Contents
- What is joint inflammation?
- Diseases as the main causes of inflammation in the joints
- Symptoms of inflammation of the joints
- How does the inflammatory process proceed in the joints and what are the complications of the disease?
- Diagnosis of inflammation of the joints
- Proper nutrition in the inflammatory process in the joints
- Treatment
- Prevention of joint inflammation
What is joint inflammation?
Inflammation of the joints is a natural reaction of the body to a particular disease-causing effect. There are several reasons that can start this process. These are injuries of various origins, and various diseases, the most common of which is arthritis. There are several of its varieties, which to a greater or lesser extent cause an inflammatory reaction in the joints. Both one and several joints can be involved in the pathological process.
Also, inflammation of the joints is defined as a reaction caused by either a general or local infection, when exposed to other factors supporting the process (endogenous and exogenous).
Most of all among this group of the population are people over 50 years old, since it is at this age that the metabolic processes in the body proceed much more slowly, the luggage of previously suffered injuries and diseases accumulates, which make themselves felt. But depending on the cause of the inflammation, middle-aged people and even children turn to doctors with this problem.
Diseases as the main causes of inflammation in the joints
As diseases leading to the launch of the inflammatory process in the joints, include:
Osteoarthritis.
Gout.
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Lupus.
Rheumatism.
Tick-borne borreliosis.
Polymyalgia rheumatica.
Ankylosing spondylitis.
Tuberculosis.
Crohn’s disease.
Coccidioidomycosis.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common disease, affecting mostly older people, approximately 40 years of age and older. The joints that the disease “prefers” to affect are on the hands, in the spine, as well as in the knees and hips of the body. With this disease, mini-protrusions begin to form in any of these areas, which lead to the appearance of irritation and inflammation in the surrounding tissues, ligaments and tendons. Osteoarthritis is usually classified as follows: primary, localized, generalized, secondary (caused by a number of reasons – after an injury or endocrine diseases).
The main signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
Unpleasant sensations intensify or even appear after the joint has “worked”. Such pains are called mechanical and appear most often in the evening. During rest, they either subside or disappear altogether.
Seals appear along the edges of the joint space in the area of the inflamed area.
After waking up, a person may experience short-term stiffness, usually not more than half an hour.
Movement is somewhat difficult and painful.
The joint is in tension.
There may be signs of joint destruction.
Cracking in the joints, called crepitus.
Gout
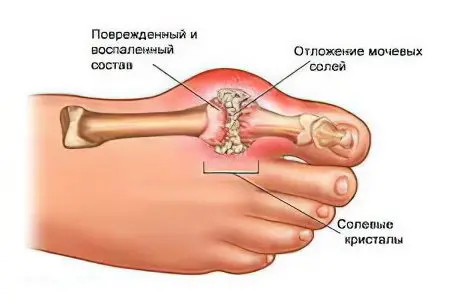
Gout is another type of arthritis that is characterized by sudden, recurring joint pain that is intense. The reason leading to the occurrence of gout is a significant increase in the level of uric acid in the blood, and as a result, the deposition of sodium crystals in the joints, which leads to their inflammation. Sometimes this disease flows into the category of chronic and leads to deformation of the articular tissue. Approximately 20% of patients have deposits of kidney stones.
With gout, it is customary to isolate patients complaining of the following symptoms:
Sharp pain that most often occurs at night.
Sharp reddening of the skin around the inflamed joint,
Weakness and trembling in the limbs.
Headache.
Redness and sharp pain in the big toe, with swelling and hardening of the tissue surrounding the joint.
An increase in body temperature to high levels.
Thus occurs the classic onset of the disease, similar symptoms are experienced by up to 80% of patients with gout.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is, although less common, but nevertheless a fairly common disease that leads to inflammation in the joints. Approximately 2% of the world’s population suffers from this disease. The process is autoimmune in nature, when a person’s own immune system begins to attack healthy cells. With rheumatoid arthritis, it is the joints that suffer from the “attack”. The causes of the development of the disease have not yet been precisely established, but infectious diseases, frequent stress, genetic predisposition, severe hypothermia or a consequence of other arthritis (reactive or infectious) are considered theoretically possible.
During attacks of rheumatoid arthritis, the following symptoms can be distinguished, which are characteristic of this particular disease:
An important distinguishing feature of rheumatoid arthritis is the symmetry of the lesion. That is, when the knee joint on the left leg becomes inflamed, then the knee joint on the right leg should also be involved in the process.
In the morning, and almost until the middle of the day, a person may experience stiffness in the joints, which disappears in the late afternoon.
