Contents
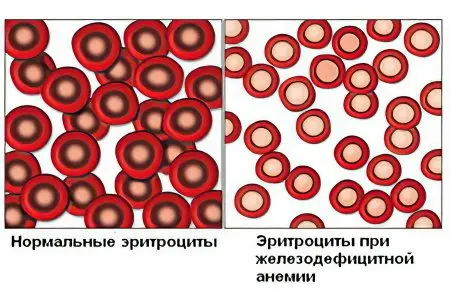
Iron deficiency anemia is a decrease in the level of iron in the body, which leads to a drop in the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is found in erythrocytes, which are red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen to organs and tissues. Without hemoglobin, this process becomes impossible. Among the people, anemia is better known under the name “anemia”, since in past years even doctors called this violation in this way.
The level of erythrocytes in iron deficiency anemia may remain within the normal range. However, they are unable to perform their function if they lack hemoglobin. As a result, organs and tissues begin to suffer from oxygen starvation (this condition is called hypoxia).
Among other anemias, iron deficiency anemia is the most common. This is easily explained by the fact that a variety of factors and causes, which will be discussed below, can lead to its development.
Iron (Fe) is a trace element without which the human body cannot function normally.
Normally, a healthy adult average male contains about 4-5 g of iron in the body:
Hemoglobin contains 2,5-3,0 g of iron.
In tissues, its level is equal to 1,0-1,5 g. This iron is contained in them as reserves in case of emergency. It comes in the form of a substance called ferritin.
Respiratory enzymes and myoglobin consume about 0,3-0,5 g of iron.
Also, a small amount of iron is found in proteins that transport this trace element. These proteins are called transferrins.
Every day, the body of an adult male removes approximately 1,0-1,2 g of iron through the intestines.
The body of an adult woman contains 2,6-3,2 g of iron. At the same time, only 0,3 g of this microelement is in the reserves of organs and tissues. Every day, the female body removes iron through the intestines. During menstruation, the loss of this trace element is also carried out with menstrual blood. During menstruation, 1 g of iron will be excreted daily. Therefore, it is quite logical that it is women who most often suffer from such a disorder as iron deficiency anemia.
In childhood, normal iron levels are equivalent to those for women. This is true for children and adolescents under the age of 14.
Unfortunately, the human body is unable to produce iron on its own. He can only get it from outside (with food or medicines). Iron absorption occurs in the duodenum and in the small intestine. With the help of the large intestine, this microelement is only excreted.
A person should not be afraid that the active use of iron with food can lead to its excessive accumulation in tissues and organs. The body has a number of mechanisms that simply block excess Fe from food.
The first signs of iron deficiency anemia

In the early stages of its development, iron deficiency anemia does not manifest itself in any way, that is, a person may not even suspect that there is a hidden lack of iron in his body. Changes at the initial stage of development of this violation are insignificant. Nevertheless, the first signs of IDA are still there, another question that few people think that they are provoked precisely by a drop in the level of iron in the blood.
So, be sure to see a doctor and take a biochemical blood test if a person begins to worry about the following disorders:
Appetite decreases. The person continues to eat food, but does so without much desire.
Perhaps a distortion of taste, the emergence of new food addictions. There may be a desire to eat something unusual, for example, clay, chalk, flour, tooth powder.
In the epigastric region, discomfort often occurs, and there may be violations with the ingestion of food.
Body temperature rises to subfebrile levels and remains at this level for a long period of time. In this case, there are no visible symptoms of an infectious disease.
Perhaps increased weakness in the performance of habitual activities.
During exercise, the heart rate increases.
There may be noise and ringing in the ears.
Sometimes patients complain of pain in the heart area.
It is not at all necessary that the patient will experience all of the listed symptoms. Sometimes anemia can have a latent course, but it is discovered by chance, during a medical examination.
Main symptoms

As the disease progresses, its clinical manifestations become more pronounced. In addition to the circulatory-hypoxic syndrome (headaches, weakness, fatigue) and problems with the digestive organs, the patient develops sideropenic syndrome. When a patient describes his complaints at a doctor’s appointment, the doctor will first of all suspect anemia.
