Contents
- What is eye inflammation?
- Causes of eye inflammation
- Inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids
- Inflammation of the cornea of the eye
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye
- Inflammation of the eyes in a child
- How to treat inflammation of the eyes?
- When to See a Doctor for Red Eyes
- How to quickly remove redness of the eyes at home
- How to prevent redness and inflammation of the eyes
What is eye inflammation?
Eye inflammation – this is a protective, as well as adaptive reaction of the organ of vision to the action of a pathogenic stimulus of any origin. It occurs at any age and regardless of gender.
Inflammation of the eyes is a complex adaptive reaction of a compensatory nature in response to the action of factors of both external and internal environment. It can be localized both in the eye itself and in the periocular region. The severity of inflammation depends on the cause of its cause. The reaction of the eye to an irritant is expressed in a whole complex of symptoms, of which the most common are: redness, pain, swelling, lacrimation, visual impairment, etc.
The eye is a complex organ responsible for human perception of up to 90% of information. Inflammation can be affected by such departments as: lower and upper eyelids, cornea, mucous membrane, orbit, conjunctiva. Any, even a slight inflammation of the visual apparatus should not be left without attention, finding out the causes of its cause and appropriate treatment.
Causes of eye inflammation
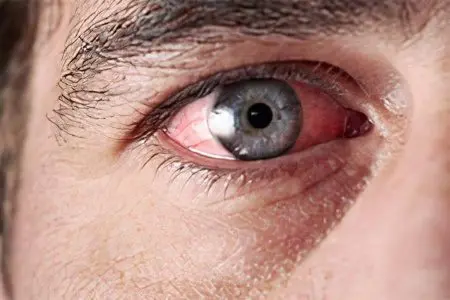
The causes of inflammation can be many, so they can be divided into four main groups:
- Causes of an infectious nature.
- Causes of traumatic origin.
- Exposure to aggressive substances.
- Causes of allergic origin.
If we consider diseases that cause inflammation of the eyes, then we can distinguish among them the following:
Blepharitis characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, is bacterial in nature, can sometimes be caused by fungi, mites, allergens and other inflammatory eye diseases. Pathology is accompanied by the appearance of crusts on the edges of the eyelids, rapid fatigue of the organ of vision, uneven growth of eyelashes, their loss and severe itching. The disease is common, 30% of the total human population meets with it at least once in a lifetime, develops bilaterally, and often recurs.
Conjunctivitis – one of the most common causes of inflammation. It has a different origin, the disease can be caused by fungi, bacteria, viruses and allergens. In each case, the symptoms and severity of inflammation will differ. All conjunctivitis, except for allergic ones, is contagious and requires an appointment with an ophthalmologist and the appointment of appropriate treatment.
Keratitis – These are inflammatory processes occurring in the cornea of the visual apparatus. This is a serious disease caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi entering the eye. In addition to the standard set of symptoms in the form of inflammation of the eye, its redness and visual impairment, keratitis is often characterized by clouding of the cornea and an increase in its sensitivity. Keratitis is dangerous for its complications.
Iritis, endophthalmitis, uevitis, iridocyclitis, choroiditis – these inflammations affect the choroid of the eye. If iritis and iridocyclitis affect the anterior part of the choroid, then choroiditis causes inflammation of its posterior part. v
Corneal ulcer – this is a destructive process that causes inflammation of the eyeball, it is accompanied by pain, decreased vision, clouding of the cornea. An ulcer can be either infectious or non-infectious.
Barley is a common cause of inflammation of the eyelids and the appearance of redness in the eyes. It appears against the background of the fact that either the hair follicle or the sebaceous gland of the eyelash is infected. Barley is always accompanied by the appearance of an abscess.
Meibomite – an ophthalmic disease leading to the development of inflammation. It is characterized by the appearance of internal barley, is located in the cartilaginous plates of the inner and outer eyelids, and is caused by pathogenic flora.
Impetigo – a skin disease caused by bacteria of the cocci group and sometimes affecting the conjunctiva.
Mug – a disease affecting the mucous membranes, including the eyes, due to the development of group A streptococcus.
Abscess century – their inflammation caused by the penetration of bacteria into their tissues. An abscess is a dangerous process accompanied by accumulation of pus, swelling, fever, inflammation and redness of the eye, etc.
Phlegmon – the process of inflammation and suppuration of the orbital tissue, characterized by rapid development, acute course, high fever, headache and other symptoms.
