replaced with a prosthesis. A period of rehabilitation is required, because. the diseased limb was immobilized for a long time.
Hydroarthrosis
Hydrarthrosis is a type of arthrosis, dropsy of the joint.
Causes of hydrarthrosis:
injury;
infection;
osteochondritis dissecans – inflammation of the cartilage;
ankylosing spondylitis;
syphilis;
allergic reaction.
Symptoms of hydrarthrosis:
a significant increase in the size of the joint, a change in its external contours;
pain;
fluctuation;
expansion of the joint space.
Treatment of hydrarthrosis
The joint is immobilized. A puncture is made to remove the exudate. Getting rid of the disease is very difficult. Frequent relapses. In rare cases, radiation therapy is performed. The affected area is exposed to ionizing radiation. Intermittent hydrarthrosis is practically not amenable to treatment – intermittent dropsy of the joint.
Gonarthrosis
Gonarthrosis is a type of arthrosis that affects the knee.
The causes of primary gonarthrosis are unknown, and the secondary occurs after injuries or as a result of impaired joint development.
Symptoms of gonarthrosis:
pain and crunch during exertion;
morning stiffness of movements;
lameness;
swelling;
cartilage destruction;
degeneration and deformation of the joint.
Treatment of gonarthrosis
In addition to the traditional complex of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, drugs are prescribed that replace the synovial fluid. The patient is recommended to use a cane, orthosis, orthopedic insoles when walking.
Coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis is a type of arthrosis that affects the hip joint.
Causes of coxarthrosis:
hereditary predisposition;
elderly age;
obesity;
traumatic injury;
hip dysplasia.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis:
discomfort in the pelvic region in the morning;
pain aggravated by physical activity;
stiffness;
inflammation;
growth of bone spurs – osteophytes.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
The articular cartilage disappears and the bones rub directly against each other. In the absence of therapy, the patient becomes lame. He cannot walk without a cane, crutches or a walker. The modern level of medicine can only stop the development of the disease. Ibuprofen is prescribed to relieve inflammation and relieve pain. The operation improves the situation a little – arthroplasty. An endoprosthesis is inserted. A rehabilitation program is required.
osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a type of arthrosis, accompanied by degeneration of articular cartilage.
Causes of osteochondrosis:
inactivity, weakness of the back muscles due to lack of exercise, respectively, constant overload of the spinal column;
flat feet;
obesity;
violation of posture, for example, due to carrying heavy bags on one shoulder;
heredity;
infection;
intoxication;
metabolic disorders;
aging of the body;
trauma;
excessive exercise;
wearing the wrong shoes;
pregnancy;
depression;
smoking.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis:
pain in various parts of the body;
numbness and aches in the limbs with their gradual atrophy;
limited movement;
muscle spasms;
vertebral artery syndrome;
displacement of intervertebral discs;
nerve root damage.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
The disease is incurable. Traditional methods are used to facilitate the well-being of the patient. When an intervertebral hernia occurs, an operation is performed.
Pseudo- or neoarthrosis
Pseudarthrosis is the formation of a new joint. A neoplasm may occur at the site of an old injury, or surgeons will provoke its appearance where a joint is needed. This operation is performed for the elderly. A false joint can be congenital or acquired.
Causes of pseudoarthrosis:
long-term dislocation or intra-articular fracture;
congenital dislocation of the hip;
palliative surgery.
Symptoms of pseudoarthrosis:
painless mobility at the site of the former injury;
lack of fusion of fragments;
immobility of the limb;
the medullary canals are blocked by the endplate;
cartilage and a false capsule of the joint are formed.
Treatment of pseudoarthrosis
A persistent bone defect can only be cured surgically. The dangling joint is removed, and homografts are inserted to speed up healing.
Spondyloarthrosis or facet arthropathy
Spondylarthrosis is a type of arthrosis, aging of the intervertebral joints.
Causes of spondylarthrosis:
increased pressure on the vertebrae;
decreased production of synovial fluid;
violation of posture;
congenital anomalies of the spine;
trauma;
metabolic disease;
flat feet.
Symptoms of spondylarthrosis:
persistent back pain;
the formation of osteophytes;
gait disturbance;
immobility and fusion of the intervertebral joints;
spondylosis – the formation of bone spikes.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis
Manual correction is required (at the initial stages of the disease), chondroprotective treatment. If inflammation has begun, anti-inflammatory drugs are additionally prescribed. Muscle spasms are relieved with muscle relaxants and acupuncture. Traction therapy is also beneficial – traction of the spine, for example, using a mechanical bed. Physiotherapy may also be used.
Epicondylosis
Epicondylosis is a type of arthrosis that affects the elbow joint.
The cause of epicondylosis is the monotony of hand movements, for example, in some sports.
Symptoms of epicondylosis:
constant pain of varying strength in the arm;
Thompson’s and Welsh’s symptoms.