The main symptoms of iron deficiency include:
Deterioration of the condition of the nail plate. It becomes thin, dull and begins to exfoliate.
Paying attention to what kind of skin the patient has, certain conclusions can be drawn. With iron deficiency anemia, it becomes very dry and flaky.
Jams appear in the corners of the mouth, lips become cracked.
At night, salivation increases.
Hair loses its former attractiveness. They begin to split, do not shine and grow poorly.
The patient’s tongue is covered with cracks, there may be a feeling of discomfort in it.
Even minor injuries of the skin will regenerate for a long time.
The immune defense is reduced. The person will be sick often and for a long time.
Muscles lose their former strength, their weakness increases.
Possibly urinary incontinence. It is released in small portions during strong laughter, when coughing or straining. This is due to the weakening of the sphincters.
The mucous membranes of the intestines and stomach become inflamed, and in some places even atrophy.
There are imperative urges to empty the bladder.
The mood of a person is always depressed, he becomes gloomy and apathetic.
In a stuffy room, the patient feels very unwell.
Drowsiness haunts a person even in the daytime.
The face is slightly swollen all the time.
The course of anemia with the onset of the above symptoms can last quite a long time – about 10 years. Sometimes the level of hemoglobin rises slightly, which helps to eliminate most of the pathological signs, and the person does not go to the doctor. However, the cause that causes iron deficiency cannot be eliminated on its own (unless it is caused by physiological factors, such as pregnancy). Therefore, iron deficiency anemia will continue to progress. Tachycardia will be present on an ongoing basis, in addition to it, severe shortness of breath will appear. Muscle weakness is constantly increasing, a person’s ability to work is significantly reduced.
The course of the disease in childhood is often hidden. By the age of 3, when the baby is transferred to a more varied diet, cases of IDA are diagnosed less frequently.
Iron deficiency often affects premature babies, babies who were born with multiple pregnancies, overweight children, and children who are gaining weight quickly. Contribute to the development of anemia in childhood, frequent infectious diseases, intestinal diseases, artificial feeding.
The course of anemia in a child largely depends on how far this disorder has gone. The degree of severity of the compensatory capabilities of the baby’s body is important. The lower the level of iron in the blood and the faster the hemoglobin falls, the more intense the symptoms of the disease will be. Sometimes anemia can last for years without any treatment. In this case, the symptoms of iron deficiency will be barely noticeable.
The following symptoms will indicate anemia in a child:
Pale mucous membranes.
White ears.
Dry and thin skin.
Poor condition of hair and nails.
Lack of appetite.
Weight loss.
Lagging in physical development.
Subfebrile body temperature.
Frequent SARS and acute respiratory infections.
Enlargement of the spleen and liver in size.
Recurrent diseases of the oral cavity.
Fainting conditions.
All these symptoms may be absent with anemia if it has a latent course.
As for pregnant women, iron deficiency threatens not only the health of the expectant mother, but also the fetus. Moreover, the child’s central nervous system will suffer, experiencing acute hypoxia. Iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women is associated with a risk of preterm birth, as well as infectious complications in the period after the baby is born.
Factors and causes of development

To understand the causes of iron deficiency anemia, it is necessary to identify the role of iron both in the process of hemoglobin formation and in the body as a whole.
Iron deficiency underlies iron deficiency anemia. If its level in the body is below the prescribed values, then this element will not be enough to complete the last stage of heme production. He will begin to take it from the depot, taking it away from ferritin. However, in order to share with heme, ferritin must also contain sufficient iron. If the ferritin of this microelement is less than 25%, then it means that due to some circumstances he did not receive it.
Low production of hemes leads to the fact that hemoglobin is not able to be produced in sufficient quantities. There are too few hemes to form a hemoglobin molecule (it normally consists of 4 hemes and globin).
