Contents
Irga Canadian is becoming popular due to the beneficial properties of berries. A detailed description of the varieties of Canadian irgi will help summer residents to navigate the choice by acquiring a seedling of an unpretentious and frost-resistant plant.
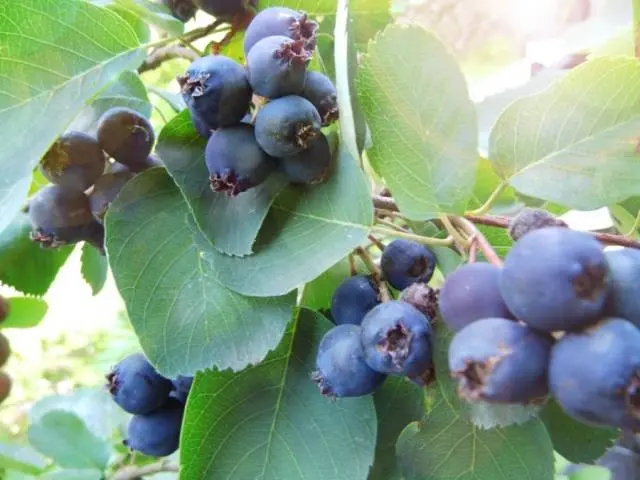

Distinctive characteristics of the species
Canadian irga or canadensis (canadensis) is a tall shrub with 3-20 trunks, depending on the variety. The plant is growing rapidly. Adult bushes grow up to 6 m, live up to 50 years. If the trunk dies, a new one is formed. Most of the roots lie at a depth of 50 cm, some deepen to 1,5 m, the branches fall below 3 m. The diameter of the bush reaches 2,5-5 m. The shoots actively rise from the roots.
The spreading crown of fruit varieties with drooping branches resembles an umbrella. The trunks are picturesquely curved, with a smooth bark of a warm brown hue. Young shoots are bright, reddish. Ovate finely serrated leaves 5-6 cm long on short, 1,5 cm petioles. The leaves are pubescent, with a silvery sheen, burgundy in autumn.
Flowers with white narrow petals, up to 2-2,5 cm in diameter, collected in clusters of 3-10 pieces, attract bees, are not afraid of frost -7 оC. Blossom from the end of April and bloom for 2 weeks.
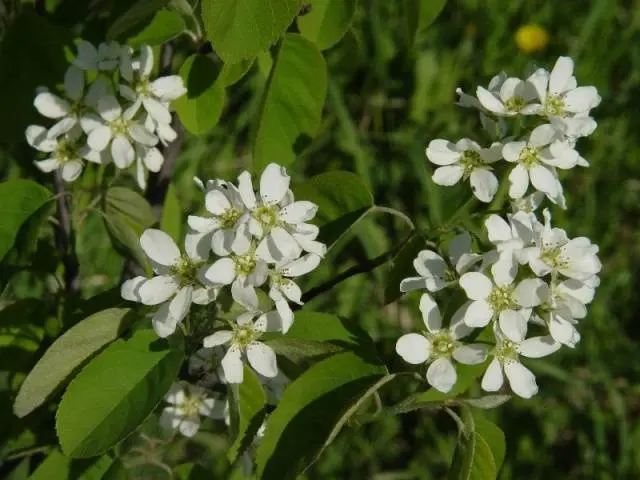

