Contents
The complex structure and physiological weakness of the muscles of the inguinal gap made this place vulnerable to protrusion of hernias. It is in the inguinal zone that they appear most often. Men are more often affected by this pathology, however, it happens that hernias protrude in women as well.
The inguinal zone is represented by layered connective tissue membranes (fascia), and the inguinal canal passes between them. In this channel, the female representatives have a nerve bundle, an artery and a ligament of the uterus of a round shape. In addition, the channel has an outer and inner opening, that is, an inlet and an outlet.
Under the influence of a number of factors, the resistance of the layers of the inguinal region may decrease and, under the pressure of the internal organs, they come out through weak points. This is how a hernia is formed.
What is an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernia among women – this is the exit of internal organs through the inguinal canal to the outside. Penetration occurs through the natural openings of the inguinal canal. Any organ that is located in the peritoneal cavity can be in the hernial sac. More often than others, a hernia is represented by the small intestine or omentum. Somewhat less often, the ovaries, the uterus and its tubes, the large intestine and the spleen are found in the hernial sac. It happens that a hernia forms the stomach and gallbladder.
The formation of a hernia is an unnatural process for the human body, which means it is regarded by physicians as pathological. Under the influence of a number of factors, prerequisites are created for the protrusion to occur in the future, and the producing factors make this process manifest. So, pathology is formed under the influence of two groups of factors.
Group of predisposing factors
Hypodynamia.
Weak ligamentous-muscular apparatus, which is caused by congenital features of the human body.
factor of heredity.
Weak constitution.
Group of producing factors:
Increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity:
Violent cough lasting for a long time. Always such a cough reflex is provoked by some disease.
In childhood, frequent screaming and crying can lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
Difficulty passing urine. This reason is due to tumors that cause a narrowing of the urinary tract.
Hard physical labor.
Prolonged vomiting.
Complicated labor activity. Of particular danger in this regard are the second and all subsequent pregnancies.
Weak muscles of the anterior wall of the peritoneum:
Diseases that contribute to the weakening of the muscular frame and contribute to weight loss.
Lack of physical activity, adherence to a sedentary lifestyle.
Increased body weight.
All pregnancies following the first birth.
Surgical interventions in the abdominal wall.
Injuries of the abdominal wall.
There are two age periods during which the risk of hernia formation increases. The first stage is the age from one to two years, and the second stage is the age over 40 years. Scientists believe that if a hernia protrudes in childhood, then it is due to anatomical weakness or a defect in the ligamentous apparatus. When a hernial sac forms in old age, one or more producing factors become the cause.
Hernia in men appears more often, due to the difference between the male and female structure of their inguinal canal. The fact is that during the intrauterine development of the male fetus, their testicles descend into the scrotum from the abdominal cavity. In the process of this omission, a hernia path is formed. In female embryos, the testicles remain in the pelvic cavity, as a result, the path for the penetration of the contents of the peritoneum to the outside is not formed.
Symptoms of a hernia in women
Women are not always able to independently detect an inguinal hernia, as its symptoms are often erased. This is due to the small size of the protrusion. When the pain intensifies during the next menstrual cycle, this indicates that the genitals have entered the hernial sac.
Among the main symptoms of a formed hernia:
The appearance of a protrusion in the groin area, which has a tumor-like shape.
The occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen. Sometimes the pain is given to the lumbar region and to the region of the sacrum.
Pain is aggravated by sneezing and coughing, as well as during physical exertion.
Women experience symptoms characteristic of impaired digestion – this is flatulence, diarrhea or constipation.
Symptoms of a hernia in women, depending on the type:
Types of inguinal hernias in women
It is customary to classify hernias according to two criteria – according to the place of their localization and according to the degree of its elimination.
So, depending on the location of the protrusion, there are:
The hernia is direct when the sac exits through the internal inguinal fossa.
The hernia is oblique, when the exit of the bag with all the contents occurred along the external inguinal fossa. This is the most common type of protrusion.
Hernia subvesical external, when the exit of the bag occurred through the supravesical fossa.
Depending on the degree of elimination of the resulting protrusion, there are:
Hernias that can be easily reduced on their own, for example, when taking a horizontal position. Sometimes they need a little help to set them back. These protrusions are called reducible.