Red blood cells leave the red bone marrow without acquiring hemoglobin. Such defective blood plates are not able to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues of the internal organs. As a result, they begin to suffer from hypoxia, a person develops a circulatory-hypoxic syndrome.
Moreover, iron deficiency leads to the fact that the tissues cease to produce enzymes to a normal extent. This is reflected in their internal metabolism. The skin and mucous membranes undergo atrophic changes, which causes the appearance of the first signs of the disease.
So, the main reason that entails iron deficiency anemia is a lack of iron and the depletion of its depot (ferritin) with a further disruption in the production of heme, and then hemoglobin.
Iron deficiency develops under the condition that it does not reach the level at which it participates in heme synthesis. It is also possible to lose iron along with red blood cells, which is observed during the development of bleeding.
After massive blood loss, acute posthemorrhagic anemia develops in the body, it does not apply to iron deficiency anemia. Such blood loss is typical for difficult childbirth, serious injuries, criminal abortions, etc. If assistance is provided to the victim on time and blood loss can be stopped, then the volume of circulating blood will be completely restored after some time. At the same time, the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin will return to normal.
The following reasons lead to the development of iron deficiency anemia:
Chronic bleeding, in which red blood cells leave the blood along with hemoglobin and ferrous iron. Such bleeding does not differ in massive loss of life-supporting fluid. These include: prolonged menstruation due to disruption of the ovaries, uterine fibroids or endometriosis, as well as gastrointestinal bleeding, nasal and gingival blood loss.
Insufficient intake of iron from food. In this case, vegetarianism or eating foods that contain extremely low levels of iron can lead to anemia.
Excessive iron requirements in humans. A similar situation is observed in adolescence, in pregnant women (this problem is especially relevant for the third trimester of pregnancy), in nursing mothers.
Iron deficiency anemia can develop in a person who has cancer, especially if the tumors grow very quickly. Foci of chronic infection in the body can also provoke a violation.
Anemia with iron deficiency develops if this trace element is not able to be absorbed normally into the blood in the intestine. The reason for this is various diseases of the digestive system: gastroduodenitis, enteritis, enterocolitis, removal of part of the stomach or duodenum.
A failure in the processes of transporting iron will also lead to the development of this problem.
If a woman suffered from anemia during pregnancy, then a lack of iron will be observed in the body of the child.
Iron deficiency anemia, which develops in children, deserves special attention. At the age of less than 2-3 years, it is precisely the lack of iron that is observed in babies more often than other deficient conditions. Errors in the nutrition of the child, which parents allow, lead to such a pathology. This is a serious problem, since in addition to iron, children often lack proteins and vitamins.
Iron deficiency anemia is considered to be more of a female disease, since it often develops with heavy blood loss during uterine bleeding, or during labor. In addition, in adolescents, iron stores run out faster than in adults, which is associated with periods of active growth of their body. Of course, young children are at risk.
Degrees of iron deficiency anemia
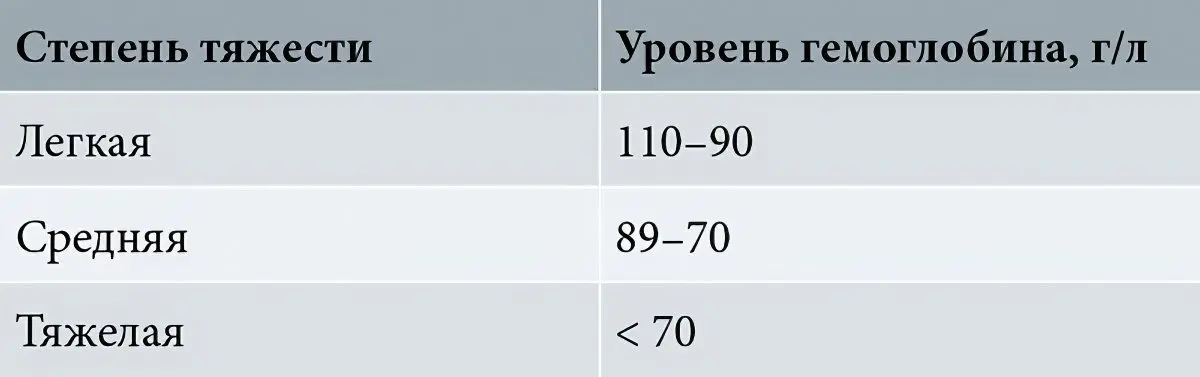
Depending on what exactly the iron deficiency in the body is, there are three degrees of anemia: mild, moderate and severe.
