Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Intermittent claudication is a condition that significantly affects the daily functioning of the patient. Pain, trouble walking, and limping are just some of the problems that come with the development of intermittent claudication. What are the causes of this disease and how is it diagnosed? Are treatment and rehabilitation bringing the expected results?
Intermittent claudication – characteristics
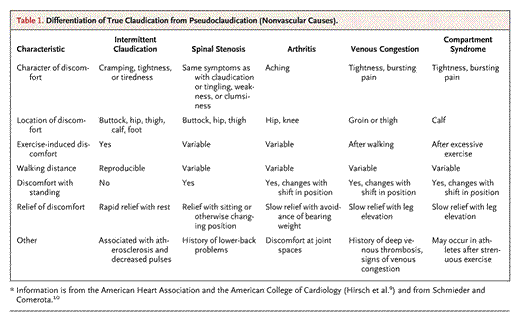
Intermittent claudication is not defined as a disease, but a symptom that results from narrowing of the arteries that supply the legs with oxygen-rich blood. The oxygen that is transported in the blood guarantees the proper functioning of the leg muscles not only during physical activity, but also during everyday walking. When the arteries are narrowed, the muscles are not supplied with adequate amounts of oxygen, causing the so-called anaerobic metabolism. The by-products of this metabolism irritate the pain receptors that are found in the lower extremities. This is manifested by severe pain, fatigue and numbness in the legs. A patient struggling with this ailment often has to stop on the way to wait for the suddenly appearing symptoms. The distance that can be traveled between attacks is called intermittent claudication distance. Chromanie not only affects the lower limbs. For example, narrowing of the abdominal aorta causes abdominal claudication, which is manifested by abdominal pain after eating.
Intermittent claudication – causes
As already mentioned, the main and most common cause of intermittent claudication is narrowing and obstruction of the blood vessels in the lower extremities. In turn, the main cause of vascular obstruction is atherosclerosis. Specialists also indicate other diseases that may contribute to the symptom of intermittent claudication:
- popliteal artery aneurysm,
- Thromboembolic arteritis called Beurger’s disease
- aortic coarctation,
- trauma or radiation damage to the artery,
- peripheral congestion,
- narrowing of the artery caused by Baker’s cyst,
- hip syndrome most common among cyclists
- periodic contractions of the arteries,
- anemia,
- lumbar discopathies,
- narrow spinal canal.
Intermittent claudication – symptoms
As a rule, intermittent claudication is very slow, so many patients ignore the initial symptoms. The first symptom is usually a slight pain in the calf, which can be confused with symptoms following physical activity or muscle strain. However, as time goes on, the pain increases and it begins to radiate towards the thigh and buttocks. The location of the pain depends on the artery that is narrowed or obstructed. Among the symptoms of claudication, there is numbness in the foot, which is so strong that it is impossible to stand on it. Pain and numbness stop when the sick person stops. Unfortunately, symptoms come back when he starts walking again. The gait of people struggling with intermittent claudication is often called the telegraphist gait, because there is a rule that can be presented in the following order: gait, pain, stop. Symptoms accompanying intermittent claudication are cooling of the limb, pain at night, lack of pulse and the limb turning pale when it is lifted and bluish when lowering.
Intermittent claudication – diagnostics
People who notice the above symptoms should perform a diagnosis of the entire cardiovascular system. The test often recommended by the doctor is the Doppler ultrasound, which measures blood flow in large arteries. This test allows you to diagnose the narrowing and obstruction of the arteries and possible atherosclerotic deposits and damage to blood vessels. People diagnosed with intermittent claudication receive the so-called intermittent claudication test. It measures the distance and time that the patient can travel until symptoms of claudication appear.
Intermittent claudication – rehabilitation
The first step in the treatment of intermittent claudication is to change the patient’s lifestyle. The patient has to quit his addictions, especially smoking cigarettes, he must take up treatment of any chronic diseases, lose extra kilos and start exercising daily to improve blood flow. In order for the intermittent claudication not to worsen and lead to complications, patients are treated with antiplatelet drugs.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.