Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Infanrix hexa is a vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, Hib infections and hepatitis B.
Infanrix hexa – properties
Infanrix hexa is diphtheria toxoid + H. influenzae type B vaccine + hepatitis B vaccine (recombinant) + pertussis vaccine (cell-free) + poliomyelitis vaccine (inactivated) + tetanus toxoid. It contains the Hib polysaccharide antigen (10 µg) combined with tetanus toxoid as a carrier protein (25 µg), as well as the HBs antigen in the amount of 10 µg.
See also: Vaccination program
Infanrix hexa – application
Infanrix hexa is used for primary and booster vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and infections caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B.
Infanrix hexa – contraindications:
Infanrix hexa should not be used if the child is hypersensitive to the active substances or to any of the excipientsas well as polymyxin B, neomycin and formaldehyde. Not recommended for children who have experienced hypersensitivity after previous administration of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio or Hib vaccines.
The use of Infanrix hexa excludes acute and severe febrile diseases – in case of mild infections the vaccine may be administered.
If a child develops an encephalopathy of unknown etiology within 7 days after vaccination with pertussis antigens, the pertussis vaccination should be discontinued and vaccinations continued with diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and Hib vaccines.
Find out more: When not to vaccinate a child? Contraindications to vaccinations
Infanrix hexa – precautions:
Infanrix hexa should not be injected intravascularly or intradermally. In the event of an anaphylactic reaction following vaccination, immediate treatment should be provided. Vaccinated children with a history of febrile seizures should be carefully monitored as these side effects may occur 2-3 days after vaccination.
The vaccine should be administered with caution to people with thrombocytopenia or bleeding disorders – in whom there is a risk of bleeding after intramuscular injection.
With concurrent administration of the pneumococcal vaccine, an increased incidence of seizures (with or without fever) and hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode and febrile reactions has been reported.
Vaccination may be postponed in infants and children with known or progressive severe neurological disorder. The vaccine may be given to premature babies, but in this case the immune response may be weaker and the degree of clinical protection remains unknown.
The risk of apnea and the need to monitor respiratory function for 48-72 h should be taken into account when priming with primary vaccination doses in very premature infants (born before 28 weeks of gestation), especially in those with symptoms of respiratory immaturity.
Also read: Vaccinations – types, compulsory vaccinations, adverse vaccination reactions
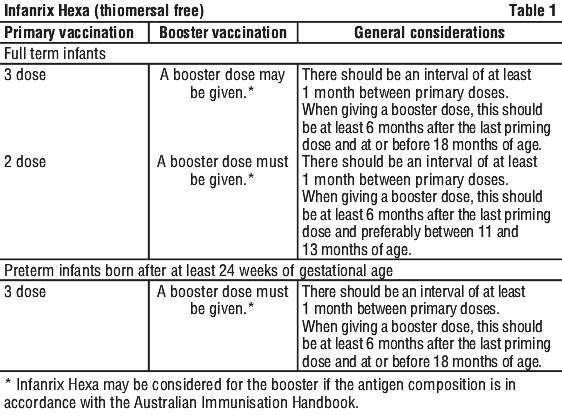
Infanrix hexa – dosage
Infanrix hexa should be dosed according to official recommendations. Primary vaccination: 3 doses of 0,5 ml (given in one of the following schedules: months 2, 3, 4; months 3, 4, 5; months 2, 4, 6) or 2 doses (given in months 3, 5). Observe at least monthly intervals between the individual doses
If your baby has been vaccinated with a dose of hepatitis B vaccine shortly after birth, Infanrix hexa may be given from the age of 6 weeks in place of the next doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Booster vaccination should be carried out according to current recommendations, however, as a minimum, a dose of Hib conjugate vaccine should be administered. Infanrix hexa can be used as a booster dose if it complies with official vaccination guidelines.
Infanrix hexa – side effects
The vaccine can cause side effects in some cases. Vaccinated persons often complained of loss of appetite, restlessness, fever, irritability and swelling at the site of injection ≤50 mm. Moreover, many of them experienced general fatigue. Side effects such as diarrhea and vomiting have also been reported among some patients vaccinated with Inhrix hexa.
In rare cases, side effects of vaccination were lymphadenopathy, anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactoid reactions (e.g. urticaria), allergies (e.g. pruritus), and even collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode), apnea, rash, angioedema. There have also been reports of swelling of the entire vaccine limb and infiltration at the injection site.
Find out more: Reaction to vaccination
Inhrix hexa – precautions
When injecting the drug, an intramuscular injection should be made. The 6in1 vaccine is not administered intravenously or intradermally. A special procedure is used when administering the vaccine to patients with coagulation disorders and thrombocytopenia – in their case, complications may arise after intramuscular injection. For these reasons, prior to the administration of the vaccine, it is necessary to consult a doctor, during which the patient will provide detailed information on the current vaccinations.
The vaccinated child should be monitored after the procedure. If side effects such as high fever or collapse appear 48 hours after injection, then it should be considered whether further doses of the vaccine should be administered. Warning signals are also crying lasting more than 3 hours after the procedure, drugs with fever – side effects may also occur after 2 days.
We also recommend: Post-vaccination fever – why does it occur, what it can mean and how to deal with it?
Inhrix hexa – drug interactions
The vaccine can be used with oral rotavirus, pneumococcal, meningococcal C conjugate, meningococcal A, C, W-135 and Y conjugate (TT conjugate), measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccines. It is also used in premature babies, but they may be less responsive to the vaccine.
Infanrix hexa – cena
The price for the Infanrix hexa is about PLN 200. The leaflet attached to the Infanrix hexa vaccine should contain all indications and warnings regarding side effects – be sure to read its content.