Contents
Hypoxia of the brain is oxygen starvation of its tissues. A variety of factors, both external and internal, can provoke cerebral hypoxia in an adult. Oxygen starvation can be the result of insufficient oxygen in the air, or the result of a violation in the system of its delivery to the brain.
Without oxygen, the human body cannot exist. Its deficiency affects all organs without exception. The most sensitive to lack of oxygen is the brain. Even a few seconds of severe hypoxia is enough for brain cells to begin to die, and after half a minute a person will simply fall into a coma. After another 4 minutes, brain death will occur. Therefore, the danger of this pathological condition should not be underestimated.
Depending on the rate of occurrence and duration of the hypoxic state, there are three forms of oxygen starvation of the brain:
Lightning hypoxia, which increases in just a few seconds, but no more than one minute. At the same time, the condition of a person is rapidly deteriorating, often this ends in death. Lightning hypoxia can occur when an aircraft flying at an altitude of 11 m is depressurized, or when large arteries in the human body rupture.
Acute hypoxia develops over several minutes, but not more than an hour. The reason for such oxygen starvation of the brain may be hidden in acute respiratory failure, or as a result of significant blood loss.
Subacute hypoxia increases over several hours, but not more than a day. In this case, chronic heart or pulmonary insufficiency, venous bleeding, etc. can lead to hypoxia.
Chronic hypoxia of the brain develops over several days or even months. It is a consequence of various diseases, such as chronic anemia.
In any case, cerebral hypoxia is a condition that requires emergency medical care for the patient, since sooner or later it will lead to his death.
Causes of cerebral hypoxia
Approximately 20% of the total volume of blood circulating in the body enters the brain. Together with blood cells, oxygen and other useful substances are delivered to the body, which are necessary to maintain its performance.
There are endogenous and exogenous types of hypoxia. The reason for the development of exogenous oxygen starvation of the brain is a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the environment, namely, in the inhaled air. Often a similar situation is observed when climbing mountains, so this condition of the body is called Altitude or Mountain sickness. A sharp drop in barometric pressure can also lead to exogenous oxygen starvation. At the same time, they talk about the development of decompression sickness in a person.
Endogenous oxygen starvation is indicated when the level of oxygen in the air is lowered, and the barometric pressure remains normal. Such a situation can happen when a person is in mines, and wells, in a submarine, or during an operation with errors in the operation of the apparatus responsible for supplying oxygen to a patient under anesthesia.
Also, brain hypoxia can develop in pathological conditions of the body. In this regard, there are:
Hypoxia of the brain, which develops against the background of disorders in the organs of the respiratory system.
The following reasons can lead to respiratory hypoxia of the brain:
Alveolar hypoventilation. This can be observed in violation of the airway, for example, against the background of an inflammatory process in the lungs, when a foreign body enters the airways, due to spasm of the airways. Also, hypoxia of the brain can lead to: pneumonia, pulmonary edema, pneumothorax, accumulation of exudate in the pleural cavity. The cause of moderate hypoxia of the brain is often impaired mobility of the chest, paralysis of the respiratory muscles, as well as its spasm against the background of tetanus or myasthenia gravis. Alveolar hypoventilation can lead to oxygen starvation of the brain in violation of the processes of regulation of respiration, when the respiratory center is affected by pathogenic factors. Other reasons include: hemorrhages in the respiratory organs, the presence of a tumor in them, trauma to the medulla oblongata, an overdose of narcotic or sleeping pills, severe pain that occurs in a person during respiratory movements.
Failure of ventilation-perfusion connections develops due to impaired airway patency against the background of bronchospasm, pulmonary emphysema, and pneumosclerosis.
Excessive shunting of venous blood, which is observed with congenital anomalies in the development of the heart.
Difficulty in diffusion of oxygen. The cause is emphysema, asbestosis, lung sarcoidosis, interstitial pulmonary edema.
Hypoxia, which develops against the background of certain circulatory disorders, leading to insufficient blood supply to the brain tissues. The reasons are: massive blood loss, dehydration during burns or cholera, etc. This also includes disorders in the work of the heart muscle, for example, myocardial infarction or cardiosclerosis, cardiac tamponade, cardiac overload. Often factors can occur in various combinations. Circulatory hypoxia of the brain develops against the background of severe infectious diseases, severe allergic reactions, electrolyte imbalance, when taking glucocorticoids, with an increase in blood viscosity, with acute and chronic heart failure, with collapse, etc.
Reduced oxygen capacity of the blood, leading to the development of cerebral hypoxia, may be the result of such factors as: severe anemia with a sharp drop in the level of hemoglobin in erythrocytes. This is often observed in diseases such as tuberculosis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and intestines, poisoning with hemolytic poisons, massive burns, malaria, exposure to ionizing radiation, against the background of a lack of vitamins and iron from food.