Joins fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, muscle pain, etc.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a disease of the connective tissue and blood vessels, in which the immune processes in the body are disrupted. The pathology is chronic. Inflammation of the joints in lupus manifests itself in the form of pain, localized in different places. However, the small joints of the ankle and hands are most often affected by the disease. Sometimes the inflamed areas swell, in some cases there is deformity in combination with joint stiffness.
Rheumatism
Rheumatism is a connective tissue disease that affects the heart and joints. The disease can overtake any person, since it occurs as a complication of a serious illness, for example, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, etc. People who have a genetic predisposition to rheumatism are also at risk. Inflamed joints with this pathology often swell and hurt. The pains are sharp, most often large ones suffer – ankle, elbow, shoulder, knee and wrist joints.
Tick-borne borreliosis
Tick-borne borreliosis is spread by ticks and transmitted by insect bites to humans. At the same time, migratory joint pains of high intensity can occur several weeks after the bite and the lack of treatment. Inflammation of the joints in this case is a complication of the disease. Most often, patients complain of pain in the knees, but in some cases other joints are also affected.
Rheumatic polymyalgia
Polymyalgia rheumatica is a disease that has an acute onset and is characterized by severe pain in the neck, pelvis and shoulder girdle. At the same time, the movements of patients are largely difficult, and the painful sensations are symmetrical, that is, both parts of the body hurt, almost in parallel. Mostly the disease develops in the elderly. The causes can be viral and bacterial infections, stress, hypothermia, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer, as well as severe hypothermia.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a disease that is caused by disorders in the immune system and leads to the development of inflammation in the joints, in the joints of the spine, as well as to disruption of cardiac activity. At risk are mainly young men – up to 30 years.
Tuberculosis of the joints
Tuberculosis of the joints is a fairly common form of extrapulmonary infection. Most often occurs in adults and affects the spine, knee and hip joint. Doctors cite injuries and overloads, hypothermia, infectious diseases and unfavorable external factors as reasons. With the disease, the synovial membrane of the joint is affected and inflammation occurs.
Crohn’s disease, characterized by inflammation of the intestinal wall, is often accompanied by inflammation of the joints, since this pathology, according to doctors, occurs against the background of a violation of the immune system. In particular, in children, the disease is practically not accompanied by pain in the abdomen, but is expressed in inflammation of the joints and fever.
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis is an infectious disease with a primary lesion of the lungs, which occurs against the background of infection with coccidioidomycosis (a type of fungus). With the development of the disease, inflammation of the joints is almost always observed, but it is worth noting that the progressive form is rare.
Symptoms of inflammation of the joints

Despite the fact that inflammation of the joints can be caused by a number of diseases, nevertheless, this pathological process has similar features. The following can be distinguished as specific and general symptoms:
Sharp pain, the intensity of which can vary. The place of its localization is an inflamed joint. The discomfort may be present all the time, even when the person is not moving.
The skin around the affected area is tense, the color can vary from slightly pink to bright red, there is swelling of varying severity.
Most often, edema is observed.
Body temperature may rise, in general, and around the inflamed joint, in particular.
During movement, the patient may hear a crunch.
The joint is deformed.
After a joint has not been moved for a long time, a person may experience stiffness in that area. Especially often this happens after a night’s rest.
Regarding the sensations in the area of the affected joint, we can say that they have their own characteristics and are called in the medical language – inflammatory pain. They are characterized by a sharp and unexpected onset, when a person sets the joint in motion. Quite often, such pains are observed at night, closer to the morning. In the acute phase of joint inflammation caused by any disease, discomfort intensifies and is almost always present. If the pathology has become chronic, then the pain reminds of itself more often during movements.
How does the inflammatory process proceed in the joints and what are the complications of the disease?
Inflammation of the joints can occur both in the acute, in the chronic, or in the subacute stage. If we are talking about the acute nature of the disease, then, as a rule, it is accompanied by an abrupt onset, constant severe pain, redness and swelling of the affected area. In this case, the disease ends quickly, the prognosis is very favorable, up to complete recovery, under conditions of adequate therapy. The motor function of the joint is completely restored.
If we are talking about a long-term sluggish disease that has turned into a chronic form, then in such cases it is even possible to disable the patient. The pains are of a variable nature, during the period of remission they are felt weakly, the joints may swell slightly, depending on the type of disease, seals form.
During the subacute stage, the patient often has an increase in the temperature of the skin around the diseased joint. Joint mobility is difficult and extremely painful, and joint deformity may occur. But most often, pain in the subacute stage is spontaneous. In contrast to the acute course of the disease, in this case, the symptoms are less pronounced.