Furuncle – an edematous purulent nodule with a rod inside, most often localized in the eyelid area. Causes inflammation of the eye, often accompanied by fever and headaches.
Molluscum contagiosum, caused by the corresponding virus and affecting the skin of the eyelids, as well as the conjunctiva, stimulating inflammation of the eyes.
Dacryocystitis – inflammation localized in the lacrimal sac, characterized by constant tearing, swelling, soreness, redness and narrowing of the palpebral fissure.
Canaliculitis – inflammation of the eyelids, lacrimal sac and conjunctiva as a result of the penetration of bacteria, viruses, fungi. Symptoms: swelling, enlargement of the lacrimal openings, discharge of a different nature, depending on the type of pathogen.
Dacryoadenitis – a disease that is caused by multiple endogenous infections, such as gonorrhea, mumps, scarlet fever, pneumonia, etc. It is characterized by swelling and redness of the eyelids against the background of headache, weakness and fever.
exophthalmos – protrusion of the eyeball. With a pronounced form of the disease, there is swelling of the conjunctiva, redness of the eyelids, and displacement of the apples themselves.
Tenonitis – an acute eye disease, most often affecting one eye.
Thrombophlebitis of the orbit – an acute process of inflammation, localized in the veins of the orbit and often occurring after infectious diseases.
All these diseases lead to inflammation of the eyes to a greater or lesser extent, are localized in different parts of the organ of vision and are caused by various pathogens.
Inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids
Inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids is caused by various pathological agents and includes a large group of eye diseases.
Among them are such as:
- Blepharitis
- Demodecosis
- Barley
- meibomeite
- Impetigo
- Mug
- Phlegmon
- Furuncle
- Abscess
- Molluscum contagiosum.
In order to prescribe treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause that caused inflammation of the eyelids. Only an ophthalmologist can do this. Common symptoms characteristic of eyelid inflammation, both lower and upper, are: swelling, hyperemia, discharge, photophobia, itching, burning, narrowing of the palpebral fissure, lacrimation. Depending on the type of pathogen and the nature of the disease, symptoms such as headache, skin rashes, fever, nasal discharge, etc. may join. Since the symptoms of many milestone diseases are quite similar, sometimes a doctor’s examination is not enough, a scraping may be required , examination of secretions, blood test. Only after that treatment is prescribed.
If the cause of inflammation is an allergy, then the patient is prescribed antihistamines, and, if possible, it is necessary to minimize contact with the allergen. It can be dust, cosmetics, drugs and other chemicals.
In other cases, drops are prescribed to fight viruses, fungi or bacteria that led to inflammation. The basis of the treatment of any disease of the century is the observance of its hygiene. For this, it is important to regularly wipe the edge of the eyelid with antiseptic solutions or rinse with boiled water. This procedure will help relieve inflammation, reduce swelling, cleanse purulent and other secretions.
In order to reduce the traumatic effect on the eyelids, it is important to stop wearing contact lenses and using eye cosmetics during their treatment.
If the treatment was started on time and carried out according to all the rules, then after two weeks the inflammation of the eyelids most often disappears. Otherwise, this condition threatens with serious complications, which are not always completely eliminated.
Inflammation of the cornea of the eye
Inflammation of the cornea of the eye is called keratitis. The disease affects the anterior part of the organ of vision and largely affects its sharpness. There are several reasons for the occurrence of keratitis, it is not only infection with fungi, viruses and bacteria, but also mechanical trauma, as well as thermal and chemical burns.
Fungal keratitis. Bacteria most often end up on the cornea of the eye as a result of eye injury, for example, when wearing and using lenses incorrectly. Fungi – parasites cause fungal inflammation of the cornea. It is this type of keratitis that is considered the most dangerous, as it significantly affects visual acuity. In some cases, fungal keratitis can cause the formation of a walleye.
Viral keratitis in most cases causes the herpes virus. This type of keratitis is dangerous with a decrease in vision with prolonged ignoring of the disease.
Herpetic keratitis It can be both superficial and deep. If with a superficial form of the disease a person does not experience any special problems in terms of treatment and recovery, then deep keratitis can provoke the development of an ulcer or thorn. This is due to the fact that it captures the deep layers of the cornea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe eye.
Ochnocerciasis keratitis. The result of a strong allergic reaction can be ochnocercotic keratitis, which is dangerous because it can lead to complete loss of vision.