To describe the Canadian fruit shadberry, the term “decorative” is often used. The plant is really beautiful not only flowering. In early spring, the bush seems to be shrouded in a light mist when the buds open, the autumn crimson and the winding graphics of trunks and branches against the background of snow are picturesque.
A three-year-old bush of Canadian shadberry begins to bear fruit. The plant enters into active fruiting from 10 years to 30-40 years of age. 6-18 kg of berries are harvested from one bush, depending on the variety. Round, apple-shaped berries with a pleasant taste, weighing 1 g, 14-18 mm wide, ripen unevenly, from mid-July to late August. In summer, multi-colored berries with a bluish bloom hang on the plant: ripe dark purple, ripening blue and unripe pink. The berries contain 12% sugar, 1% fruit acids, 40% ascorbic acid, carotene, tannins and other active substances.
Sweet, slightly tart berries are rich in vitamins, have an anti-inflammatory effect, affect metabolic processes.
Advantages of irgi:
- large-fruited;
- self-pollination;
- Annual stable yield;
- Undemanding to the soil;
- Survives urban smoky conditions and effectively absorbs noise;
- Drought and frost resistance: tolerates -40 оC;
- Rapid growth, 40 cm per year.
Among the shortcomings are:
- Extended fruiting;
- Difficulties with uprooting: shoots break through for a long time.
Irgu Canadian love to use in landscape design. Thanks to active growth, the bushes are planted like a hedge after 0,7-2 m. You should not expect a harvest with this planting scheme, but a fence with lush greenery will quickly form. Irga Canadian is magnificent as a soloist, acts as a textural element in the landscape compositions of a group of different plants.
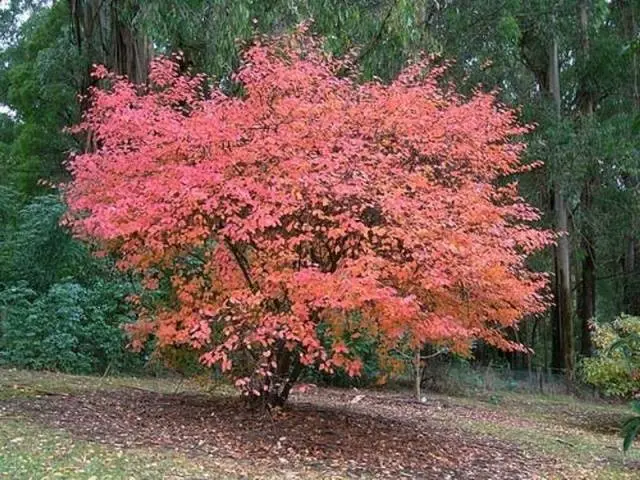

What varieties belong to the species of Canadian irgi
Irga – trees and shrubs from the Apple subfamily, are found in the wild in Europe and Asia. Plants were cultivated for gardening art, as tall, up to 8-11 m Lamarck irgu. Canadian breeders have had particular success, who have developed large-fruited varieties with tasty berries based on bushes growing in North America.
Pembina
Yielding shrub grows in width and height up to 5 m, forms little overgrowth. Oval berries up to 1,4-1,5 cm in diameter, sweet. The variety withstands severe frosts.
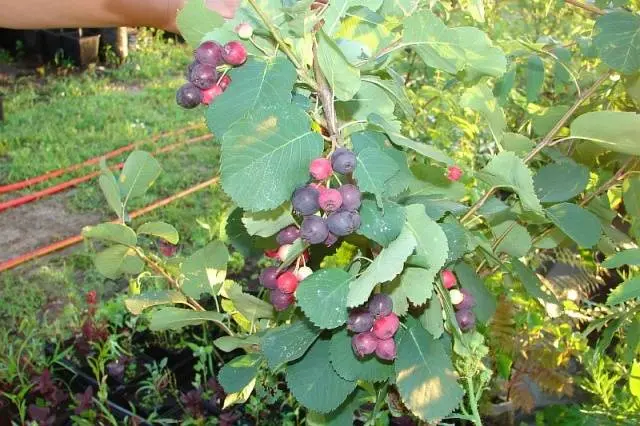

Tissen
The earliest of the varieties of Canadian shadberry, blue berries are harvested at the end of June. Due to early flowering in the conditions of the northern regions, the plant may fall under return frosts. Frost resistance of a shrub growing up to 5 m in height and 6 in width – up to 28-29 оC. Large, juicy berries 17-18 mm, pleasant taste, with original refreshing sourness.
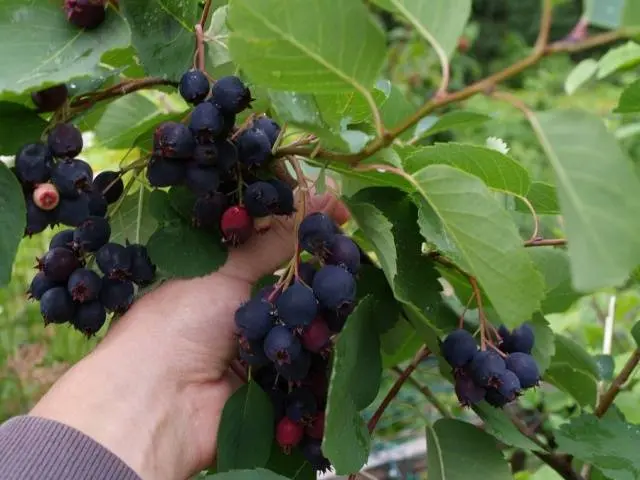

