Contents
Hypoxia in newborns can lead to serious disturbances in the functioning of the brain. This problem is quite acute, since almost every 10th infant suffers from hypoxia to one degree or another. Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is the most common complication that develops against the background of oxygen starvation of the newborn. Often it is diagnosed in children who were born prematurely.
To date, there are simply no effective methods to combat hypoxia in newborns, although scientists do not stop working in this direction. Moreover, against the complications that hypoxia causes, science is completely powerless. No drug is capable of restoring dead brain cells. Although, according to scientists, such funds have already appeared and are at the stage of clinical trials.
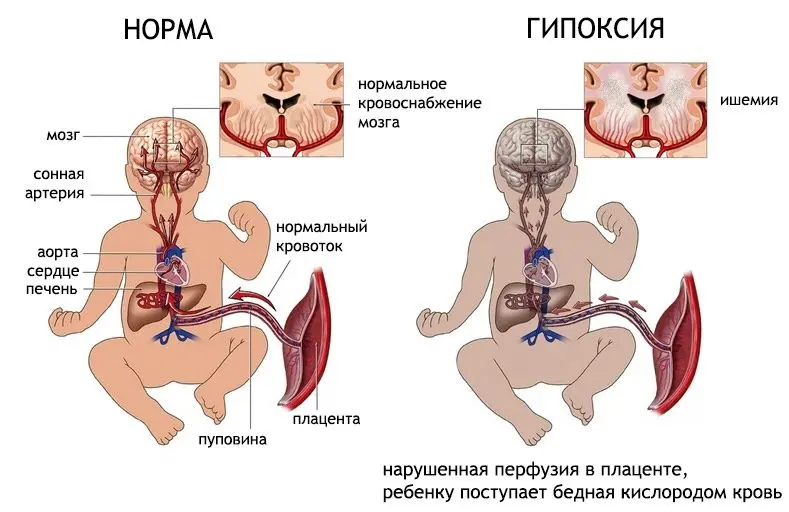
The central nervous system reacts painfully to a lack of oxygen. When it comes to a newborn child and a child in the womb, the issue of oxygen starvation becomes even more acute. The baby’s brain is at the stage of development, so he needs constant and uninterrupted nutrition. Any pathogenic influences that a pregnant woman has experienced, or that were received during childbirth, can negatively affect the state of the central nervous system of a child. Nervous tissue will be damaged, which in the future will manifest itself as neurological disorders.
The degree of hypoxia varies. It can be mild or severe, it can last for several minutes or for several days and even months. However, hypoxia will definitely provoke disturbances in the work of the brain.
If, with mild hypoxia, these disorders do not have pronounced symptoms and can pass on their own after a certain period of time, then with deep hypoxia, the changes will be irreversible. In this case, the brain undergoes organic lesions, which can make the child disabled.
Hypoxia can develop both during the intrauterine life of the fetus and during childbirth, provided that they have a pathological course. In addition, hypoxic-ischemic disorders are observed in children who suffer from pathology of the respiratory system, with problems associated with blood clotting, with a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and not only.
In medical terminology, two concepts are used. Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is said when the complications of hypoxia are severe. Also in this context, the term hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy can be used. It is most often used when the brain is affected in a mild degree.
Although up to the present time, disputes have not subsided over whether the brain can recover after undergoing hypoxia, most doctors are convinced that this is possible. The nervous system of children is armed with certain mechanisms that are aimed at protecting themselves on their own. Moreover, some scientists insist that the child’s brain can even regenerate. After all, not every newborn who has suffered deep oxygen starvation becomes disabled. Moreover, not all of them develop any neurological disorders in the future.
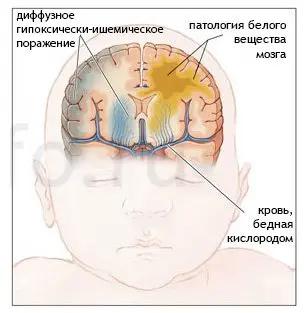
If hypoxia is severe, then the most immature areas of the brain located in its stem part, as well as subcortical nodes, will be damaged first of all. Not only acute, but also prolonged hypoxia is dangerous, which may not be accompanied by severe symptoms. Such oxygen starvation provokes diffuse damage to the cortical structures of the brain. During hypoxia, the child’s body starts a certain mechanism that redistributes the blood flow in such a way that most of it will be directed specifically to the brain stem. Therefore, with prolonged oxygen starvation, its gray matter will suffer mainly.
Because the complications of hypoxia can be fatal, neurologists must pay close attention to the examination of infants. This is especially true for those children who have suffered hypoxia during childbirth, regardless of its severity. All adaptive manifestations of the organism (for example, tremor) should be excluded, the neurological status of the child should be established, possible disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system should be detected. When detecting hypoxic lesions abroad, they rely on the principle of staging of pathology. In Russia, a systematic approach is used, focusing on syndromes that may indicate the development of complications.