Unlike conjunctivitis, any keratitis leaves marks on the cornea. If with a superficial form of the disease they are almost invisible, then with a deep form, serious scars are formed, leading to varying degrees of visual impairment.
Treatment of inflammation of the cornea
As for the treatment of keratitis, it completely depends on the cause of its cause. Antiviral, antimicrobial, and antifungal drugs, supplemented by diet, may be prescribed.
In no case should treatment be completed after the disappearance of the first signs of the disease. This is a long and systematic process that takes months. Only in this way will it be possible to avoid the formation of scars and scars on the cornea, which lead to visual impairment. The decision to end therapy can only be made by an ophthalmologist.
Creeping ulcer of the cornea. Separately, it is worth highlighting such a disease as a creeping corneal ulcer. This is a severe disease of the corneal membrane caused by pneumococci, streptococci and other pathogens. The disease develops acutely, a person suffers from severe photophobia, severe lacrimation, in the place where the infection penetrates, an infiltrate appears, which, after its decay, forms an ulcer. Treatment should be carried out under strict medical supervision with the determination of the agent that caused the pathological process in a hospital setting.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye
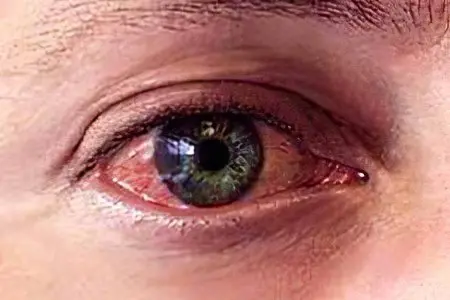
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye is the most common ophthalmic problem. Doctors with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ of vision make a diagnosis – conjunctivitis. The reasons for the development of the disease can be very diverse: this is a metabolic disorder, and the penetration of allergens, viruses, bacteria, fungi into the conjunctiva, and malnutrition, and eye injuries, and inflammatory diseases of nearby organs, and vitamin deficiencies.
The disease can be both acute and chronic. Acute disease is caused by pathological agents – viruses, bacteria, fungi. Chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s immune forces, or with improper treatment of an acute infection.
What is characteristic of conjunctivitis of any origin is the similarity of symptoms. A person feels itching, burning, tingling and pain in the eyes, photophobia appears, tear production increases. All of these symptoms are aggravated in the evening. The discharge from the eyes will differ, they can be catarrhal or purulent, depending on the type of pathogen. Some conjunctivitis are characterized by the appearance of grayish films that are easily removed.
Treatment of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye depends on the cause of its occurrence. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the factor that provokes the development of the disease. In all cases, a long-term local antiseptic treatment is prescribed, if necessary, antibacterial drops, hormonal eye remedies, and specialized ointments are used. Treatment of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye is a process that is extended in time and its mildest forms pass after only two weeks.
Inflammation of the eyes in a child
Inflammation of the eyes in children has some features. Infants most often suffer from dacryocystitis. This pathology is characterized by complete obstruction of the lacrimal canal, or its significant narrowing.
Reasons there may be several – this is the presence of an overlapping membrane that does not completely resolve by the time the baby is born or a stagnant gelatin plug.
Symptomscharacteristic of dacryocystitis is increased tearing, it is observed when the child is at rest. Then the eye begins to redden, and the process is most often one-sided. Stagnation of tears provokes the development of an infectious process, and after an average of 10 days, the baby has purulent discharge from the eyes, which appear when pressure is applied to the lacrimal sac.
Most often, this pathology disappears in children by six months and does not require surgical intervention. The doctor recommends massage using a special technology, washing the eye with antiseptic solutions. If these measures do not help, the child is prescribed special drops with an antibacterial effect.
Older children often get conjunctivitis from other people. Children who start attending kindergarten are especially susceptible to this disease.
Often, the eyes of young patients undergo various inflammatory processes as a result of external stimuli entering them. It can be bath, pool, light, dust inflammation.
Treatment It is based on finding out the cause of inflammation and eliminating the irritating factor. In no case should you wash your eyes with saliva or breast milk, because in this way you can introduce an infection and aggravate the pathological process. Also, babies up to a year are contraindicated in antibacterial ointments based on antibiotics. It is better to use antiseptic solutions in a certain concentration. In any case, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is fraught with the fact that it is possible to spoil the child’s vision due to the immaturity of his visual apparatus. In addition to pharmaceutical products, after consulting a doctor, you can use infusions of herbs, such as chamomile, to wash your eyes. It is always important to treat both eyes, regardless of whether the infection has affected one or two organs of vision.