Hernias that enter back is not possible. They remain protruding all the time, regardless of the position of the person’s body. These are irreducible hernias. The fact that they cannot be introduced inside is most often due to the formation of adhesions. In addition, it is this type of hernia that causes digestive failure, vomiting and the inability to perform work duties in full.
Complications of groin hernia in women
Naturally, the formed inguinal hernia gives the woman some discomfort, and also represents a cosmetic defect. However, these are far from the most serious complications that a protrusion can provoke.
Inflammatory process. The development of inflammation inside the hernial sac occurs infrequently, but can significantly affect a woman’s health. Within the hernia, appendicitis may begin to develop, inflammation of the genital organs, colitis may develop. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, body temperature will rise, and general well-being will be disturbed. However, even a slight inflammation can provoke the formation of adhesions, which, in turn, lead to the fact that the hernia becomes irreducible. In addition, emergency surgery may be required when acute inflammation develops. Its signs: a significant increase in body temperature, the appearance of vomiting and nausea, severe pain.
Fecal blockage. When a section of the colon enters the hernial sac, it can cause intestinal obstruction. This process develops gradually, with the accumulation of feces in the sunken area. As a result, the woman suffers from a violation of the digestive process. If this pathology is left untreated, it can lead to the death of the intestine. This occurs against the background of insufficient blood supply. Most often, this process affects older people with overweight. As for treatment, massage or taking laxatives can temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. However, to fully eliminate the stagnant process, surgical intervention is necessary.
Infringement of a hernia. This is one of the most dangerous complications, as it occurs unexpectedly and abruptly for the patient. The entire contents of the hernial sac is compressed in the area of the excretory opening. There is a sharp violation of blood circulation and clamping of nerve fibers. According to statistics, up to 15% of patients are subject to such a process.
The following symptoms indicate infringement:
The impossibility of reducing the protrusion, which had previously been freely reduced.
The occurrence of severe pain in the groin area. Pain extends to the entire abdominal cavity.
The bag itself becomes dense, tension is felt in it.
The patient experiences vomiting and nausea.
In some cases, there is an increase in body temperature.
Diagnosis of inguinal hernia in women
According to the characteristic complaints of the patient, the doctor may already suspect a hernial protrusion.
The examination is reduced to the following manipulations:
Palpation. This method is called palpation.
Feeling is used in the following situations:
The doctor determines the type of hernia – reduced or unreduced.
Cough sign. To confirm it, the patient is asked to cough and assess the vibration that occurs at this time. It is transmitted to the hernial sac.
A sign of a stretched string. If a woman’s inguinal protrusion is accompanied by an adhesive process, then this forces her to adhere to a certain position, which reduces pain. Such patients lean forward slightly when sitting or standing.
Ultrasound. An ultrasound machine will reveal the contents of the hernial sac. This is important information, it must be obtained before performing a surgical intervention.
Bimanual diagnostics. This method is performed through the vagina and intestines. This diagnostic method is mandatory when the ovaries or other genital organs of a woman are in the hernial sac.
Treatment of inguinal hernia in women
If an inguinal hernia is found in a woman, the only effective method of getting rid of her will be her surgical removal. You can find a lot of other recommendations that supposedly allow you to get rid of the protrusion, for example, doing exercises, using physiotherapy techniques, wearing bandages, applying compresses, etc. However, all of them are unable to rid the patient of the pathology.
In addition, the time that will be spent on ineffective treatments will be lost. Do not forget that complications can develop at any time that threaten not only health, but also life. The same statement is true for women of all ages, including young children. An important difference between an inguinal hernia and an umbilical hernia is that it is not able to eliminate itself.
The goal pursued by surgeons in the process of performing surgery is to eliminate the protrusion and prevent subsequent recurrence of the disease. Throughout the centuries of practice of hernia removal, the techniques have been transformed more than once. Modern medicine offers to get rid of the protrusion in several ways, the advisability of using one or another type of hernia removal will be decided by the attending physician.