mild anemia
Mild anemia is characterized by the level of hemoglobin in the blood in the range of 90-110 g/l. At this time, iron deficiency anemia is in a latent stage. It can last for a long time. A sharp transition to anemia of moderate severity does not occur. Sometimes iron deficiency can only be detected by a blood test, but it will be necessary to study the concentration of serum iron, since hemoglobin will remain within the normal range.
More: Anemia 1 mild degree
Average
The average degree of iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a hemoglobin level in the range of 70-90 g / l. At this time, the patient develops sideropenic syndrome and he begins to present certain complaints to the doctor. From the moment of manifestation of a mild degree of anemia to the development of anemia of moderate severity, several years (8-10 years) may pass.
Tissue sideropenic syndrome is characterized by symptoms such as: disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, changes in the skin, deterioration of hair and nails.
More: Anemia 2 moderate
Heavy
A severe degree of iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin levels to 70 g/l. At the same time, the patient develops the whole complex of syndromes: circular-hypoxic, sideropenic, hematological. It is no longer possible to ignore or ignore their manifestations, a person seeks medical help.
More: Anemia 3 severe
Diagnostics

Complaints of the patient who came to the appointment may lead the doctor to the idea that he is developing iron deficiency anemia.
To confirm this assumption, it is necessary to order a number of laboratory tests, which include:
General blood analysis. The following signs will indicate iron deficiency anemia: a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, the growth of small red blood cells (microcytosis), hypochromia, an increase in the level of reticulocytes. Although sometimes the number of reticulocytes remains within the normal range.
Decreased serum iron levels. Normal values for men are 13-30 µmol/l, and for women – 11-30 µmol/l.
The level of transferrin in the blood rises, the normal values of which should be in the range of 27-40 µmol / l.
In the gland, the content of transferrin will not exceed 25%, which is also a characteristic sign of anemia.
Serum ferritin in the blood decreases with IDA. Its normal values for a healthy man are 30 ng / ml, and for a healthy woman – 10 ng / ml.
However, it is not enough to simply establish the fact that a person has iron deficiency anemia. It is imperative to identify the cause that led to its development. It cannot be ruled out that the impetus was a serious illness or other life-threatening conditions. To determine the cause of IDA, the following tests may be required:
It is imperative to clarify with the patient whether he is an adherent of a vegetarian type of food. It is possible that the cause of anemia lies precisely in the peculiarities of the patient’s diet.
The development of anemia for hidden internal bleeding is characteristic, therefore, most patients are recommended to undergo FGDS, colonoscopy, and sigmoidoscopy. This will make it possible to detect hidden bleeding in the organs of the digestive system.
Women must be referred to an appointment with a gynecologist.
The search for the cause of IDA should be completed before the point in time until he is prescribed treatment. Therapy for anemia based on assumptions is not possible.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia

There are several fundamental principles for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, including:
It is impossible to get rid of the disease simply by adjusting the menu. The patient should take iron supplements.
Treatment of IDA consists of 2 stages. First you need to eliminate anemia, which takes 30-45 days (an increase in hemoglobin levels will occur after 21 days of treatment). The next step is to replenish iron in the reserves of the body. The duration of this stage is 60 days.
After the level of hemoglobin returns to normal, therapy should not be stopped. A full course cannot be less than 3-4 months.
The reticulocyte crisis that develops on days 5-8 of therapy indicates that it was chosen correctly. At the same time, the level of young erythrocytes, which are called reticulocytes, increases 20-50 times.