In case of an eye burn, it is important to deliver the child to the ophthalmology department as soon as possible. Before that, you can drip adrenaline, apply a cotton pad and cover your eyes with a dark bandage on top.
A disease such as congenital glaucoma can be detected immediately after the birth of a child, or during the first year of life, due to an increase in intracranial pressure.
Tumors of the eye in children occur, but quite rarely, however, and in childhood they can be both benign and malignant.
Eye injuries most often occur at school age and can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, it is important to explain to children how to preserve their eyesight and stipulate the rules of safe behavior.
How to treat inflammation of the eyes?

Inflammation of the eyes is treated depending on which area was affected and what caused the onset of the pathological process.
Therefore, we can consider the basic principles of treatment for the area of inflammation of the eyes:
- Therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation of the eyelids depends on the pathological factor that caused it. Processes such as abscess, barley, furuncle, phlegmon require oral antibiotics. It can be ampicillin, oxacillin and other agents. Sulfamilanide preparations are also prescribed – Biseptol or Bactrim. The locally inflamed area is treated with various antiseptic solutions. Sometimes it is required to open abscesses surgically. A pronounced effect comes from the imposition of eye ointments that have an antibacterial effect. For the treatment of blepharitis, local treatment is carried out with mercury ointment, and then with tetracycline, furacilin, gentamicin and others. Drops of sodium sulfacyl, Sofradeks and others are shown. For the treatment of molluscum contagiosum, it is necessary to scrape the nodule, and then treat it with brilliant green. Impetigo is also treated locally, after treating the surface with salicylic alcohol, it must be lubricated with brilliant green or iodine. The instillation of sodium sulfacyl and the application of ointments – erythromycin or tetracycline are shown.
- Treatment of the cornea depends on the pathogen that led to the inflammation. For this, antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal drugs are used in combination with eye treatment with solutions of antiseptics, penicillin, furacillin, sodium sulfacyl, etc. After the organ of vision is cleaned and disinfected, ointments are placed inside the eyelid – gentamicin, erythromycin and others. If local therapy was not effective enough and keratitis does not go away, then intravenous or intramuscular administration of antibiotics is indicated. As for herpetic keratitis and creeping corneal ulcer, these conditions need to be treated in a hospital.
- Treatment of conjunctivitis, like other eye diseases, depends on what caused it. Antifungal, antibacterial and antiviral agents are also prescribed. If conjunctivitis becomes chronic, then long-term treatment with local preparations is indicated – antiseptic solutions and antibacterial agents. In some cases, the use of hormonal drugs such as prednidazole or hydrocoritzone is recommended. When the disease is complicated by blepharitis, it is necessary to apply ointments with an antibacterial effect, for example, gentamicin, tetracycline and others.
Most inflammatory eye diseases can be successfully prevented by following simple recommendations. Sometimes it is enough to stop rubbing the organs of vision with a handkerchief and rub your eyes regularly. If a person is prone to frequent irritation of the conjunctiva and allergic reactions, then you need to wash your eyes as often as possible with ordinary boiled water, saline or chamomile decoction.
Do not forget about glasses with dark glasses that can protect your eyes from burns.
Do not use eye drops on your own in order to prevent diseases. Such self-medication can lead to undesirable consequences in the form of loss of vision and the occurrence of side effects.
It is advisable to visit an ophthalmologist once a year for a preventive examination of the organ of vision.
How to wash eyes with inflammation?
For washing the eyes, antiseptic and antibacterial agents are used. One of the effective solutions for washing the eyes is a solution of furacilin. You can prepare it yourself, just dilute 2 tablets with 200 ml of boiled water and let them dissolve completely. With the help of such a solution, you can cope with conjunctivitis, scleritis, dacrocystitis, blepharitis in complex therapy. The remedy is also shown when any foreign body enters the eye, as well as in case of mechanical damage to its mucous membrane.
Often, for washing the eyes, it is recommended to use an infusion of chamomile. It can also be used as a lotion, as it has an anti-inflammatory effect, helps to quickly and safely remove small foreign objects from the eyes.
An equally effective eye wash is strong brewed tea. It helps relieve inflammation and has an antiseptic effect.
