Gout is a somewhat puzzling disease with many uncertain theories still circulating. Firstly, doctors do not know its cause, and secondly, there is no effective cure for it. Gout, gout and arthritis are all words for one disease caused by excess uric acid.
How to recognize that we have gout? Its main symptoms include severe joint pain. The development of the disease is caused by the overproduction of uric acid, which begins to crystallize when there is too much of it. Only a certain amount can dissolve in the blood. When this function is disturbed, crystals called urates are deposited, thus growing in the periarticular tissue and the joints themselves. Although the white blood cells try to neutralize and absorb them, they often have no effect. This is when uric acid cuts tissue and causes wounds, thereby causing inflammation.
Types of gout
There are two types of this disease:
- Primary gout – an inherited metabolic disorder, when the human body produces too much uric acid for unexplained reasons and cannot excrete it.
- Secondary gout – it usually occurs as a result of leukemia, chronic kidney disease, radiation, fasting, alcohol abuse, taking certain dehydration medications, excess vitamins B1 and B12, and even overeating. It accounts for about 10% of cases. Sometimes it occurs with lipid metabolism disorders, overweight, abdominal obesity, hypertension, or type II diabetes.
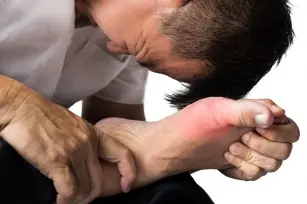
Usually, gout affects the big toe joint, but crystals can also be deposited in other joints: wrist, shoulder joint, elbow, spine, knees.
Symptoms. How to detect it?
Unfortunately, gout develops even for several years without any clear symptoms. Only an elevated level of uric acid in the blood can testify to it, but we have a poor chance of detecting it – after all, those who feel well rarely get tested.
- First symptom: usually the first symptom is pain in the joint. Sudden, sharp, appearing in the early morning or at night, increasing and becoming more and more noticeable over time.
- Other symptoms: after a few days the pain becomes almost unbearable; the joint is red, there is swelling, pain when touched, the skin in its vicinity is blue-purple, tense, shiny, red.
If we do not take appropriate steps after the first such attack, urate crystals they will also begin to accumulate in other tissues: heels, ears, toes, bursae of various joints. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to change the diet, limit the consumption of purines and at the same time take drugs that lower the concentration of uric acid in the blood.