Complications of joint inflammation include:
Perhaps purulent inflammation of the tissues surrounding the affected joint.
Sepsis or blood poisoning.
Subluxations, displacement of bones.
Bone inflammation.
Complete exit of the head of the joint from its fossa.
Joint dysfunction.
Phlegmon and panartitis.
Contractures.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the joints
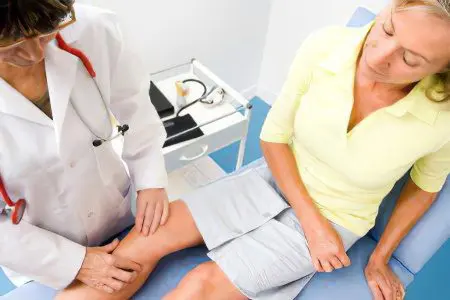
Since inflammation of the joints can be caused by a number of diseases, the doctor faces a rather difficult, but at the same time, the basic task is to determine the disease that led to the pathological process.
Therefore, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor needs to obtain the following information:
A complete and thorough history in order to establish a possible connection of the inflammatory process with previous infectious diseases, injuries or allergies.
Assessment of the course of the disease by listening to the patient’s complaints. Palpation of the inflamed area.
Conducting laboratory diagnostics, which, in addition to studying the general blood and urine analysis, should include tests for the presence of antibodies to hemolytic streptococcus, and the study of the level of uric acid.
Ultrasound diagnosis.
Radiography, which is the most effective method for determining the causes that led to inflammation in the joints.
MRI and computed tomography.
Collection of synovial fluid for study.
Carrying out arthroscopy, when it becomes possible to examine the joint itself.
Biopsy of existing nodules.
Joint puncture.
When carrying out all the necessary studies and the connection of the results obtained with the clinical picture of the disease, it is possible to fairly accurately establish the diagnosis and determine the disease that caused inflammation in the joints.
Proper nutrition in the inflammatory process in the joints
As with almost any other disease, with an inflammatory process that takes place in the joints, it is simply necessary to adhere to a certain type of nutrition. After all, there are products that help to reduce the pathological process, the flesh to its complete extinction. There are those that only aggravate the course of the disease. The latter can definitely include meat, especially fatty, fast food and sugar. Sausages that have undergone heat treatment and contain a large amount of dyes, flavors and salt should not be consumed.
If you include in your menu those products that will help reduce inflammation, then you can improve the patient’s condition and reduce the occurrence of relapses to a minimum:

Do not completely abandon fats and oils. But you should carefully approach their choice. So inflamed joints “love” Omega-3 fatty acids, which have long been proven to have anti-inflammatory properties. Useful compounds can be found in fatty fish, nuts, seeds (flaxseed and pumpkin), as well as rapeseed oil. Olive oil is also a champion in containing a much-needed component for people suffering from joint inflammation. If it is not possible to often eat such products, then you can always use their pharmacy counterparts in the form of a variety of supplements.
Fiber and carbohydrates must necessarily enter the body of a sick person. And it doesn’t have to be simple carbohydrates. Their complex “brothers” are found in whole grain bread, fruits and vegetables. The recommendation of doctors for people with joint pain is to consume at least five servings of different fruits and vegetables daily. Do not forget about berries, and in particular, blueberries and strawberries. They are rich in antioxidants and other substances that help reduce the inflammatory process.
As the main drink, it is best to use plain water, and be sure to refrain from carbonated liquids. Naturally, alcohol in inflammation of the joints will only have a detrimental effect.
Treatment
If we consider therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammation of the joints, it should be understood that their choice will be determined by the disease that is the cause of the pathological process.
So for the local treatment of diseased joints, doctors often use physiotherapy procedures, prescribe intra-articular injections, and also practice non-specific treatment.
Surgery
Surgical treatments include:

Replacement of a “live” joint with an artificial one, or a certain part of it.
Restoration of weakened or completely torn tendons.
Removal of the lining of the joint if it is inflamed or severely damaged.
If it is impossible to perform arthroplasty, then the patient is recommended an operation to merge the joints. At the same time, he is given the desired position, which significantly reduces the pain symptom and makes life easier for the patient.
Naturally, surgical intervention is carried out in the case when other methods of therapy have been ineffective or the disease has gone too far.
Treatment of inflammation in osteoarthritis
As the main principles of treatment, it is customary to single out the following:
Regular joint exercises. Their choice is based on the selection of optimal complexes depending on the degree of damage and inflammation. Properly performed exercises not only improve mood, but improve joint flexibility, increase blood flow to them, thereby relieving pain. For the most competent selection of the complex, consultation with an exercise therapy specialist is necessary.