When starting to wash the eyes, it is important to remember these two rules: one swab is used for one eye, and the other for the second. Moreover, each of them must be sterile. The direction of movement is from the temple to the bridge of the nose, this will avoid the spread of infection to the inner layers of the eye, in particular, to the cornea.
Drops and eye gels for inflammation

Eye drops have a local effect, affect the mucous membrane of the organ of vision, the cornea and surrounding tissues. They differ in composition and effect, so their use is possible only after consulting a doctor. To eliminate infectious inflammation, drugs such as sodium sulfacyl, levomethicin, sulfapyridazine are most often prescribed. The term of their use and dosage is determined by the ophthalmologist.
To eliminate inflammation of the cornea of the eye, sodium sulfacyl, dexamethasone, norsulfazol are used.
Children can not always use drops prescribed to adults. Therefore, to combat eye inflammation in a child, drugs such as Atropine, Florax, Levomecithin, Albucid, synthomycin, Torbex are used.
In order to remove redness from the eyes and moisturize the mucous membrane, the following drops are used: Vizin, Oftolik, Oksikal, Inoksa and others.
If inflammation of the eyes is caused by allergies, then in order to reduce the effect of the allergen, special antihistamine drops are used, these can be Ocumentin, Vizin, Naphthyzin, Dexamethasone. It is important to note that the latter drug, in addition to eliminating allergy symptoms, is able to relieve the organ of vision from non-purulent inflammation that has developed as a result of injury or other mechanical irritation. Dexamethasone is often prescribed to people who have undergone eye surgery. However, it should be used with caution in women who are carrying a child, since hormones are part of the remedy.
For very young children, at the age of 1 month, you can use tools such as Cromoglin and Hi-krom. Older children who have reached the age of 4 are prescribed Opantol, Allergodil, Lekrolin and others.
Vizomax, Oculist, Zorro and others are used as prophylactic agents that improve vision and moisturize the mucous membrane of the eye. They nourish the cornea, relieve irritation and tension.
According to their action, eye drops can be divided into several large groups:
- Antibiotics – aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, glycopeptides, etc.
- Antibacterial synthetic drops – fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides.
- Antiseptic drops.
- Antiviral agents.
- Antifungal drops.
- Antiparasitic drops.
Combined drops that combine antiviral and immunomodulatory effects include Oftalmoferon. Also, Aktipol, Oftan-Idu drops have an antiviral effect.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qEsi5dYghlo
When to See a Doctor for Red Eyes
If severe redness of the eye (or both), including in a child, is systematic and is accompanied by itching, dryness, headache, decreased visual acuity, this is a cause for concern and a visit to the doctor. Such a complex of signs should be taken seriously, because they can indicate diseases such as hypertension, migraine, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid dysfunction, type 1 diabetes, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, psoriasis.
When you find yourself reddening of the eyes, which complicates any accompanying symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations, including:
- ophthalmoscopy
- eye pressure measurement
- ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
- pupillary reaction to light
- fundus examination
- in some cases, CT and MRI
- blood analysis
Pharmacy drops for redness of the eyes
Due to the heavy load and excessive fatigue, the smallest vessels located on the surface require delicate handling. Eye drops from redness and irritation save not only from external manifestations, but also effectively fight painful sensations: they relieve pain and dryness in the eyes.
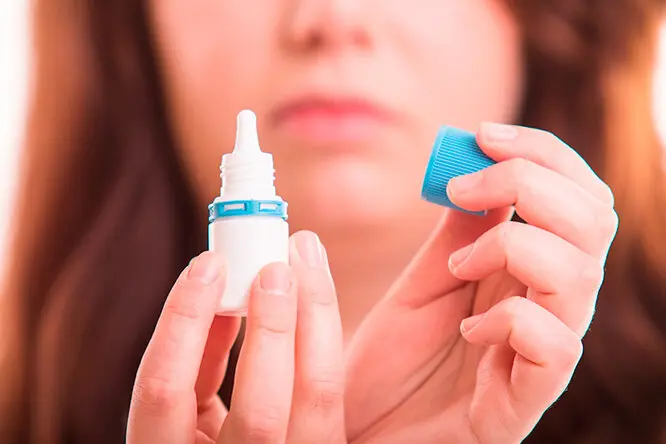
Let’s list what drops from redness of the eyes exist. According to the type of impact and components in the composition, they are divided into anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and anti-allergic (antihistamine).
- Vizin – eye drops that help relieve redness of the eyes, inflammation and irritation of their shell. They have a vasoconstrictive effect.