Smokey
Very common, high-yielding, latest variety, grown in large areas in Canada. The bush is low, 4,5 m, the same width, the branches are drooping, it forms a lot of overgrowth. The plant is resistant to diseases, blooms by the end of May, avoiding frost. Berries 14-15 mm, covered with dark blue skin, juicy, with tender, fleshy pulp. From one plant, up to 25 kg of sweet, without astringency, berries are harvested, tasty due to the balance of sugars and acids.

Sturgeon
The undersized irga is a recent success of breeders. It grows up to 2,5-3 m, stably bears fruit. Berries on long racemes, tasty, sweet, large.

Northline
A multi-stemmed plant with vertical trunks – 20-25 pieces, up to 6 m in circumference, rises up to 4 m. Creates a lot of overgrowth. This variety needs a pollinator. Egg-shaped berries are large, with black-blue skin, 16 mm, ripen together.
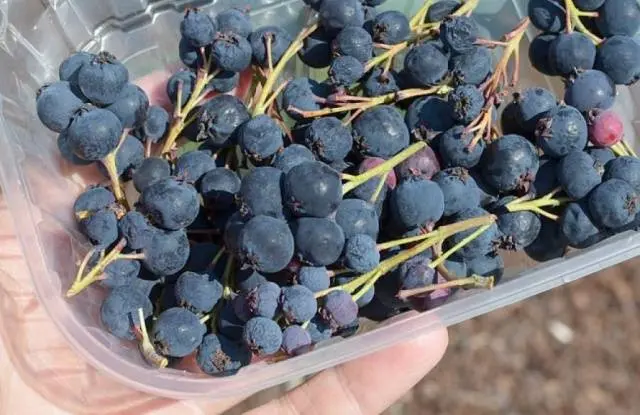

Reproduction of Canadian irgi
There are several ways to propagate a favorite variety: green cuttings, seeds, division of the root system, layering and shoots.
- 12-15 cm cuttings are cut from the last decade of June to the second decade of July from the tops of 5-6-year-old branches. Rooted in greenhouses, planted in the spring;
- Berries for seeds are selected from the most productive bushes, allow them to fully ripen. Sow immediately in the fall, covered with foil. If the sowing is spring, the seeds are stratified for 80-90 days in the basement, placed in a bag of wet sand;
- Having dug up the plant, the rhizome is separated with a sharp tool and cut off long branches. Remove old branches and place delenki in new holes;
- In early spring, a groove is dug near the lower healthy 1-2-year-old branches, where the branch is laid, pinned with garden staples. Cover with soil and water. Plants develop from buds;
- In autumn or spring, young shoots are separated from the mother bush.
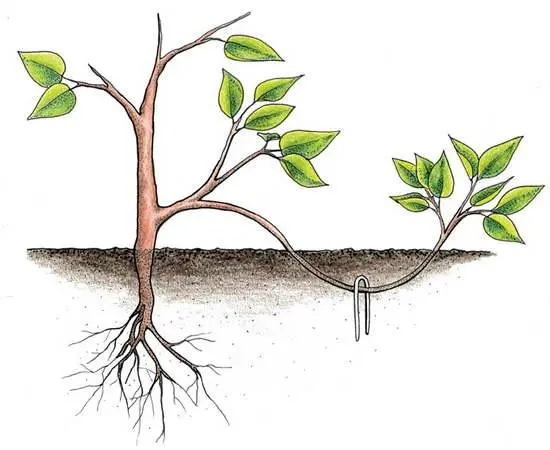
Planting and caring for Canadian irga
Landing a non-capricious Canadian shadberry is a standard procedure. Any planting period, depending on the climate of the region. In the south and in the middle lane they are planted in autumn, until November. In areas with early frosts, it is best to plant Canadian shadberry in the spring.