If the patient is prescribed oral iron intake, then no more than 20-30% of the total dose will be absorbed. The rest is simply excreted by the intestines. Therefore, the doctor should deal with the selection of the dosage of the iron preparation.
Although it is impossible to get rid of iron deficiency only with the help of dietary nutrition, this does not mean that the patient should refuse it. Compliance with a diet enriched with this microelement is a prerequisite for recovery. First of all, a person should receive meat products that do not contain a lot of fat. These are beef, hot lamb and veal. The menu is supplemented with buckwheat, fish, citrus fruits, apples.
In addition, the patient is prescribed vitamin-mineral complexes with the charming inclusion of ascorbic acid, vitamins A, B and E.
Preparations – sources of iron must be taken according to the following rules:
Short-acting drugs are taken a quarter of an hour after a meal, or in between approaches to the table. Long-acting drugs can be taken before meals, as well as at night. These include drugs such as: Sorbifer durules, Tardiferon-retard, Ferrograd, Ferrogradum. It is enough to take them once every 1 hours at the dosage prescribed by the doctor.
Do not take iron supplements with dairy products or whole milk. They contain calcium, which prevents the normal absorption of iron.
Chewing medicines, if they are not chewable tablets, is prohibited. They are taken whole and washed down with water. Also, a rosehip broth, or any light juice that does not contain fruit pulp, can be used as a drink.
For children who have not reached the age of three years, iron preparations are prescribed in drops. Children 3-6 years old can be offered syrups. At an older age, chewable tablets are suitable for the treatment of anemia, which small patients do not refuse.
Modern pharmacology offers a wide range of drugs designed to compensate for iron deficiency. They can be found in different forms of release, so choosing the best option is not difficult.
The most common drugs containing iron include:
Ferrum Lect.
Maltofer.
Ferroplex.
Aktiferrin.
Gemofer.
Ferroceron.
Tardiferon.
Ferrogradum.
Hefferol.
Ferrograd.
Sorbifer Durules.
Medicines on the list should not be taken on one’s own initiative. They must be prescribed by a doctor. To begin with, the doctor selects a therapeutic dose, and then reduces it to a prophylactic one.
Intramuscularly, iron is administered only if a violation of its absorption at the level of the gastrointestinal tract is established. This leads to surgical interventions on the intestines and stomach, as well as various pathologies of the digestive system.
It should be taken into account that intramuscular and intravenous administration of iron preparations can provoke an allergic reaction, up to anaphylactic shock.
In addition, the treatment of some other types of anemia with iron-containing drugs is strictly contraindicated. Therefore, before starting therapy, you should make sure that the diagnosis is correct.
In some cases, a blood transfusion is required, indications for this procedure are:
Prenatal or preoperative preparation of a patient with a hemoglobin level below 50 g/l.
The impossibility of taking iron preparations in the form of tablets and an allergy to their parenteral administration.
Transfuse with IDA only erythrocyte mass, which has been washed at least 3 times.
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia is an important measure to prevent serious disorders in the body. Particular attention should be paid to children and women in position. To prevent the development of anemia in children under the age of one year, it is necessary not to refuse breastfeeding. If the child is on artificial mixtures, then they must contain a sufficient amount of iron. Be sure to timely introduce complementary foods with meat and fish dishes.
All pregnant women who are in their third trimester of pregnancy should take iron supplements. Women who have not entered menopause are required to remember the need for prophylactic iron supplementation in early spring. The prophylactic course should last 4 weeks. A separate risk group includes teenage girls, athletes and blood donors.
If a person discovers the first signs of anemia, then treatment should not be delayed. You need to consult a doctor and get adequate therapy.
Useful articles on the restoration of hemoglobin in the blood:
List of iron preparations for the treatment of anemia
Diet and proper nutrition for anemia
TOP 5 foods to increase hemoglobin in the blood
Which doctor should I contact for anemia?
Video: iron deficiency anemia, RIA Novosti story:









