Contents
If the intestines or stomach are affected by one of the three dozen infectious diseases, the patient is diagnosed with an “intestinal infection”. All of them are caused by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa.
What is an intestinal infection?
Кишечная инфекция – это поражение пищеварительного тракта микроорганизмами, вызывающими интоксикацию, диарею, рвоту, боль в животе, слабость и гипертермию. Одно из самых характерных проявлений кишечной патологии – воспаление слизистой оболочки желудка и кишечника.
There is no age category that is insured against the occurrence of an intestinal infection, but due to the characteristics of immunity, children, the elderly, and those who have recently suffered a serious illness most often suffer from it. In developed countries, intestinal infection ranks second after SARS in terms of the number of visits to the doctor.
Infection occurs due to the ingestion of infectious agents into the body of a healthy person by the fecal-oral or alimentary route: through water, household items, food. These microbes are excreted in feces, vomit, saliva, urine by sick people or those who have recently had an intestinal infection.
Approximately three dozen infectious diseases cause infection of the digestive system with pathogenic microorganisms.
Infections caused by bacteria:
Dysentery;
Cholera;
Salmonellosis;
Shigellosis;
Botulism;
Typhoid fever;
Yersiniosis;
Campylobacteriosis;
Стафилококковое пищевое отравление;
Escherichiosis (E. coli);
Proteus infection;
Infection caused by clostridia;
Klebsiella infection;
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection;
Paratyph a and b.
Intestinal infection caused by viruses:
Rotavirus;
Adenovirus;
coronavirus;
Reovirus;
Norfolk group virus;
Enterovirus.
Intestinal infection caused by protozoan organisms:
Giardiasis;
Schistosomatosis;
Amebiasis;
Cryptosporidiosis.
Classification
There are two grounds for separating intestinal infections by type: clinical pathogenetic, used in practice, and etiological classification, used in scientific research.
Reasons for classification:
For pathogenetic – features of the course of the disease;
For etiological – the type of pathogenic flora that provoked the infection.
Etiological classification – types of intestinal infections:
Bacterial – transmitted by the fecal-oral and alimentary-household route (violation of hygiene, low-quality products), caused by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Pathogenic microbes enter from the outside, opportunistic microbes are normally found in the human body in a small amount, restrained by beneficial microflora.
Viral – more often represented by rotavirus and enterovirus intestinal infection, the transmission route does not differ from the transmission route of a bacterial infection plus airborne infection. The patient, even after 0,5-1 month, remains a source of infection for others.
Protozoan – rarely diagnosed, affects a person when water enters the body from reservoirs, have a long period of flow.
Pathogenetic classification:
The infection is caused by an unidentified pathogen – up to 70% of cases;
The causative agent of infection is established – up to 20% of cases;
Bacterial dysentery – up to 10% of cases.
Symptoms of an intestinal infection
Since pathogens are insensitive to the effects of gastric juice, they penetrate the intestine and invade epithelial cells (Shigella, Salmonella) or displace representatives of beneficial microflora (E. coli, Vibrio cholerae). Some pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus) release their toxins outside the human body, while still on food, from where they enter the intestines.
All these microorganisms cause inflammation of enterocytes – cells of the intestinal mucosa, indigestion. The main symptom of the disease is diarrhea, or diarrhea, which manifests itself repeatedly. Other manifestations differ in the clinical picture of different diseases.
Other symptoms:
Nausea and vomiting;
Гипертермия в течение нескольких часов или дней;
Thirst;
Abdominal pain;
Appetite disorders;
Rumbling in the abdomen, bloating;
Weight loss;
Weakness;
The admixture of blood in the feces;
Watery stool.
In all cases, intestinal syndrome and general intoxication syndrome are manifested, occurring with varying degrees of intensity.