Site selection and preparation
Irga fruit varieties grow on all types of soils, in shady places, it does not care about cold winds, but wetlands should be avoided. Bushes can be planted from the north of the site both as a fruit crop and as a hedge. If shadberry is grown for picking berries, the holes are located at a distance of 4-5 m. For pollinators, sea buckthorn, wild rose, and other varieties of shadberry are selected. Although the varieties are mostly with maximum self-fertility, the yield will increase.

How to choose seedlings
When buying a shadberry seedling not in a container, make sure that the roots are fibrous, fresh, not shorter than 20 cm. The stem is without scratches, growths, with smooth bark and swollen buds, at least 80-100 cm high. seedlings.
Canadian irgi landing procedure
The hole is dug in advance. Drainage is laid at the bottom. The depth of the pit for the bush is 0,5 m, the width is 0,6-0,65 m. The substrate is prepared on the basis of soil, adding humus, peat and sand. They also put 400 g of superphosphate, 150 g of potassium sulfate and 100 g of lime.
- The root neck is not deepened;
- The seedling is tilted at an angle of 45 degrees;
- Having fallen asleep with soil, they water it, as in the photo of a seedling of Canadian shadberry, the trunk circle is mulched;
- Shoots are shortened by a third, up to 15-20 cm, or 5 buds.

How to transplant an adult irgi bush to a new place
Moving the irgu, the roots are carefully dug out and lightly cut with a sharp tool. Old branches and trunks are removed. A bush older than 6 years takes roots deeper than 1 m and far in width. It is better to keep a clod of earth near the roots, not less than 100 x 100 cm in size, up to 70 cm high. The pit should be larger and deeper in volume. The transplanted irgu is watered and mulched.
Caring for the Canadian Irga
Planting and caring for the Canadian Irga is simple. With good care, undemanding fruit varieties reach their full potential.
Watering
The developed roots of the shadberry absorb the necessary moisture if it rains regularly. Irgu of all varieties is watered only during prolonged drought: 2 waterings per month of 20-30 liters are enough, through a small diffuser. Young bushes are given the same norms.
Weeding and loosening the soil
The soil in the trunk circle is loosened after watering, removing weeds. Shallow weeding contributes to greater air permeability of the soil and better vital activity of the roots.