Treatment of epicondylosis
Anesthesia is carried out with the help of injections of anesthetics: Novocaine or Lidocaine. Physiotherapy is also used.
Hip dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a congenital dislocation of the hip.
The cause of hip dysplasia is the abnormal development of the fetus during fetal development.
Symptoms of hip dysplasia:
asymmetry of skin folds in unilateral pathology;
hip shortening;
symptom of “click” Marx-Ortolani;
limited hip abduction.
Treatment of hip dysplasia
Be sure to use fixing orthopedic devices. But they should not completely restrict the movement of the child. The key to success in early treatment. Gymnastics is carried out daily with a special set of exercises. Massage shown. In severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary.
Bursitis
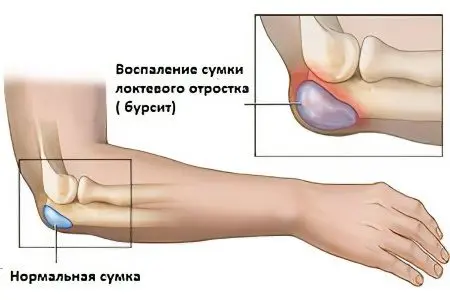
Bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular sac.
Bursitis reasons:
excessive stress on the joint;
injury;
inflammatory and autoimmune diseases;
metabolic disorders;
calcification;
violation of the integrity of the skin;
allergy;
intoxication.
Bursitis symptoms:
accumulation of exudate – inflammatory fluid;
pain syndrome;
limited movement;
deposits of lime salts in the walls of the bag;
edema;
hyperemia;
increase in local or general body temperature up to 40 °;
general malaise, weakness;
nausea;
lymphadenopathy – an increase in the surrounding lymph nodes.
Treatment of bursitis
The therapeutic course includes the suppression of the inflammatory process with antibiotics, anesthesia, strengthening the immune system, physical rest, massage and physiotherapy. If conservative treatment fails, surgery is performed. The bursa is opened and cleaned or removed partially/completely.
Hygroma
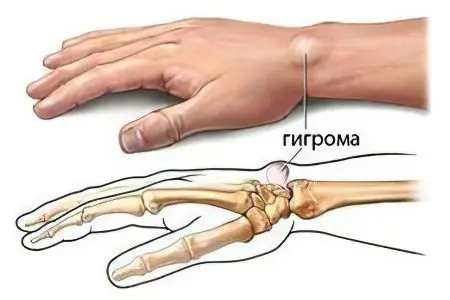
A hygroma is an accumulation of fluid in the synovial sac.
Causes of hygroma:
tendovaginitis – inflammation of the tendons;
bursitis;
trauma;
monotonous movements that require muscle tension.
Hygroma symptoms:
the appearance of foci of hemorrhage and necrosis in the walls of the bag;
increased pain with an increase in the tumor;
venous congestion;
when squeezing the nerve roots, a sensitivity disorder occurs: hyperesthesia or vice versa paresthesia;
fluctuation phenomenon.
Hygroma treatment
Conservative methods rarely work, so the tumor is removed surgically. Bursectomy does not take long.
Synovioma or synovialoma
A synovioma is a tumor in a joint. It can grow from the synovial wall, vagina, or bursa. Malignant sarcomas form anywhere in the body, even where there are no joints.
The causes of synovioma have not been precisely established. There are suggestions about its genetic conditionality. A weak relationship with injuries and physical overload was revealed.
Synovioma symptoms:
pain;
limited movement;
increased body temperature;
deterioration of appetite;
weight loss;
general malaise;
fatigue;
metastasis of sarcoma.
Synovioma treatment
The tumor is removed surgically. Relapses are possible. Benign neoplasms tend to degenerate into sarcomas.
Systemic scleroderma or dermatosclerosis
Scleroderma is a systemic progressive sclerosis that affects internal organs and tissues.
Causes of scleroderma:
genetic predisposition;
infectious diseases;
hypothermia;
injuries of a different nature;
endocrine shifts.
Symptoms of scleroderma:
dense edema, thickening and then atrophy of the skin;
гиперпигментация;
calcification;
vascular and trophic disorders;
articular syndrome from mild pain to deformity;
osteoporosis;
pneumosclerosis and other types of sclerosis;
significant weight loss;
Hair loss;
increase in ESR.
Treatment of scleroderma
Drugs such as:
Prednisolone;
Hingamine;
Acetylsalicylic acid;
vitamins B1 and B6;
Angiotrophin;
Depopadutin;
Lidase;
Novocaine.
In addition to medicines, exercise therapy, physiotherapy and massage are used.
Joint diseases are very diverse. But among them there is not one that could not cause serious damage to human health. Health is a fragile thing, it requires care and attention. Some diseases of the musculoskeletal system with the current level of development of medicine are incurable, some inevitably lead to death.
Video: treatment of joints quickly and reliably, forever. Recipes and methods from Frolov Yu.A.