Tension-free hernioplasty
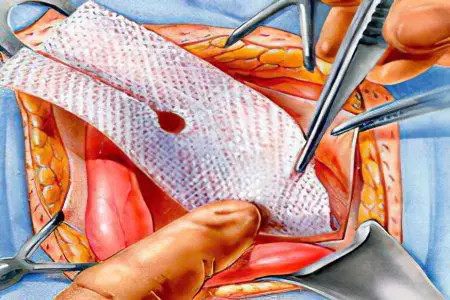
The method of surgical intervention is to strengthen the walls of the canal. For this purpose, synthetic materials are used. The most common technique for tension-free hernioplasty is the Liechtenstein operation. The prosthesis, made in the form of a mesh, is sewn to a wide tendon plate – aponeurosis. At the same time, muscle tissue does not suffer, and tension is not created. As a result, the risk of re-bulging is minimized. The modern material used to make the mesh does not cause allergies, does not dissolve in the conditions of the human body and does not contribute to the spread of infection. However, the search for even better material used for prosthetics has not stopped.
Surgeons suspend the wall using both laparoscopic techniques and open access. Laparoscopy allows minimizing the cosmetic defect after surgery, as it is a low-traumatic technique. However, most surgeons prefer open surgery. Experienced doctors consider this method the safest and most effective. In addition, laparoscopy requires the introduction of general anesthesia without fail.
Tension hernioplasty
This is a time-tested, inexpensive and easiest to implement method of surgical intervention. It boils down to the fact that the tissues are pulled together and sutured in the area of the hernia exit. However, modern surgeons use it quite rarely, as it is fraught with frequent relapses and contributes to the formation of a scar.
Extra-abdominal endoscopic hernioplasty
This type of surgery is a kind of tension-free method. Its main distinguishing feature is the installation of a prosthesis over the peritoneum, that is, access for manipulation is carried out outside the peritoneum. The prosthesis in this case is located directly under the skin. This method avoids the formation of adhesions in the future, but it is quite difficult to perform.
Due to the fact that the anatomical features of the structure of the female body do not require much time and effort in relation to the treatment of inguinal hernia, the number of unsuccessful operations is minimal.
Recovery after surgery
After the intervention, a woman will remain disabled for a certain time. If it was carried out in an open way, then it will increase slightly compared to laparoscopic techniques. They can be performed almost in an outpatient setting. However, any modern operation is a non-traumatic and safe procedure.
If a woman has an increased threshold for pain sensitivity, then she may be prescribed an anesthetic drug. In addition, on an individual basis, each woman is given advice on going to work and starting physical activity.
It is unacceptable to ignore the recovery process, as this can provoke a relapse of the disease. At the request of the patient, he may be recommended to wear a bandage, although the recovery period after hernioplasty does not necessarily require this.
Complications after surgery
Complications are possible with any surgical intervention, and hernioplasty is no exception. The most common infection of the wound, a decrease in intestinal motility, up to its complete inhibition and the development of problems in the work of the heart and lungs. This is especially true for patients suffering from chronic diseases. However, complications from the hernial protrusion itself are much more common, for example, after its infringement, the intestine often dies. Therefore, it is so important to find a truly professional surgeon and seek medical help in a timely manner.
Sometimes surgery does not solve the problem permanently. Hernia recurrences occur even after its timely removal by a highly qualified professional surgeon.
The reason for re-bulging can be:
Medical error.
Infections after the intervention.
Hard physical labor.
Anatomical features associated with weak tissues of the inguinal zone.
Chronic diseases of the intestines and respiratory system.
It is quite difficult to eliminate a recurrent protrusion, so doctors try to apply a method that was not used to remove it during the first operation.
Prevention of inguinal hernia

Building a diet plan that will prevent weight gain.
Avoid injury to the groin.
Maintaining muscle tone through physical activity.
With a hereditary predisposition to hernial protrusion, it is worth avoiding increased physical exertion.
If you experience symptoms that make you suspect a protrusion, you should seek the advice of a doctor.
Leading a healthy lifestyle, rejection of pseudoscientific methods of treatment and prevention of pathology.
Questions frequently asked by the doctor at the appointment
Is there pain in the groin area? What is their nature and distribution?
What features of a hernia can be noted by the patient herself?
When did the first signs of the disease appear?
Is anything known about protrusion during childhood?
Have there been previous infringements of the protrusion? What is their outcome?
Features of professional activity?
Have you had surgeries to remove the hernia before?
What are the physical activities of a woman? Does she play sports?
What diseases and surgical interventions were performed earlier?
Features of pregnancy and labor activity?
What are the health complaints?