Top dressing Canadian irgi during the season
Fertilizing the plant, improve its development, productivity and quality of berries. Feeding begins 2-3 years after planting.
- In early spring, up to 50 g of any nitrogen fertilizer is applied to the near-stem circle during loosening;
- 2 weeks after flowering, foliar top dressing of the shadberry bush is carried out, dissolving 10-1 g of boric acid, zinc sulfate and copper sulfate in 2 liters of water;
- During the summer season, the bush is fed monthly with organic matter: infusions of mullein, bird droppings or mowed grasses. Solutions are introduced into 2-3 annular grooves along the projection of the crown;
- Potash fertilizers (25-50 g) and 100 g of superphosphate are fed with irga in the fall. Potassium preparations can be replaced with 0,5 l of wood ash;
- According to gardeners’ reviews of Canadian irga, it is more convenient to feed the plant with complex fertilizers.
Pruning: terms and rules
Pruning increases the yield of the shadberry bush. The plant consists of 10-15 shoots, which are periodically updated, replacing with shoots. The signal for the removal of the old shoot is a small increase per year – only 10 cm. The fruit irgu is cut off before sap flow.
- Sanitary pruning: removal of damaged branches that thicken the crown, shoots are carried out in early spring;
- Cutting off young shoots, leave 1-2 to replace old ones that are more than 10-12 years old;
- Vertical shoots on young bushes are cut to a quarter of last year’s growth;
- To stimulate the growth of the bush, young side branches are shortened to the sides;
When rejuvenating pruning of fruit varieties, shoots with a weak growth per ring are removed, and the rest are shortened to 2,5 m;
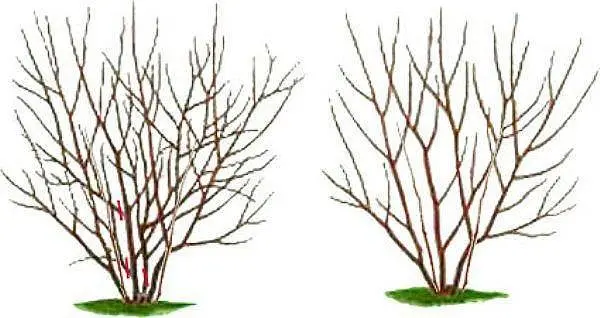
Preparing the Canadian shadberry for winter
In autumn, the irgu is prepared for a dormant period. After leaf fall, inspect the branches and cut off dry and broken ones. All foliage is removed, the site is shallowly dug up. A frost-resistant plant is not covered. Snow is thrown to young seedlings, which is removed in the spring.
The nuances of planting and caring for the Canadian Irga in the Moscow region
In the Moscow region, shadberry bushes of all varieties are planted in the spring. The plant does not need shelter. Only in frost without snow, the seedling is covered with agrofiber over hay. An adult irgi bush is not covered. The trunk circle of a plant of a fruit variety is mulched with humus, sprinkled with snow.
What diseases and pests can threaten the culture
Diseases | Symptoms | Control measures | Prevention |
Tuberculosis | Shoots and foliage crimson, wither. There are red bumps | Affected shoots are removed and burned. Irgu is treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid or blue vitriol 2 times in 10 days
| Cleaning up fallen leaves and damaged branches |
Gray mold | The base of the shoots and petioles, the berries are covered with dark wet spots, then with a gray coating | Irgu and the near-stem circle of the plant are sprinkled with wood ash or colloidal sulfur
| Reduce volume and frequency of watering |
Leaf spot | On the leaves there are spots of different colors, depending on the type of fungus affected. | Treatment with fungicides Horus, Skor, Topaz 2-3 times a week | Spraying before bud break with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid |
Moniliasis | Young branches dry after flowering | Sick parts of the irgi bush are removed and burned | In early spring, the bush is treated with copper-containing preparations. |
vermin | Evidence | Control measures | Prevention |
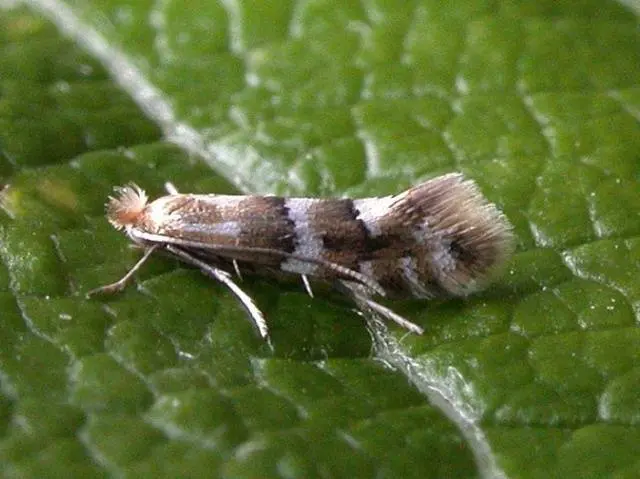
leaf roller | Leaves curled, with caterpillars | Treatment with insecticides Detox, Alatar | In the bud phase, the irgu is sprayed: Nexion |
Irg seed-eater | The beetle lays in the ovary. Berries fall | After flowering sprayed: Karate, Decis | Remove fallen unripe berries |
Hawthorn | caterpillars eat leaves | Sprayed on buds: Nexion | Unblown buds are treated with Arrivo, Decis |
apple aphid | Young leaves are twisted, inside the aphid colony. Leaves dry | Spray the affected tops by dissolving 300 g of laundry soap in 10 liters of water | Unblown buds are sprayed with insecticides (Sumition) |
Moth moth | The larvae feed on leaves, gnaw out passages | Apply insecticides Confidor-Maxi, Mospilan, Kinmiks
| After collecting the berries, they process: Bitoxibacillin, Lepidocid |

Conclusion
Guided by the description of the varieties of Canadian shadberry, they choose a suitable seedling, preferably with a closed root system. Irga is unpretentious, resistant to diseases and vagaries of the weather. A vitamin harvest of healthy berries, even from one plant, will delight for many years.