Tissue hypoxia of the brain develops when the tissues of the body lose the ability to absorb oxygen from the blood. A similar situation develops against the background of cyanide poisoning, with an overdose of barbiturates, antibiotics, and when the body is exposed to toxic substances of various origins. Also, a deficiency of thiamine, riboflavin and other vitamins can provoke tissue hypoxia of the brain.
Hypoxia of the brain in a mixed type develops when several factors lead to it at the same time. It should be noted that any severe hypoxia occurs in a mixed type, for example, with various types of traumatic shock or during coma.
Features of the course of cerebral hypoxia and adaptive reactions of the body
The severity of hypoxia in various organs and tissues may vary. So, in the event of a threatening situation, the body will independently redistribute blood in such a way that the brain is supplied with it better than other organs and tissues. This process is called centralization of blood circulation. It can be activated, for example, in case of acute blood loss.
The result of this mechanism is that the brain suffers from hypoxia less than peripheral organs, such as the liver or kidneys, where irreversible changes do not develop at such a high rate.
How is hypoxia of the brain manifested?

Depending on the severity of brain disorders during hypoxia, there are:
Easy degree. This is manifested by such symptoms as: lethargy, stupor, or, on the contrary, a person becomes hyper-excited, he has euphoria, blood pressure rises, and heartbeat quickens. The palpebral fissures become uneven in size as a result of paresis of the facial nerve. If the pathogenic factor that affects the oxygen starvation of the brain is not eliminated, then after a few hours or days, it will move to the next stage.
Average degree. The patient retains paresis of the facial nerve, reflexes of the mucous membranes and tendon reflexes are most often reduced. From time to time, seizures may occur, which begin with the front part, and then spread to the trunk and limbs. Anxiety and psychomotor agitation increased. The victim has difficulty orienting in space, his memory and other cognitive abilities are deteriorating.
Severe degree. The patient has a deep depression of consciousness with the loss of voluntary activity, but the reflexes are preserved. This condition is called constipation. Sometimes already at this stage a person falls into a severe coma. He develops convulsions of the upper and lower extremities, grasping and sucking reflexes appear, and muscle tone drops. Perhaps persistent fever, increased sweating and lacrimation.
A critical degree that poses a threat to life. This condition is characterized by a deep coma, all brain structures are affected. The patient’s skin is cold, facial expressions are absent, the eyeballs are motionless, the pupils are dilated, they do not react to light. The mouth remains half open, the eyelids are closed, the skin is cyanotic. The heart works weakly, vascular tone is reduced. As hypoxia progresses, the functions of the cerebral cortex fade away. A person dies if his life is not supported with the help of an artificial respiration apparatus and means for toning up the cardiovascular activity.
Separately, the symptoms of chronic cerebral hypoxia should be described, which include:
Increased fatigue.
Excessive irritability.
Emotional incontinence.
Decreased intelligence.
Violations of the emotional-volitional sphere.
Deterioration of memory and attention.
Bad mood.
Increased tearfulness.
Apathy.
Most often, people become indifferent to everything that happens, less often they are complacent and are in euphoria.
Often a person experiences headaches, dizziness.
Periodic bouts of nausea are possible.
Night rest is disturbed, and during the day a person experiences bouts of drowsiness. He falls asleep with difficulty, sleep is superficial, intermittent. The patient often has nightmares. After a night, a person feels tired and not rested.
Chronic hypoxia is characterized by vegetative disorders, including: increased pulsation in the head, the appearance of tinnitus, frequent episodes of darkening in the eyes, a feeling of a rush of heat to the head. The heartbeat becomes more frequent, pain in the heart and shortness of breath may occur. Even episodes of loss of consciousness are not excluded.
Why is brain hypoxia dangerous?
Even mild hypoxia of the brain is a dangerous condition for health, which leads to pathological changes that affect the entire body as a whole. The stronger the oxygen starvation, the more severe its consequences. The prognosis depends on the degree of damage to the brain tissue and how long the hypoxia lasted.
If a person fell into a coma for a short period of time, then the chances of a full rehabilitation are quite high. If the patient was not in a coma, then he will recover even faster (subject to the provision of adequate and timely medical care).
If a person was in a coma for a long time, but got out of it, then such a state cannot remain without consequences. The life expectancy of such patients most often does not exceed one year. At the same time, bedsores form in bedridden patients, they are more susceptible to infectious diseases, the causative agents of which are hospital strains of bacteria. They are characterized by increased resistance to ongoing therapy. In immobilized patients, the risk of blood clots in the veins increases.
After undergoing clinical death, a person may lose a number of neurological functions.
The forecast may be as follows:
A full recovery of brain functions and normalization of the state can occur in a few days or months if the brain tissue has not been destroyed. In this case, the patient will experience asthenic syndrome throughout the entire rehabilitation period. Sometimes, after a significant improvement in well-being, its secondary deterioration may occur, while neurological disorders will be persistent.