- Oksial is a moisturizer designed to get rid of dryness and irritation of the mucous membrane, after applying the drops, the redness of the eyes disappears.
- Oftolik – eye drops for protection and moisturizing. Forms a tear film and softens the cornea.
- Innoxa – eye drops for redness, fatigue and irritation of the mucous membrane. Indispensable for daily wear lenses.
- Likontin – the best eye drops for redness and dryness prevention, which have a disinfectant effect. Eliminate the feeling of sand in the eyes.
In order for eye drops to have the right effect, you need to use them correctly. When instilling drops into the eyes, slightly raise the chin, gently pull the lower eyelid and with the other hand, drip inside (as if behind the eyelid) a miraculous drug.
If drops for redness of the eyes do not suit you, there are cheap alternatives. Wonderful and no less effective “artificial tears”, which can also be purchased at the pharmacy. Polyvinyl alcohol and hypromellose are sold without a prescription. These liquids perfectly moisturize the mucous membrane of the eyes, which helps to quickly eliminate redness.
To prevent allergic symptoms, it is necessary to approach the selection of drops with special care so as not to aggravate the situation. Frequent and severe inflammation of the mucous membrane should be controlled by the doctor, if necessary, changing the drugs. Whatever the reason, how to treat redness of the eye, only the optometrist should decide. Even if the drops are sold without a prescription, don’t risk it because your eyesight is at stake.
How to quickly remove redness of the eyes at home
When it is not possible to apply eye drops, inexpensive improvised means will relieve redness. Inflamed eyes in the morning or at the end of the working day can be soothed in the following ways.
- Cold compress. Cold is the most affordable and one of the most effective means to relieve redness of the eyes and eliminate irritation. Apply ice cubes wrapped in gauze or a napkin to the eyelids or moisten cotton pads in cool water and apply to the eyelids for 5-7 minutes. Be careful: your eyes can get cold if you keep the cold too long.
- Chamomile solution or strong tea. Pharmaceutical chamomile in sachets or brewed flower heads of this plant effectively fight all kinds of eye fatigue. Apply cotton pads soaked in chamomile solution to your eyelids, or use strong tea leaves. Such a compress can be kept for 10-15 minutes, and then washed with cool running water.
- Potato slice. A peeled slice of fresh potato quickly and gently eliminates redness of the eyes and relieves an unpleasant burning sensation. To do this, apply a slice of potato to the closed eyelids, wipe the skin around the eyes with light massage movements. The healing root crop can be used within 5-10 minutes. You can also grate fresh potatoes on a grater, wrap in gauze and put on your eyes. And if you recently made mashed potatoes, this will do. Just do not use it hot, for the comfort of an important organ, the substance should be warm or at room temperature.
- Cold milk. One can argue endlessly about the dangers and benefits of cow’s milk, but as a remedy for redness of the eyes, it works flawlessly. Simply soak a cotton pad or gauze bandage in cool cow’s milk and apply the compress to your closed eyelids. Such a compress should be kept for at least 7 minutes, rinse off the remaining liquid with cool water. It is necessary to make sure in advance that there is no allergy to dairy products!
- Cucumber compress. It turns out that cucumber lotions help not only relieve puffiness under the eyes and reduce dark circles, but also remove redness of the eyes. Rub a fresh vegetable on a grater, wrap the resulting slurry in gauze and put it on your eyes for a few minutes.
- honey solution. Dilute a drop of honey with one tablespoon of warm water and drop the solution into your eyes. But when using this method, you need to be sure that there is no allergy.
- Aloe juice. You can buy aloe eye drops or make your own at home. True, this process is laborious and not at all fast. For those who decide to cope on their own, we give a recipe for drops from aloe juice.
Removing redness of the eyes: a recipe with aloe juice
If you have three-year-old aloe at home, you can make effective eye drops from it for redness and fatigue.
- About two weeks before the planned “extraction” of juice, stop watering the plant.
- After the allotted time, cut off the fleshy bottom leaves and refrigerate for 12-14 days.
- Then rinse the leaves with hot water, cut off the skin from them and squeeze the juice into a disinfected container.
- To make the juice sterile, it should be boiled for two to three minutes.
- Then the liquid must be cooled to room temperature and after that you can make gauze lotions with it.
- To do this, soak cotton pads with aloe juice and put on your eyes for 20 minutes. You can add a drop of honey to the composition.