Why do CNS lesions occur, stages of their development
Perinatal damage to the central nervous system is said to be in the case when the child was exposed to negative factors during the neonatal period, during childbirth, or while in the mother’s womb.
Causes that can provoke disorders in the functioning of the nervous system of the child:
Violation of blood flow in the uterus and placenta. Thrombosis of the placenta, fetal growth retardation, bleeding in a pregnant woman.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy, smoking and undergoing therapy with certain drugs.
Severe blood loss during labor, entanglement of the umbilical cord around the baby’s neck. Hypotension or bradycardia in a child, birth trauma.
Heart defects, DIC, pathologies of the respiratory system, episodes of respiratory arrest in a baby who was born.
The lack of oxygen in the arterial blood is a factor that triggers metabolic disorders in the nervous tissue. At the same time, individual neurons, or their entire groups, begin to die. Under such conditions, brain tissue becomes maximally susceptible to any fluctuations in blood pressure. If at this time the child develops hypotension, then the pathological process is further aggravated.
Violations of metabolic processes in the brain provokes acidosis of its tissues, which entails cerebral edema with an increase in intracranial pressure. This causes massive death of brain cells.
Deep asphyxia affects the functioning of all organs of the child. Kidneys, intestines, liver suffer. Hypoxia causes tissue death of these organs.
There are differences in the course of complications caused by oxygen starvation in full-term and premature babies. So, if a child who was born on time underwent hypoxia, then the cerebral cortex, its subcortical structures and the brain stem will be affected to a greater extent. If the child is premature, then he is likely to develop periventricular leukomalacia, that is, areas of necrosis will be concentrated in the region of the lateral ventricles of the brain.
The severity of hypoxic encephalopathy has a direct relationship with the depth of ischemic brain damage.
In this regard, there are:
Light or 1 degree of severity. Neurological disorders are transient, after 7 days they will be completely stopped.
Medium or 2 severity. Hypoxic-ischemic disorders persist for more than one week. At the same time, the child’s nervous system is either depressed or hyperexcitable, convulsions are observed, intracranial pressure is increased, but the increase is not stable. There are also disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Severe form of violations or 3 degrees of severity. In this case, the child will be either in a coma or in a stupor. He has convulsions, there is swelling of the brain, the work of internal organs is disturbed.
Symptoms of hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system
If a child is affected by the central nervous system, then doctors will establish this fact from the first minutes of his life. Symptoms directly depend on the severity of the infant’s condition.
1 degree
If hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy has a mild course, then the child’s condition will be stable. On the Apgar scale, the baby gets 6-7 points. He will have a cyanotic staining of the skin, muscle tone is somewhat reduced.
From the side of the nervous system, the following symptoms are observed:
Nervous reflex excitability is increased.
Sleep is disturbed, the child shows anxiety.
Chin and limbs tremble slightly.
The child vomits often.
Perhaps an increase, or, conversely, a decrease in reflexes.
As a rule, over the next 7 days after the birth of the baby, all these pathological symptoms will be stopped. The baby becomes calmer, begins to gain weight. There are no pronounced disorders of the nervous system.
2 degree
With the second degree of hypoxic brain damage, the symptoms will be more intense. Most often, infants with moderate severity of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy suffered from oxygen starvation while still in the womb, and were also exposed to adverse factors during labor. According to the Apgar scale, such a child is given a mark of 5 points, arrhythmias are traced in him, muffled heart sounds are heard.
Nervous system disorders include:
Reflexes are depressed, this is true, including with respect to the sucking reflex.
Muscle tone is reduced, voluntary movements are minimal or absent altogether.
Intracranial pressure rises.
The skin is bluish in color.
Vegetative disturbances are observed: periodic respiratory arrests occur, the pulse can accelerate, bradycardia is often diagnosed. The intestines contract weakly, thermoregulation is impaired.
The child often spit up, may suffer from constipation or diarrhea, gaining weight slowly.
The higher the intracranial pressure of the child, the more anxiety he will show. The skin has increased sensitivity, sleep is restless. The chin and hands of the child tremble, the fontanelles bulge. The baby has oculomotor disorders, nystagmus. Seizures can also indicate increased intracranial pressure.
By the 7th day from the moment the child is born, his condition stabilizes. However, he must receive intensive care. Completely by this time, neurological symptoms do not go away. If the pathology progresses, then the inhibition of brain activity increases, there is a drop in muscle tone. The child may go into a coma.
3 degree
If a child is diagnosed with a 3rd degree of hypoxic-ischemic lesions, then a woman always has severe preeclampsia in the second half of pregnancy. She suffers from high blood pressure, she has impaired kidney function, pronounced edema.
The baby is born already with symptoms of oxygen starvation. Developmental delay is clearly visible. If the birth proceeded with complications, then the existing violations will only worsen.
The child suffers from severe circulatory disorders, may not breathe, muscle tone and reflex activity are often absent. If resuscitation is not carried out urgently, the child dies.
In the very first hours after his birth, there is an inhibition of the brain, a coma develops. The reflexes and motor activity of the infant are absent, the pupils are dilated, the reaction to light is zero.