Types and symptoms of intestinal syndrome:
gastritis syndrome – stomach pain, nausea and vomiting after eating and drinking, single, less often 2-4 times diarrhea, caused by viruses or Staphylococcus aureus;
Gastroenteritis syndrome – pain in the projection of the stomach and around the navel, vomiting, frequent mushy, then watery stools with mucus and food debris, has a brown or greenish color, a sharp unpleasant odor;
Gastroenterocolitic syndrome – vomiting, frequent loose stools with painful defecation, contains mucus and blood, is characteristic of salmonellosis;
Enterocolic syndrome – severe pain, frequent urges with alternating secretion of mucus or liquid feces, characteristic of salmonellosis or dysentery;
colitis syndrome – pain in the lower abdomen, frequent defecation with the release of liquid feces with blood and mucus, false urges (tenesmus), short relief after defecation, characteristic of dysentery.
Infectious-toxic syndrome is manifested by a different set of symptoms, it is felt even before the onset of signs of intestinal damage.
Most often, the patient feels the following symptoms:
Weakness;
Headache;
High body temperature;
Lack of appetite;
Body aches;
Dizziness.
All these signs are caused by an increase in the amount of toxins resulting from the growth of the pathogen colony.
temperature in intestinal infections

The range of temperature values for this pathology depends on the type of pathogen. It can rise for several hours, or stay for several days. Sharp temperature fluctuations arise at accession of complications. Often such a symptom is a reason for hospitalization in a hospital.
Hyperthermia is the first sign of infection of the digestive tract. It appears before other symptoms (abdominal pain, diarrhea). Diarrhea in some cases occurs against the background of normalization of temperature, after it has dropped to normal values. It is recommended to prevent dehydration to prevent an increase in temperature, reducing it with antipyretics.
Vomiting
This symptom is not always manifested often, vomiting can be single, multiple, absent altogether. It is forbidden to stop it with antiemetics, as this disrupts the removal of toxins from the body.
Drinking plenty of fluids to replenish lost fluids and trace elements will help improve the condition. With indomitable vomiting, hospitalization is required, frequent drinking in small sips, infusion of saline solutions.
Causes of an intestinal infection
The source of infection is a sick person or a carrier of infection, excreting pathogens into the external environment with feces, urine, and vomit. It is capable of isolating pathogens throughout the course of the disease and 2-4 weeks after its completion.
Ways of infection:
Oral-fecal;
Domestic;
Airborne.
Возбудители попадают в пищеварительную систему через ротовую полость, то есть алиментарным путём.
Causes of infection:
Несоблюдение правил гигиены во время еды и при её приготовлении;
Violation of neighborhood rules during the storage of products and their heat treatment;
Contact with household items infected by the patient;
Питьё некипячёной воды или случайное заглатывание её во время купания;
Long-term storage of products not intended for this purpose.
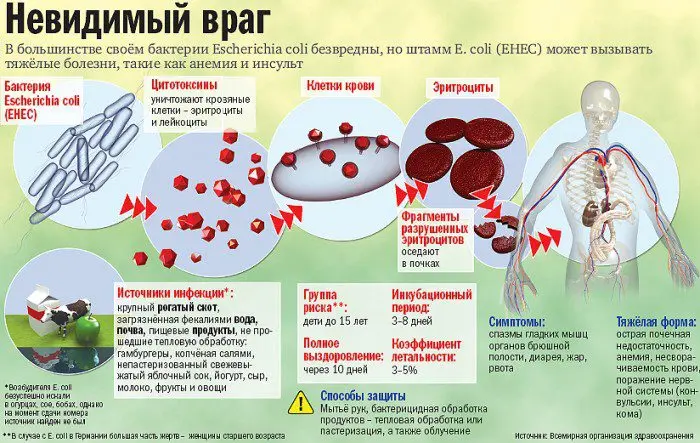
The relationship between the type of causative agent of intestinal infection and consumed products contaminated with microbes:
Staphylococcus – mayonnaise, pudding, custard;
Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli – unboiled water from infected reservoirs, drinking this water and washing food with it;
Clostridia is a nosocomial infection;
Salmonella – eggs and poultry meat;
Yersinia – meat and milk;
Parahemolytic vibrio – raw and cooked seafood.
Viral infections are transmitted by household and airborne droplets, with saliva, through the skin, into the mouth and intestines. This happens with kissing, spitting, biting. The most susceptible to infection are children, the elderly, people suffering from alcoholism, patients with gastrointestinal pathologies.
Video about the causes and symptoms of common intestinal infections:









