Contents
What is an infiltrate?
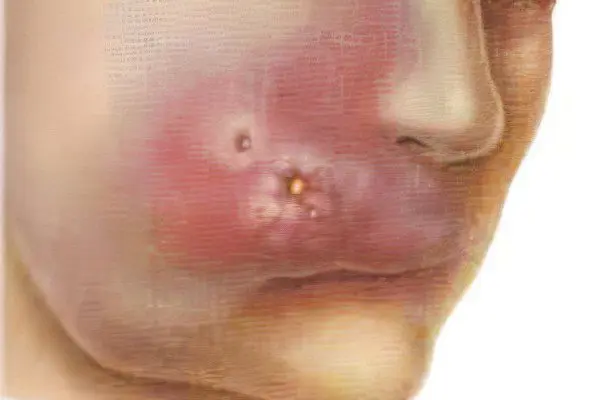
Infiltration on the face – inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues of the face (in muscles, tendons, adipose, connective tissues, synovial membrane, blood vessels and nerves) form a group that is united by individual nosological forms and a common causal mechanism for the onset of the disease and its development. It includes boils, furunculosis, abscess, phlegmon and some others.
Causes of infiltration on the face
The causative agent of the inflammatory infiltrate on the face are pyogenic bacteria, especially staphylococci, in rare cases putrefactive and anaerobic infections. Microbes penetrate the tissue in the event of an open injury, microtrauma (combing the skin, an injection made in violation of the rules). It is impossible to exclude the introduction of microflora by hematogenous or lymphogenous species, as well as by contact from the primary foci of inflammation.
Inflammatory processes take different forms, it all depends on the characteristic changes in soft tissues, which are serous, purulent, very rarely putrefactive. An abscess is a disease with an already formed purulent exudate. One of the causes of the disease can be weakened immunity and depletion of the body with chronic diseases, endocrine disorders, fungal diseases, beriberi.
Symptoms of an infiltrate on the face
Symptoms of inflammatory processes of soft tissues on the face with a variety of forms of nosological nature and localization of the process have common manifestations that are predetermined by the presence of the inflammation process and are important when choosing a physiotherapeutic method of treatment.
The onset of inflammation on the face is characterized by the appearance of a dense infiltrate with mild itching and tingling. About a day later, an inflammatory-type infiltrate forms over a dense nodule. When the infiltrate protrudes above the surface of the face, and the surrounding skin becomes red and painful, pus forms on its top.
Then the capsule breaks through, dries up, on the third day the purulent infiltrate melts and the rod necrotizes. Only after that the pus comes out. The resulting wound is filled with granulation tissue and heals, and a whitish retracted scar remains in its place.
Severe pain is caused by inflammatory infiltrates that have arisen in the nose and ear canal. A large edema occurs with inflammation on the lips and forehead, as there are areas with loose subcutaneous tissue. The nasolabial, periocular and upper lip areas are also marked by a severe clinical picture, due to the peculiarities of the venous and lymphatic system on the face, which supports the rapid spread of infection.
Treatment of infiltrate on the face
All stages that an inflammatory disease goes through are treated with physiotherapy methods, the purpose of which is to sanitize the foci of infection and eliminate the inflammation process – bactericidal methods. Infiltration without purulent tissue fusions or a small amount of purulent filling is treated with physiotherapy aimed at resolving inflammation, minimizing edema, reducing pain syndrome – this is an anti-inflammatory and analgesic method.
The reparative-regenerative physiotherapeutic method is aimed at restoring the regeneration of the body, and its resistance to non-specific pathogenic factors is increased by immunostimulating methods. The antibacterial effect in the presence of superficial inflammation is achieved by using electrophoresis with antibiotics, sulfonamides. To delimit the inflammatory focus, calcium electrophoresis is indicated.
The surgeon determines whether there are indications for surgery or whether it is possible to be treated with physiotherapy methods. The physiotherapist determines the tactics of treatment, assesses the absence of any contraindications.