By the way, honey is also an excellent preservative that will help preserve the beneficial properties of aloe for as long as possible. Store the mixture in the refrigerator and use whenever needed or on a regular basis, not only to treat but also to prevent eye redness.

How to prevent redness and inflammation of the eyes
Reviews of oculists suggest that redness of the eyes is easier to prevent than to treat. To keep your organ of vision healthy, and there is no trace of redness, try to follow these simple tips daily:
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- During daytime sleep, use an eye patch or purchase dark curtains for the bedroom.
- Wash off your makeup at night.
- Apply only those products on the skin around the eyes that are specifically designed for this.
- Ventilate the room 1-2 times a day for 20 minutes: lack of oxygen leads to blockage and vasoconstriction.
- Wet clean the room at least once a week and install a humidifier if this is not enough.
- Keep your contact lenses and glasses clean.
- Do not abuse alcohol and tobacco.
- Reconsider your daily facial skin care: some products can cause inflammatory reactions.
- With increased load due to work at the computer, set aside 10-15 minutes for exercises for the eyes in the morning and evening.
The dependence of eye redness on computer work
Many office workers complain of dryness, fatigue, redness and peeling of the eyes. Ophthalmologists even have a special concept of “office eye”. If you too constantly face this, check if your workplace meets the following criteria:
- The illumination of the screen should be comfortable for the eyes, not too bright, but not too dim.
- The monitor should be positioned so that its center is slightly below eye level.
- the light in the room should also not cause discomfort, for example, too bright lighting will blind and cause eye strain
Eye hygiene rules to avoid redness of the eyes
- When working at a computer for a long time, it is recommended to take five-minute breaks every hour or take your eyes off the monitor for a couple of minutes every 20-30 minutes. At the same time, it is useful to do visual gymnastics, take a walk, or at least just look into the distance.
- Get yourself the right lighting. Ideally, it should be natural, but this is not always possible. As an artificial light source, ophthalmologists advise choosing yellow light lamps with a power of up to 60 watts. Sometimes the redness of the right or left eye is due to the choice of the wrong side. For right-handers, the lamp should be placed on the left, and for left-handers, on the right.
- You can buy special glasses for the computer and work in them. These are sold in most opticians.
- An excellent option to relieve tension and redness of the eyes after working at the computer is massage glasses.
- The eyes rest when you look at something green. Get a houseplant on your desktop and admire it more often.
- Dryness and redness of the eyes often occur due to insufficient humidity in the room. A humidifier will help solve this problem. You can also instill moisturizing drops into your eyes (Sistein, Gilan, Hilokomod). But, we repeat, after consultation with a doctor.
- With vasoconstrictor eye drops for redness and irritation, you need to be careful and use them only in case of emergency. These drugs can cause addiction and vascular disorders.
- If you wear contact lenses, try changing them temporarily to glasses. In the absence of such an opportunity, you can at least replace long-term lenses with daily ones. Sometimes reducing the duration of wearing lenses for at least a couple of hours helps with redness of the eyes.
- Drink more water, it also helps to moisturize all tissues of the body, including the eyeballs.
How to remove redness of the eyes: a diet for sharp vision
For eye health, the body needs to get enough vitamins, minerals and other trace elements. Here is a nutrition cheat sheet that will help eliminate redness and eye fatigue.
- Vitamin A (retinol) is the first assistant in maintaining eye health. Look for it in blueberries, carrots, grapefruit, liver.
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is responsible for normal eye pressure. It is found in wholemeal bread, legumes, spinach and organ meats.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) improves the blood supply to the eyeballs. The sources of this trace element are seeds, eggs and green vegetables.
- Vitamin B6 is also necessary for the normal functioning of the vessels of the eye. Eggs, fish and liver will help provide the body with these vitamins.
- Without vitamin C, the eyes will suffer from impaired blood supply. Stocks of ascorbic acid will replenish citrus fruits, rose hips, bell peppers, berries.
- Vitamin E (tocopherol) is found in sea buckthorn, carrots, broccoli, egg yolks, vegetable and butter. Tocopherol protects the eyes from stress and overwork, and therefore from the likelihood of redness.
- Beta-carotene: yellow and orange vegetables, fruits and berries. It is a useful antioxidant.
- Lutein supports visual acuity, is found in spinach, parsley, pumpkin.
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids support vascular health. They are present in large quantities in fatty fish and cod liver.