Cerebral edema is manifested by convulsions, respiratory and cardiac arrest is possible. The pressure in the pulmonary artery rises, urine filtration deteriorates, blood pressure falls, intestinal tissues begin to die, the liver ceases to function, DIC develops.
Post-asphyxia syndrome is a consequence of severe hypoxia of the newborn. The child is practically immobilized, does not cry, does not respond to painful stimuli, to touch, the skin is pale, the body temperature is lowered. The baby hardly makes swallowing and sucking movements, so the woman cannot feed him on her own. Without intensive care, the child will die. The prognosis is unfavorable, the stability of the condition cannot be concluded earlier than 10 days from the moment of his birth.
The subsequent increase in neurological deficit characterizes all forms of hypoxic-ischemic disorders. The fact is that neurons that were damaged as a result of hypoxia continue to die.
Possible options for the course of pathology:
The child’s condition is improving rapidly. The prognosis is favorable.
Neurological disorders disappear by the time the baby is discharged from the maternity hospital. The prognosis is favorable.
Neurological disorders continue to progress. The prognosis is unfavorable.
During the first month of life, the child becomes disabled.
An unfavorable course with a hidden increase in neurological disorders that develop during the first six months of a child’s life.
Encephalopathy of the newborn is divided into 3 periods:
An acute period that lasts for the first month. At this time, maximum disorders of nervous activity are observed. They can be mild, or reach a coma.
A recovery period that can last up to a year. At this time, the child may develop a convulsive syndrome, hydrocephalus, neuro-reflex excitability increases, and there is a lag in physical and mental development.
The remote period when the consequences of the transferred hypoxia manifest themselves. Some symptoms may disappear, while others appear, for example, a child may experience a delay in speech development.
Treatment
To make a diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, it is required to identify the characteristic symptoms in an infant, to study the history of a pregnant woman. Instrumental examination methods also help in the diagnosis of a pathological condition, including:
Neurosonography.
Echocardiography.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
Blood coagulogram.
Doppler study of cerebral vessels.
The difficulty in the treatment of hypoxic-ischemic complications lies in the fact that no drug can restore once damaged nerve tissues. However, it is still possible to normalize the work of the brain to one degree or another.
Depending on the prevalence of specific symptoms and the severity of hypoxia, the therapeutic regimen will differ.
If hypoxia is of moderate or mild severity, then the child is shown taking diuretics, nootropic drugs, drugs to eliminate seizures. Provided that hypoxia has a severe course, the patient is urgently given intensive care.
When a child has symptoms of mild hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, but there are no convulsions, the doctor may limit himself to only monitoring the patient. Sometimes with such a clinical picture, Diazepam may be indicated, but for a short period of time. This drug is able to inhibit the development of the child, so it is prescribed only for strict indications.
Pantogam and Phenibut have a complex nootropic and inhibitory effect on the child’s nervous system. Nitrazepam is prescribed to normalize a child’s sleep. Also for this purpose, valerian extract, lemon balm, motherwort, mint can be used. Massage and hydrotherapy have a sedative effect.
If hypoxia has a severe course, then the child is prescribed anticonvulsants, diuretics (Furosemide, Mannitol, Diakarb) and Magnesium sulfate.
The child is urgently resuscitated if he has a breath holding or cardiac arrest. It is shown that the patient is connected to a ventilator, the introduction of cardiotonic drugs, and infusion therapy.
Diuretics are prescribed as the main drug for hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome. Preference is given to a drug called Diakarb. It can be used to treat children of any age. Surgical intervention is resorted to in the case when conservative therapy does not bring the desired effect. For this purpose, bypass operations are performed with the withdrawal of cerebrospinal fluid into the peritoneal cavity or into the pericardial cavity.
To relieve seizures and reduce the excitability of the nervous system, drugs such as Diazepam, Phenobarbital, Clonazepam, Phenytoin are prescribed. If the child is a newborn, then preference should be given to barbiturates, namely Phenobarbital. If the child is breastfeeding, then he is prescribed Carbamazepine.
To relieve increased muscle tone, use Baclofen or Mydocalm. If the muscle tone, on the contrary, is lowered, then Dibazol and Galantamine are prescribed to the child. Physiotherapy is helpful in the treatment of complications caused by hypoxia. For this, the child is sent for a course massage, they are engaged in therapeutic exercises with him. Reflexology and water procedures have a good effect.
If a child has difficulties in speech development, which becomes apparent by the end of the first year of life, then he is shown taking Nootropil and Encephabol, vitamins of group B. Be sure the baby should interact closely with a speech therapist and defectologist.
Prescribing a large number of drugs is not always the right tactic for treating children who have undergone hypoxia with subsequent encephalopathy. Often, without need, the child is prescribed Diakarb, nootropic drugs, vitamins, Actovegin. However, if the encephalopathy is mild, these medicines will not be helpful, as the body can recover on its own. Moreover, they have age-related contraindications, so their unreasonable use can even be harmful.