Partial restoration of neurological functions is observed when some brain cells die. Rehabilitation and return of the patient to normal life is slow. Some functions may not be restored at all.
Complete recovery is rare, but if the treatment is carried out correctly, a stable remission can be achieved.
Brain cells do not recover after hypoxia, however, it is possible to achieve normalization of the state of the body. The brain has the ability to take over the functions of neighboring cells, but only partially. Therefore, help with hypoxia should be immediate. Otherwise, the complications and consequences of oxygen starvation of the brain will be critical.
Diagnosis of cerebral hypoxia
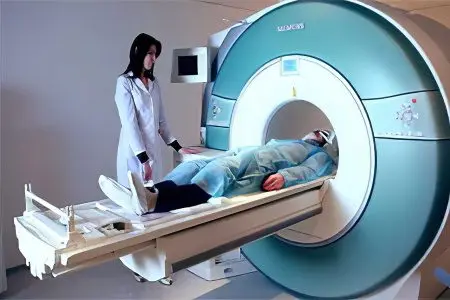
In order to diagnose cerebral hypoxia, it is possible to use the following instrumental and laboratory methods:
Blood sampling for general and gas analysis.
Performing an encephalogram of the head.
Conducting rheovasography, which provides information about the state of the vessels of the brain.
General or selective angiography, which allows you to evaluate the blood flow to the brain.
MRI is one of the most informative research methods, which gives the maximum amount of information about the state of the brain.
Capnography, which allows you to determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the air exhaled by a person. This method makes it possible to clarify the role of the lungs in terms of the development of cerebral hypoxia.
In addition, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition, it is necessary to determine the presence of shortness of breath and tachycardia. Of no small importance is the examination of the patient, the determination of reflexes and other symptoms that characterize this condition. To clarify the reasons that could provoke hypoxia, you need to find out if the patient has diseases of the internal organs, whether he had a stroke, etc.
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia
Since cerebral hypoxia is most often associated with a number of factors, it is necessary to conduct complex therapy, which depends on the cause that led to this pathological condition.
If hypoxia was the result of a lack of oxygen in the inhaled air, then the person should be transferred to breathing normal air as soon as possible. Provided that the brain cells have not been destroyed, the recovery will not take much time, and all functional disorders will be eliminated. Sometimes patients are shown adding 3-7% carbon dioxide to ordinary oxygen. This will expand the vessels of the brain, stimulate the work of the respiratory center.
Provided that there is a foreign object or other obstruction in the airway, tracheal intubation and tracheotomy may be required. The patient is given a position that facilitates breathing.
In case of severe respiratory failure, or in the complete absence of breathing, auxiliary or artificial respiration, artificial lung ventilation is necessary. Oxygen therapy should be continuous and prolonged until it is no longer needed.
Blood transfusion, the appointment of cardiac and hypertensive drugs is required for circulatory hypoxia. In this case, it is important to normalize blood circulation. If the patient has a cardiac arrest, his indirect massage is required, the use of a defibrillator. The doctor may administer epinephrine, atropine, and take other resuscitation measures. All these activities should be as fast as possible, so it is possible that they can be carried out even in an ambulance.
For the treatment and prevention of cerebral hypoxia, drugs with an antihypoxic effect can be used. These are narcotic and neuroleptic drugs, drugs to reduce body temperature, etc. Sometimes glucocorticoids can help.
It is imperative to restore the acid-base and electrolyte balance in the body, but this already applies to symptomatic treatment. Seduxen, which is administered intravenously, allows to relieve convulsions. If this does not help, then the introduction of muscle relaxants is indicated.
The patient will definitely have to visit the massage therapist’s office and perform therapeutic gymnastic complexes.
First aid for a person with cerebral hypoxia
The only thing that a person who does not have a medical education for a victim with cerebral hypoxia can do is to provide him with fresh air and call an ambulance as quickly as possible. Until the arrival of doctors, the room should be ventilated, all items of clothing that interfere with breathing should be removed from the victim.
Forecast

The prognosis depends on how long the brain has suffered from oxygen starvation and on the severity of its damage. With pronounced changes, the foci of softening of the brain remain forever.
If a person has experienced a mild degree of hypoxia, then asthenic manifestations will persist for 2 weeks, but no more. With hypoxia of moderate severity, pronounced violations can remain throughout the year. They are expressed in hyperkinesis, mental disorders, unmotivated aggression and arousal, blindness and hallucinations.
If a person has suffered severe hypoxia, then psychopathy can be observed throughout life. The intellect suffers, convulsive seizures periodically occur, motor functions are disturbed, and sensitivity is lost.
With a deep coma, the prognosis is the most unfavorable.