Weight control and getting rid of excess body weight. This is necessary in order to unload the already inflamed joints. To achieve optimal results in a short time, it is necessary to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition in combination with adequate physical exercises.
Taking painkillers. In some cases, doctors prescribe only analgesics, and sometimes prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs. They help relieve swelling. In the most advanced cases, intra-articular injections of short steroids are used.
If necessary, the consent of the patient to the operation. During it, the diseased joint is replaced with an artificial one. In connection with the development of medicine in this area, in most cases, such an intervention ends successfully, limb mobility is almost completely restored.
With the right combination of these principles, you can achieve very good results.
Treatment of inflammation in gout
With inflammation of the joints caused by gout, the doctor’s first priority is to relieve the pain symptom. This can only be achieved by reducing inflammation. The most commonly used drug for this purpose is colchicine. Its effect will be noticeable after about a day, and sometimes even earlier. Completely pain subsides 12 hours after the first application. They take the medicine orally, but in case of vomiting and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, it is prescribed as an injection.
It should be noted that many doctors refuse to prescribe colchicine, as it can cause serious damage to the bone marrow. That is why non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (we are talking about ibuprofen and indomycin) are increasingly used to relieve the pain symptom of gout. Prednidazole is also able to relieve swelling. Especially effective is the introduction of the drug into the diseased joint with the removal of the collected fluid from it. In addition to taking medications, the diseased joint must be immobilized.
After the primary task in the form of reducing the pain symptom is solved, it is necessary to ensure that the disease does not recur. For this, drinking plenty of water, avoiding alcohol and a low-protein diet are recommended. It is also essential to reduce excess weight, if any. Often, when losing weight and taking blood for a uric acid test, doctors find that the indicators return to normal.
For those patients who have kidney stones and high levels of uric acid in the blood, a drug such as allopurinol is often prescribed. It leads to blocking the production of acid, but has a number of side effects: it causes an upset in the digestive tract, has a negative effect on the liver and reduces the number of white blood cells circulating in the blood.
Treatment of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis

To relieve inflammation in the joints with rheumatoid arthritis, I use various methods. Sometimes all doctor’s prescriptions come down to recommendations in ordinary rest, and sometimes surgical intervention is also required. Naturally, with the undeveloped stages of the disease and with minor inflammation, therapy begins with the most benign.
It is important to reduce the load on the joints as much as possible and give them, if incomplete, then at least partial rest. If it is impossible to comply with bed rest, then it is recommended to immobilize diseased joints, at least for the rest. This is done using a special immobilizing bandage.
As with any disease that causes inflammation of the joints, proper nutrition and recommendations for a healthy lifestyle are prescribed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, as well as long-acting drugs and immunosuppressants are prescribed as therapeutic agents. Naturally, the more severe the disease, the more potent drugs the patient needs.
Prevention of joint inflammation
In order for the joints to remain healthy as long as possible, doctors give the following recommendations:
Careful control of your own weight. Maintaining it in the normal range is the best prevention of joint inflammation. With even a seemingly insignificant increase, knee and hip joints begin to suffer first of all, the load on the spine increases, which will definitely lead to an inflammatory process.
Regular exercise. Physical exercises in which all joints are involved lead to the fact that their flexibility and mobility improves. But with already existing pathological processes, it is necessary to exclude with a shock load. Even if you can’t exercise regularly, you still need to increase your physical activity to the maximum.
Muscle training contributes to the fact that the joints will be under reliable protection, but before proceeding with this or that type of exercise, it is necessary to consult a doctor in advance.
Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are a guarantee that inflammation of the joints will not overtake a person until old age. Unless of course there is a genetic predisposition to the disease.
If possible, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia of the body, since it is this that contributes to the development of many diseases of the joints, leading to their inflammation.
Prevention of acute respiratory infections, influenza and other colds. For this purpose, it is necessary to vaccinate, avoid contact with sick people, and take vitamins. These rules are relevant during epidemiological outbreaks.
If there is a genetic predisposition to any kind of arthritis, then all pain in the joints should be treated several times more carefully.
In what cases is it necessary to urgently consult a doctor?

If one or more symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor:
If the body temperature rises to significant numbers and this symptom is accompanied by redness and swelling of any joint.
If the joints are inflamed symmetrically.
If a person experiences severe pain in the joint area.
In case of deterioration of the heart and difficulty breathing.
With a clear deformity of any joint.
If the pain is paroxysmal in nature and overtakes at night.
With a crunch in the joints and a clear sensation of internal friction.









